What Are Casting Parts and How Are They Used in Manufacturing?

From engine blocks to plumbing fixtures, casting parts form the foundation of countless industrial products. At our ISO-certified foundry, we produce over 10,000 tons of casting parts annually for global manufacturers.
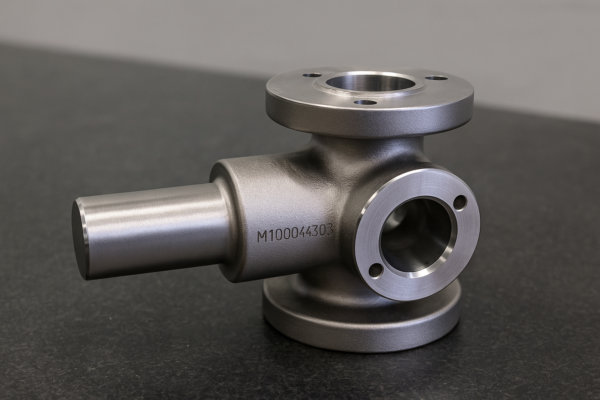
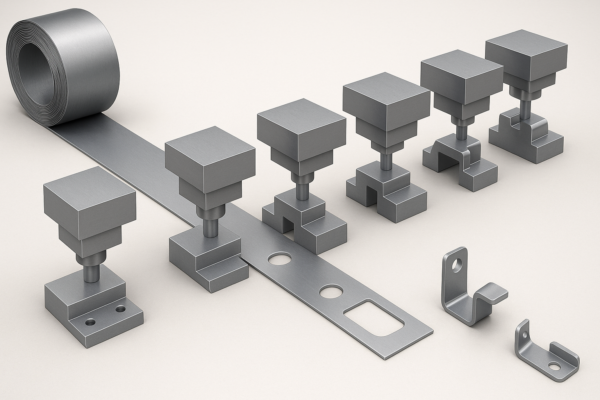
Snippet paragraph: Casting parts are metal components created by pouring molten metal into molds – a cost-effective process for producing complex shapes in materials like iron, aluminum, and steel that would be difficult or expensive to make otherwise.
Understanding the different casting processes and applications can help you select the right method for your project needs.
LOOP_START
What Are the Most Common Types of Casting Processes?
Several casting methods exist, each suited to different production requirements and material types.
Snippet paragraph: The four primary casting methods are sand casting (versatile, low-cost), die casting (high-volume aluminum/zinc), investment casting (precision parts), and centrifugal casting (hollow cylinders) – each offering distinct advantages for different applications.

Casting Process Characteristics
Volume vs. Complexity Comparison
| Process | Annual Volume | Part Complexity | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | 1-10,000 | Moderate | ±1.5mm |
| Die Casting | 10,000+ | High | ±0.1mm |
| Investment | 100-10,000 | Very High | ±0.3mm |
| Centrifugal | 100-5,000 | Low | ±2.0mm |
Material Application Matrix
| Material | Best Process | Typical Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Gray Iron | Sand Casting | Engine blocks, gears |
| Aluminum | Die Casting | Housings, brackets |
| Stainless Steel | Investment | Turbine blades, valves |
| Bronze | Centrifugal | Pipes, bushings |
Process Selection Factors
- Tooling costs range from $5k (sand) to $200k (die)
- Lead times vary from days (sand) to weeks (investment)
- Surface finish quality differs significantly
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What Industries Rely Heavily on Casting Parts?
Casting parts serve as critical components across multiple sectors.
Snippet paragraph: The automotive industry consumes 40% of castings (engine blocks, wheels), while construction (25%) uses pipe fittings and structural parts, and aerospace (15%) requires precision turbine components – demonstrating casting’s widespread importance.

Industry Usage Breakdown
Market Share by Sector
| Industry | % of Castings | Primary Materials | Key Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 40% | Iron, Aluminum | Engine blocks, transmission cases |
| Construction | 25% | Ductile Iron, Steel | Pipe fittings, structural supports |
| Aerospace | 15% | Superalloys | Turbine blades, housings |
| Industrial | 20% | Various | Pumps, valves, machinery parts |
Specialized Applications
| Application | Unique Requirements | Casting Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Marine | Corrosion resistance | Bronze naval props |
| Energy | High temperature | Steel turbine casings |
| Medical | Biocompatibility | Cobalt-chrome implants |
Emerging Uses
- Electric vehicle battery housings
- 3D-printed sand molds for prototypes
- Lightweight aluminum structural parts
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
How Do You Ensure Quality in Casting Parts?
Quality control measures at multiple stages guarantee casting part reliability.
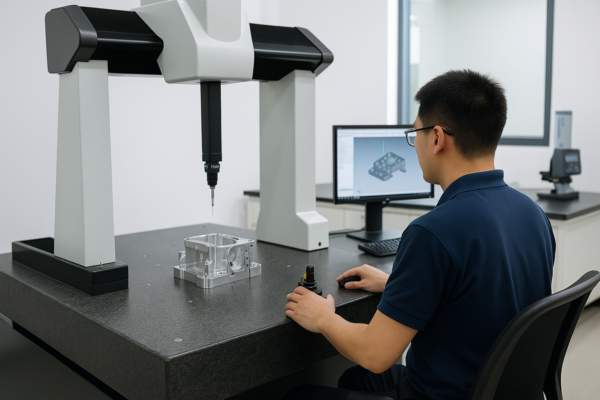
Snippet paragraph: Foundries implement X-ray inspection (void detection), spectrographic analysis (material verification), and dimensional checks (coordinate measuring machines) to maintain casting quality standards under ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications.

Quality Assurance Process
Inspection Methods Comparison
| Method | Detection Capability | Speed | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual | Surface defects | Fast | Low |
| X-ray | Internal voids | Slow | High |
| Ultrasonic | Subsurface flaws | Medium | Medium |
| CMM | Dimensions | Slow | High |
Common Defects and Solutions
| Defect Type | Causes | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Gas entrapment | Better venting, degassing |
| Shrinkage | Cooling issues | Improved riser design |
| Misruns | Low metal temp | Higher pour temperature |
| Inclusions | Mold contamination | Cleaner mold materials |
Quality Metrics
- Acceptable porosity: <2% by volume
- Dimensional tolerance: Typically ±0.5% of dimension
- Surface finish: 125-500 µin RMS typically
LOOP_END
Conclusion
Casting parts remain indispensable across industries, with various processes available to produce durable, complex components efficiently while meeting stringent quality requirements.