What Are Die Casting Parts and Why Are They Essential?
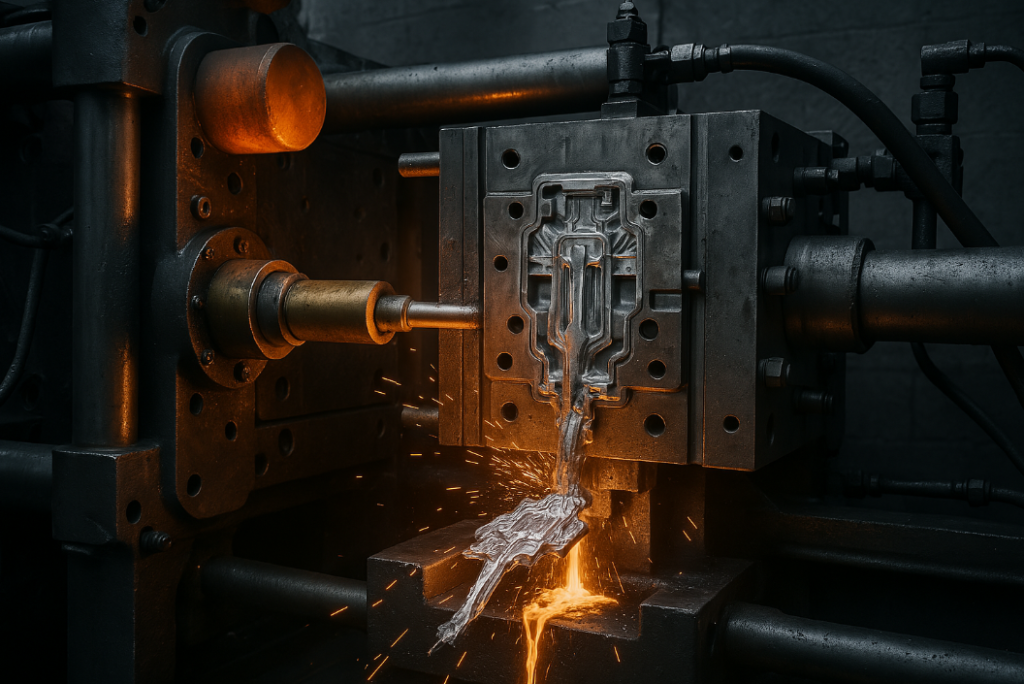

In our 30 years of metal fabrication, we’ve produced over 5 million die-cast components for industries ranging from automotive to consumer electronics. These precision parts solve critical manufacturing challenges.
Snippet paragraph: Die casting parts are metal components created by forcing molten metal under high pressure into reusable steel molds – producing dimensionally accurate, smooth-surfaced parts at rates up to 200 shots per hour with minimal post-processing.
Understanding die casting’s capabilities helps determine when it’s the optimal manufacturing solution.
LOOP_START
How Does the Die Casting Process Work?
Die casting transforms liquid metal into finished parts through meticulously controlled steps.
Snippet paragraph: The process involves injecting molten aluminum, zinc, or magnesium alloys at 10-175 MPa pressure into temperature-controlled steel dies, with cycle times ranging from 30 seconds to 2 minutes depending on part size and complexity.

The 5-Stage Die Casting Cycle
| Stage | Duration | Key Parameters | Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clamping | 5-15s | 200-4000 tons force | Die casting machine |
| Injection | 0.01-0.5s | 10-175 MPa | Shot sleeve |
| Cooling | 10-60s | Die temp 150-250°C | Cooling channels |
| Ejection | 3-8s | Ejector pin force | Ejector system |
| Trimming | 2-5s | Shear clearance | Trimming press |
Material Flow Characteristics
| Alloy | Melting Point | Fluidity | Shrinkage Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| A380 | 565°C | Excellent | 0.7% |
| ZA-8 | 404°C | Good | 1.1% |
| AZ91D | 598°C | Fair | 1.2% |
Critical Process Controls
- Gate velocity: 30-50 m/s for optimal filling
- Die temperature gradient: ±5°C tolerance
- Plunger acceleration profile: 3-stage ramp-up
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What Are the Main Advantages of Die Casting Parts?
Die casting outperforms other methods for specific applications.
Snippet paragraph: Compared to sand casting, die casting provides 10x better dimensional accuracy (±0.025mm), 3x faster cycle times, and superior surface finishes (1.6μm Ra typical) – while enabling complex geometries unreachable through machining.

Performance Benchmarking
| Characteristic | Die Casting | Sand Casting | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | ±0.025mm | ±1.5mm | ±0.01mm |
| Surface Finish | 1.6μm Ra | 12.5μm Ra | 0.8μm Ra |
| Wall Thickness | 0.5-5mm | 3-25mm | No limit |
| Production Rate | 200/hr | 20/hr | 1-5/hr |
Economic Comparison
| Factor | Die Casting Advantage |
|---|---|
| Labor Cost | 60% lower than machining |
| Material Waste | <15% vs. 50% machining |
| Tooling Life | 100,000+ shots |
| Post-Processing | Often eliminated |
Unique Capabilities
- Thin walls: As low as 0.5mm
- Near-net-shape: 95% final dimension
- Integrated features: Threads, knurls, logos
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
Which Industries Use Die Casting Parts Most?
Nearly every engineering sector benefits from die casting’s advantages.
Snippet paragraph: Automotive (38% of market) uses die cast transmission cases and brackets; electronics (27%) requires heatsinks and housings; while appliances (18%) incorporate die cast frames and mechanisms – showing remarkable versatility across sectors.

Industry Application Matrix
| Sector | % Usage | Common Parts | Material Preferences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 38% | Gearboxes, brackets | A380, ADC12 |
| Electronics | 27% | Housings, connectors | AZ91D, ZA-8 |
| Appliances | 18% | Motor frames | A360, A413 |
| Industrial | 17% | Hydraulic components | A390, No.2 Alloy |
Emerging Applications
| Technology | Die Casting Solution |
|---|---|
| EVs | Battery enclosures, motor housings |
| 5G | Antenna bodies, RF shields |
| IoT | Sensor casings, mounting brackets |
Material Innovation Trends
- Hypereutectic aluminum (A390) for wear resistance
- High-thermal-conductivity alloys for cooling
- Recycled-content alloys meeting OEM specs
LOOP_END
Conclusion
Die casting parts deliver unmatched precision and efficiency for medium-to-high volume metal components across virtually every engineering sector.