Fasteners 101: Types, Applications, and How to Choose the Right One
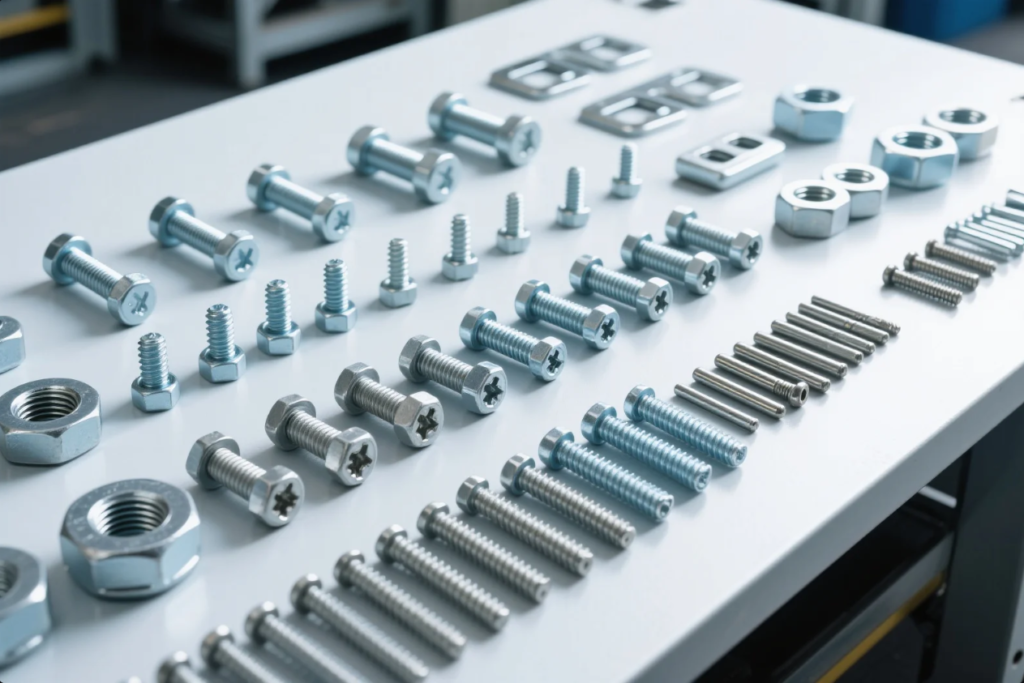

Using the wrong fastener leads to part failure, safety issues, and increased costs.
From bolts to rivets, this guide covers fastener types, applications, and key rules for choosing the right one.
Let’s simplify your fastener decisions—whether you're sourcing for CNC assemblies, stamped brackets, or structural castings. This article helps you avoid trial and error.
Table of Contents
- What are 7 types of fasteners?
- How to determine what fasteners to use?
- What are the rules to follow when choosing fasteners?
- What are the five basic types of fasteners?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What are 7 types of fasteners?
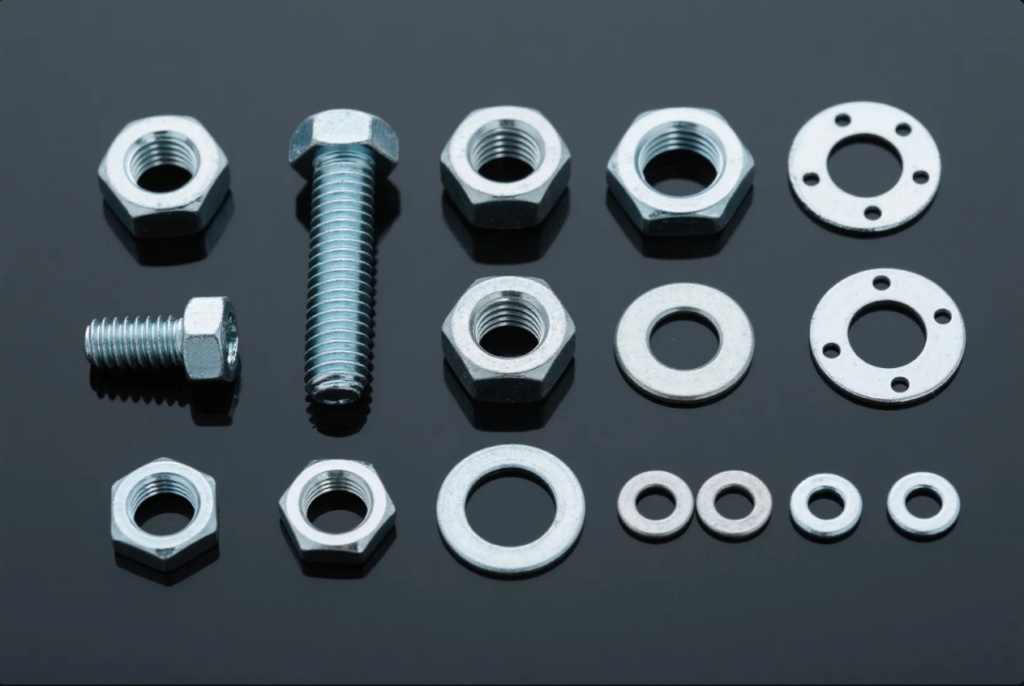

Different fasteners serve different functions. Choosing without understanding the types can lead to wrong-fit parts.
The 7 main types of fasteners include: bolts, screws, washers, nuts, rivets, pins, and anchors.
At Prime, we supply industrial fasteners in all these categories—across stainless, alloy, and carbon steel. Each type supports a specific mechanical or assembly need.
🔩 Fastener Types and Uses
| Fastener Type | Primary Use |
|---|---|
| Bolt | Clamping parts with nuts |
| Screw | Self-threading into components |
| Washer | Load distribution + surface protection |
| Nut | Threaded clamp with bolts |
| Rivet | Permanent joining (no thread) |
| Pin | Positioning or temporary locks |
| Anchor | Attaching to concrete or masonry |
For more examples, see Fastenal’s Fastener Overview.
How to determine what fasteners to use?

Guessing fastener specs often leads to structural failure or rework.
To determine the right fastener, consider the material, environment, load, and assembly process.
We help clients match fasteners to the job by analyzing strength, coating, thread type, and reusability. For example, a self-tapping screw fits well with sheet metal, but a socket head cap screw is better for precision parts.
✅ Factors That Help Choose the Right Fastener
- Material of the part (steel, plastic, aluminum)
- Static or dynamic load conditions
- Environmental exposure (corrosion, temperature)
- Assembly method (manual, automated, vibration-prone)
- Required reusability and disassembly access
Check out Engineers Edge's fastener selection chart for technical guidance.
What are the rules to follow when choosing fasteners?

Choosing fasteners without clear rules leads to misfit or corrosion failure.
Always follow basic rules—use matching materials, consider mechanical strength, and verify thread compatibility.
At Prime, we often see clients struggle with mismatched coatings or galvanic corrosion. We recommend testing a fastener in the actual part under real load whenever possible.
📌 Rules for Smart Fastener Selection
- Match material grades: e.g., stainless screw with stainless part
- Avoid dissimilar metals: prevents corrosion (see galvanic chart from AGA)
- Choose the right finish: zinc-plated, black oxide, or passivated
- Verify thread specs: coarse vs fine thread matters
- Use washers when needed: protect surfaces and distribute load
- Follow torque specs: especially for structural or safety-critical joints
See McMaster-Carr’s fastener torque tables for more data.
What are the five basic types of fasteners?

There are hundreds of fastener types, but most fall into 5 essential categories.
The five basic types are: bolts, screws, nuts, washers, and rivets.
These fasteners are the building blocks of most industrial, mechanical, and structural assemblies. At Prime, we ship thousands of tons of these fasteners yearly—fully traceable, quality-inspected, and ISO-certified.
🛠️ Fastener Categories Explained
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Bolt | Requires nut to clamp two parts |
| Screw | Threads into material, often self-tapping |
| Nut | Clamps and threads onto bolt or stud |
| Washer | Protects surfaces and distributes pressure |
| Rivet | Permanent, deformation-based fastening |
Want to go deeper? Check Bolts & Nuts’ Fastener Classification.
FAQs
Q1: What is the strongest type of fastener?
A1: Grade 8 hex bolts or alloy steel socket head screws offer very high tensile strength.
Q2: Can I mix different metal fasteners?
A2: Avoid mixing metals like zinc and stainless—it may cause galvanic corrosion.
Q3: What coating is best for outdoor fasteners?
A3: Hot-dip galvanized or stainless steel are ideal for corrosion resistance.
Q4: Are rivets better than bolts?
A4: Rivets are better for permanent joints. Bolts offer flexibility and reusability.
Q5: What standards should I check?
A5: Refer to ISO, DIN, or ANSI/ASME for global standards.
Conclusion
Fasteners are small, but choosing the right one has a big impact on durability, cost, and safety.
Want help selecting fasteners for your next project? Reach out to Prime for expert support, wide inventory, and fast delivery.
📩 Contact us: [email protected]