Top Materials Used in Custom Metal Mold Making and Their Advantages?

Choosing the wrong mold material causes early tool failure, longer cycle times, and poor surface finish.
In custom metal mold making, selecting the right material is a key step that affects mold durability, casting quality, cooling efficiency, and cost. Whether you’re creating molds for automotive die casting or medical injection parts, each mold material comes with unique performance advantages.
In this article, we explore the most commonly used materials in custom metal mold manufacturing and guide you on how to choose the best one for your project.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is the best material for metal casting molds?
- 2. What materials are used in metal casting?
- 3. What material is useful for making molds?
- 4. What material is most commonly used for molding?
- 5. Material Comparison Chart
- FAQs
- Conclusion
1. What is the best material for metal casting molds?
The answer depends on your production volume, casting method, and alloy type.
H13 tool steel is widely considered the best material for high-volume, high-pressure die casting. It handles repeated thermal cycling and resists cracking.
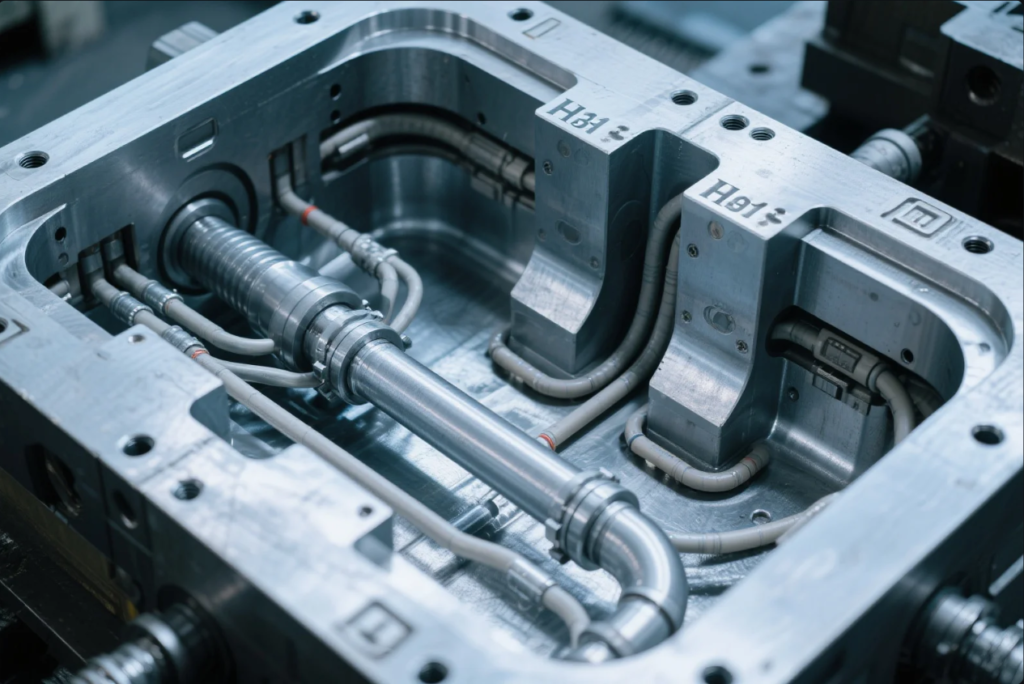
If you're prototyping or producing fewer than 10,000 shots, Aluminum 7075 may be more cost-effective. It’s easier to machine and reduces mold fabrication time by 40%.
| Mold Type | Ideal Material | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Die casting mold | H13 | Long tool life, heat stability |
| Prototype mold | Aluminum | Fast lead time, low cost |
| Plastic mold | P20 | Good balance of cost and hardness |
2. What materials are used in metal casting?
This refers not to the part being made—but to the mold material that forms the part.
Custom mold makers use a combination of steel grades, copper alloys, and aluminum, depending on the mold’s function, operating temperature, and cycle time.

Common mold materials include:
- P20 Tool Steel — Pre-hardened steel for medium-run molds
- H13 Tool Steel — For high-pressure aluminum or zinc casting
- S136 Stainless Steel — Used in medical and optical components
- Beryllium Copper — High heat transfer, ideal for cooling channels
- Aluminum 7075 — Lightweight, machinable, and ideal for trial runs
These materials can also be combined—for example, using a P20 base with beryllium copper inserts in high-heat areas.
3. What material is useful for making molds?
The most useful material is the one that balances strength, thermal control, and cost for your application.
At Prime, we evaluate part geometry, production goals, and required lifespan before choosing a mold material.

| Project Type | Recommended Material | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics housing | P20 + BeCu inserts | Smooth finish + thermal control |
| Medical part tooling | S136 Stainless | Cleanroom-compatible, corrosion-resistant |
| EV battery enclosures | H13 | Withstands repeated heat cycles |
If your product has varying wall thickness or undercuts, using a modular mold with multiple materials helps improve part release and extends mold life.
4. What material is most commonly used for molding?
P20 and H13 tool steels are the most widely used in the global mold industry.
P20 is used for medium-precision plastic injection molds and zinc die casting, while H13 is the preferred material for high-pressure aluminum die casting.

| Material | Mold Type | Application |
|---|---|---|
| P20 | Plastic, zinc cast | Packaging, appliance parts |
| H13 | Die casting | Automotive engine parts |
| S136 | Injection mold | Transparent medical devices |
Prime always stocks P20, H13, and S136, ensuring no delay in material availability.
5. Material Comparison Chart
| Property | P20 Steel | H13 Steel | S136 SS | BeCu (Copper Alloy) | Aluminum 7075 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRC) | 28–32 | 48–52 | 48–54 | 38–42 | 30–35 |
| Thermal Conductivity | Medium | Medium | Low | High | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low | Medium | High | Medium | Low |
| Machinability | High | Medium | Medium | Medium | Very High |
| Tooling Cost | \$\$ | \$\$\$ | \$\$\$ | \$\$\$\$ | \$ |
| Lifespan (cycles est.) | 100,000–200,000 | 500,000+ | 400,000+ | 100,000+ | <50,000 |
| Cooling Efficiency | Medium | Medium | Low | Excellent | Good |
Prime engineers review every mold requirement with clients to ensure the material aligns with product function, tolerance, and delivery expectations.
FAQs
Q1: What’s the best mold material for aluminum die casting?
A: H13 tool steel. It resists thermal fatigue and offers long tool life.
Q2: Can I use aluminum molds for high-volume production?
A: No. Aluminum molds wear out quickly under pressure and high heat.
Q3: Is beryllium copper dangerous to use?
A: Only if inhaled in dust form. Machined parts are safe and widely used in aerospace and electronics.
Q4: How long does a P20 mold last?
A: Typically 100,000–200,000 shots, depending on part geometry and cycle speed.
Q5: Does Prime offer mold material consulting?
A: Yes. We help customers balance performance, cost, and lead time when selecting mold materials.
Conclusion
Your mold material decision affects part quality, delivery speed, and long-term cost.
📩 Get expert help: [email protected]
🌐 Learn more at: https://primecustomparts.com
With over 30 years of experience, ISO certification, and a full stock of premium mold steels and copper alloys, Prime ensures you get the right mold—built to last.