Top 4 Metal Forging Methods Explained: Which One Fits Your Project?
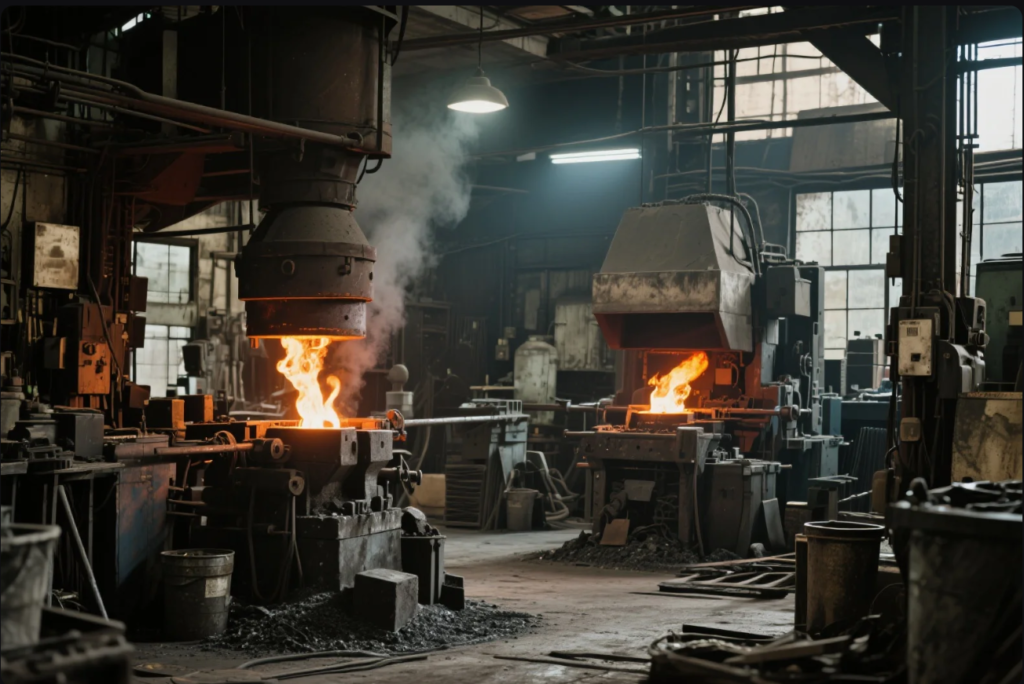

You’re sourcing metal parts. But something’s off. Quality varies. Prices swing. Deliveries miss your schedule. It could all come down to one thing—choosing the wrong forging method.
You’re not alone. Many B2B buyers struggle to pick the right forging approach for their parts. But don’t worry. I’ll walk you through the 4 key forging methods and explain which one fits your project best.
Table of Contents
- Hot Forging vs Cold Forging
- Open Die vs Closed Die vs Rolled Ring Forging
- Forging Presses vs Hammers
- Choose by Shape and Material
- FAQs
- Contact Prime
Hot Forging vs Cold Forging: Key Differences in Strength and Cost
Hot forging shapes metal by heating it above recrystallization temperature, usually above 1000°C. This makes the metal easier to deform, resulting in better grain flow and structural strength.
Cold forging happens at room temperature or slightly warm. It demands higher force but enhances part hardness and surface quality.

External Link: Learn more at AZO Materials
| Feature | Hot Forging | Cold Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | >1000°C | Room temperature |
| Strength | Uniform grain flow | Higher hardness |
| Surface finish | Rough | Excellent |
| Tooling cost | Lower | Higher |
| Part complexity | High | Medium |
| Common metals | Steel, titanium, copper | Aluminum, low carbon steel |
Choose hot forging for structural parts like crankshafts. Go for cold forging for small precision parts like fasteners or gears.
Open Die vs Closed Die vs Rolled Ring Forging: Process Breakdown
Choosing the wrong die setup wastes time and money. Here’s how they compare.
Open-die forging uses flat dies and allows metal to flow freely. Great for large parts or custom jobs.
Closed-die forging compresses metal in custom-shaped dies. Excellent for precise, repeat parts.
Rolled-ring forging transforms a punched disc into a seamless ring. Strong, lightweight, perfect for turbines and bearings.
External Link: Forging Industry Association
| Forging Method | Best For | Precision | Tooling Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Die | Shafts, large disks | Low | Low |
| Closed Die | Complex repeat parts | High | High |
| Rolled Ring | Bearings, flanges | Medium | Medium |
Use open die forging when your geometry is basic but the size is huge. Closed die fits custom parts with tight tolerances. Use rolled ring forging when you need strong, round parts with aligned grain flow.
How Forging Presses and Hammers Affect Precision and Durability
You can choose the right process but still mess up results with the wrong equipment.
Forging presses apply a steady, controlled force—ideal for precision parts.
Drop hammers strike fast, shaping quickly but with less accuracy.

External Link: See equipment differences at TheFabricator.com
| Machine Type | Precision | Force Speed | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Press | High | Low | Aerospace parts, medical tools |
| Mechanical Press | Medium | Fast | Repetitive forging jobs |
| Drop Hammer | Low | Very Fast | Shafts, hammers, simple tools |
At Prime, we use all three. That way, you get flexibility depending on your job size, part complexity, and required finish.
Choosing the Right Forging Process Based on Part Geometry and Material
No process works for all shapes and metals.
Steel usually needs hot forging to prevent cracking. Aluminum alloys often favor cold forging for finish and tight tolerance.
Shape matters too. Complex cavities need closed-die. Long rods? Go open-die. Circular rings? Rolled ring.

External Link: Read material behavior at Engineers Edge
| Shape / Material | Suggested Forging Type |
|---|---|
| Gear blanks | Closed die, hot forging |
| Engine shafts | Open die forging |
| Bearing races | Rolled-ring forging |
| Aluminum brackets | Cold forging |
| Steel tool heads | Hot closed-die forging |
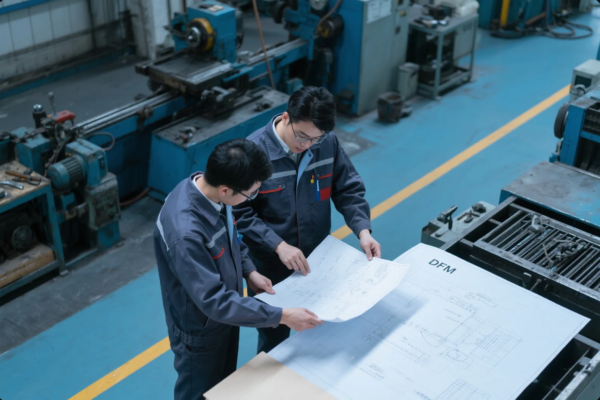
Prime offers free consultation to choose the right forging based on your drawings and expected loads.
FAQs
Q1: What is the most cost-effective forging for low volume?
A1: Open-die forging. It needs minimal tooling and works well for prototypes or custom parts.
Q2: Can I request forging with my logo?
A2: Yes. We support custom logo engraving on all closed-die forged parts.
Q3: Do you ship internationally with full packaging?
A3: Absolutely. We export globally with rust-proof wrapping, wooden crates, foam, and steel strip reinforcement.
Q4: What tolerance can you guarantee for CNC-finished forgings?
A4: Up to ±0.01mm for final machined surfaces.
Q5: Is your factory certified?
A5: Yes, Prime is an ISO-certified forging factory.
Contact Prime
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com
We offer:
- ✅ Custom metal forging solutions
- ✅ Precision CNC parts manufacturing
- ✅ Fast lead times: 15–20 days
- ✅ Free design consultation and DFM review
- ✅ Support for low to high volume orders
Conclusion:
Choose forging methods by shape, material, and function. Get ISO-level quality with custom fit.







