CNC Machining Tolerances Explained: From ±0.01 mm to ±0.001 mm?
Table of Contents
- 1. What Factors Control CNC Tolerance Accuracy?
- 2. Tooling Design & Machine Calibration Best Practices
- 3. Inspection Methods: CMM, Gauges, First Article Testing
- 4. Real-World Examples: Aerospace vs Automotive Parts
- 5. FAQs
- 6. Conclusion
Problem: You need CNC parts with tight tolerances—but what’s the real difference between ±0.01 mm and ±0.001 mm?
Agitate: You worry about part rejection, missed fits, and supplier claims that don't match results.
Solve: This guide explains how tolerance is set, managed, inspected—and how to choose the right level for your application.
Snippet paragraph:
✔️ Learn how CNC tolerance is influenced by machine setup, environment, and material.
✔️ Discover how tooling and calibration ensure repeatable precision.
✔️ See the best inspection methods to verify ±0.001 mm accuracy.
✔️ Compare aerospace vs automotive requirements with real examples.
What Factors Control CNC Tolerance Accuracy?
Achieving a CNC machining tolerance of ±0.01 mm is standard. Going tighter—like ±0.005 mm or ±0.001 mm—requires more control.
Key Influencing Factors:
- Machine Rigidity & Repeatability
- Ambient Temperature Control
- Material Expansion Characteristics
- Feed Rate & Spindle Speed
- Fixture and Clamping Stability
| Factor | Risk at ±0.01 mm | Risk at ±0.001 mm | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature change | Low | Very High | Use climate-controlled workshops |
| Operator error | Medium | High | Automation and G-code simulation help |
| Machine brand | Important | Critical | Use ultra-precision VMCs or jig borers |
Read: Controlling Thermal Expansion in CNC
Tooling Design & Machine Calibration Best Practices
High tolerance needs better tooling. Tool stiffness, condition, and balance directly affect accuracy. Calibration ensures machine consistency over time.
Best Practices Include:
- Short, rigid cutting tools
- On-machine probing systems
- Laser calibration (e.g., Renishaw)
- Ballbar diagnostics for backlash
| Technique | Purpose | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|
| Tool presetting | Maintain length/tool offset | Presetter, Z-height gauges |
| Laser calibration | Axis verification | Laser interferometers |
| Warm-up routines | Thermal stabilization | Internal macros or schedules |
Explore: Renishaw Tool Probing Systems
Inspection Methods: CMM, Gauges, First Article Testing
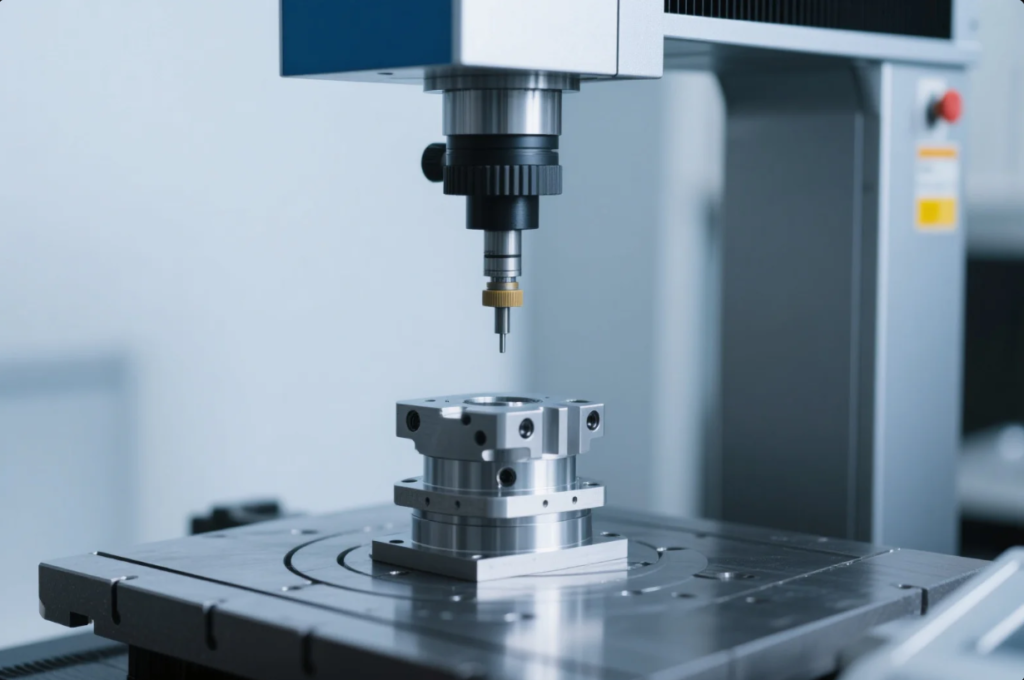

Verification is as important as machining. Here are common ways to inspect high-tolerance parts:
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine): 3D precision, ideal for tight specs.
- Precision Gauges: Fast for bores and shafts, not suitable for contours.
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Used in aerospace/defense for full documentation.
| Method | Tolerance Capability | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| CMM | Up to ±0.001 mm | Complex geometry, traceability |
| Gauges | ±0.005 mm | Quick check, production line |
| FAI | All levels | Certification, new projects |
Guide: CMM Inspection – Quality Magazine
Real-World Examples: Aerospace vs Automotive Parts

Aerospace: Maximum Precision
- Tolerance: ±0.005 mm to ±0.001 mm
- Surface: Ra < 0.4 µm
- Full documentation: AS9102, lot tracking, material certs
Automotive: High Volume, Consistent Fit
- Tolerance: ±0.01 mm to ±0.05 mm
- Surface: Ra < 1.6 µm
- Focus: Speed, cost, and repeatability
| Industry | Typical Tolerance | Focus | Inspection Depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | ±0.001 mm | Precision + traceability | 100% dimensional + FAI |
| Automotive | ±0.01 mm | Cost + cycle time | Spot-check + SPC |
PPAP Guide – AIAG
AS9102 Overview – SAE
FAQs

Q1: What’s the difference between ±0.01 mm and ±0.001 mm?
±0.001 mm is 10x tighter. It’s used where micro-alignment is critical.
Q2: Can all shops deliver ±0.001 mm?
No. Only climate-controlled, precision CNC factories can do this reliably.
Q3: Is CMM required for tight tolerances?
Yes. Manual gauges lack the resolution needed for ±0.001 mm.
Q4: What industries require ±0.001 mm?
Aerospace, medical devices, optics, and sensors.
Q5: Does tighter tolerance cost more?
Yes. More setup, slower cutting, and full inspection are needed.
Q6: Can I see a sample inspection report?
Yes. Always request one before approving production.
Conclusion
Understanding CNC tolerances—from ±0.01 mm to ±0.001 mm—is essential. You now know what affects it, how to inspect it, and when to specify tighter limits.
✅ At Prime, we offer:
- ISO 9001 & AS9100-certified CNC machining
- CMM reports for all tolerance levels
- Expert consultation to help you specify the right tolerances
- Fast quoting and global delivery
📧 Get your quote now: [email protected]
🌐 Visit us: https://primecustomparts.com
Choose Prime—where tolerance meets trust.







