Plastic Prototyping Methods: CNC Machining vs. 3D Printing vs. Soft Mold Tooling?
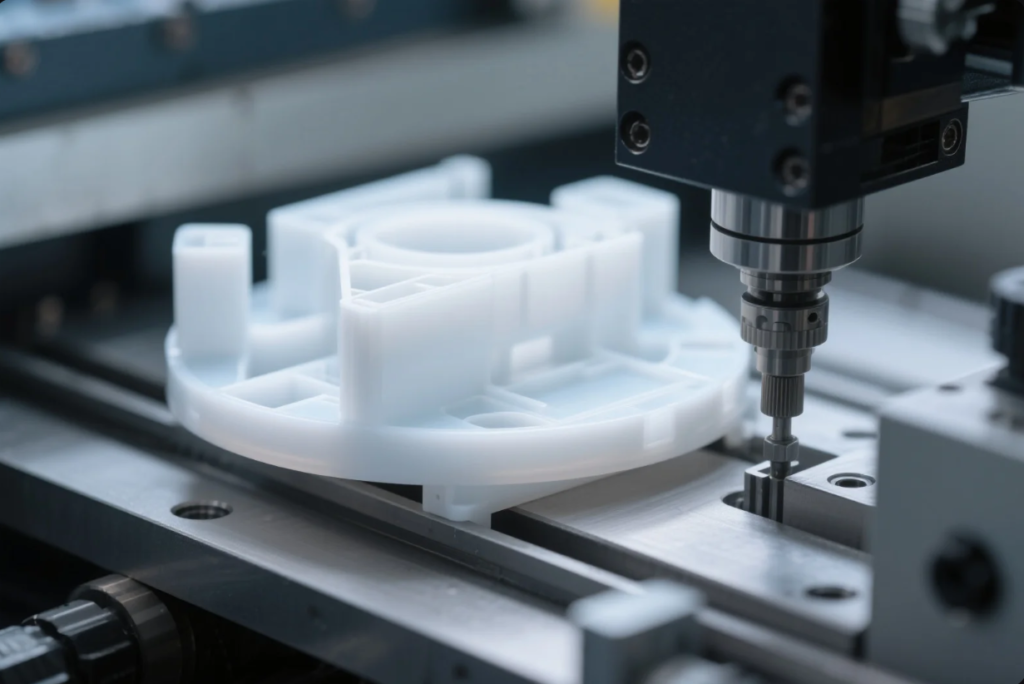

Selecting the right prototyping method impacts speed, cost, and validation for final production.
Choosing between CNC machining, 3D printing, and soft tooling depends on desired precision, material properties, and volume. This guide dives into each method, compares their advantages, and explains how to move from prototype to mass production smoothly.
📌 Table of Contents
- CNC Machining for Prototype Plastic Parts
- Advantages of Soft Tooling for Low‑Volume Production
- 3D Printing vs. Injection Molding Resins
- Transitioning to Mass Production
- FAQs
- Contact Us
CNC Machining for Prototype Plastic Parts
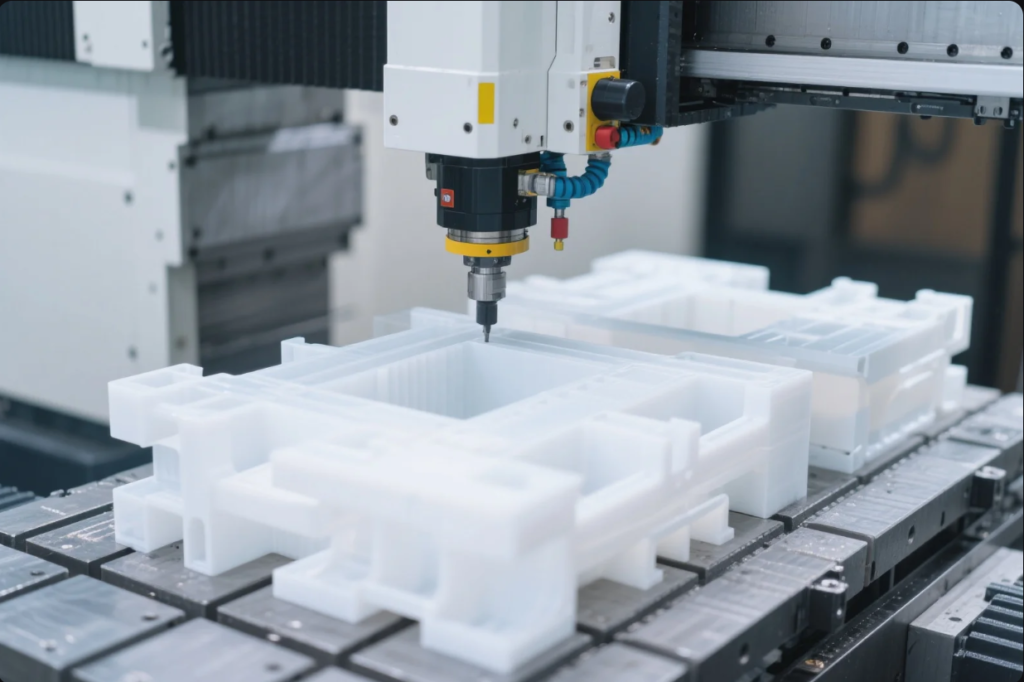

Why choose CNC?
- Achieves tight tolerances (\~±0.05 mm) on real engineering plastics (PC, PA, PEEK).
- Preserves material strength and isotropy unlike 3D prints.
- Great for functional testing with mechanical loads or threaded inserts.
Ideal for:
- End-use feel and fit evaluation
- Precision holes and threads
- Material performance testing
Providers like Protolabs and Xometry offer fast quoting and delivery.
Advantages of Soft Tooling for Low‑Volume Production

Soft tooling is a middle-ground between prototyping and production tooling.
Benefits
- Mold build in 2–4 weeks; much faster than steel tooling.
- Cost-effective for 100–5,000 injection-molded parts.
- Enables quick design iterations with production-like parts.
Soft mold types
- Aluminum milled tools – 5,000–10,000 cycle life
- Epoxy/silicone molds – 50–200 parts, ideal for medical plastics
Used by firms like PTI Engineered Plastics and RapidDirect. Supports functional testing, FDA-resin trials, and early regulatory submissions.
3D Printing vs. Injection Molding Resins: Pros & Cons

Comparison Table
| Tech | Materials | Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | ABS, PETG, ULTEM | Fast, low cost, mechanically capable | Layer lines, anisotropy | Draft prints, concept models |
| SLA | Engineering resins | Smooth, detailed geometry | Brittle parts, lower thermal stability | Aesthetic prototypes, intricate features |
| SLS | Nylon PA11/12 | Strong, no supports, heat-resistant | Rough surface, expensive | Functional, small-batch parts |
| MJF | Multi-material | Strong, multi-color, elastomeric parts | High cost, not mold-representative | Demonstration parts, multi-feature prototypes |
Takeaways:
- 3D prints are perfect for early-stage design, aesthetic models, or quick-fit tests.
- They cannot replicate the mechanical properties of molded parts.
- Soft tooling bridges the gap, producing parts with real material performance and finish.
Transitioning to Mass Production

Step-by-step strategy
- CNC prototyping for engineering verification
- 3D print form/fit prototypes for aesthetics and usability
- Soft tool injection runs for functional and compliance testing
- Design steel production mold in parallel
- Run pilot parts, compare geometries, and validate processes with quality standards (ISO 9001, PPAP)
Quality & process alignment
- Transfer process parameters from soft to steel molds
- Produce dip-tests (30–100 parts) to check consistency
- Document all settings, measurements, and batch data
Prime ensures process control, documentation, and a smooth shift to volume production.
FAQs
1. Which method is fastest for prototyping?
FDM 3D printing can deliver parts in under 24 hours for basic form checks.
2. Do 3D prints act like injection molded parts?
No – only soft-tool or molded parts replicate real material properties.
3. When is CNC preferred over 3D?
Use CNC when material strength, tight tolerance, or threaded features are critical.
4. Is soft tooling durable enough for production?
Yes – aluminum tools typically yield several thousand parts suitable for validation runs.
5. Can I FDA-qualify a prototype?
Yes – soft-tool parts using FDA-grade resins can support regulatory acceptance and validation.
Contact Us
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com
Conclusion
Choosing the right prototyping path—from CNC durability, 3D print speed, to soft-tool molding—ensures your design is validated efficiently and transitions smoothly to mass production. With Prime’s expertise, you get tailor-made workflows, material accuracy, and reliable documentation to support global launches.