What Is a Casting Part? A Complete Guide to Materials, Processes, and Applications

Casting parts confuse many industrial buyers. Wrong process, material, or supplier leads to delays and waste.
Casting parts are formed by pouring molten metal into a mold. Choosing the right method or supplier avoids rework, high cost, and delivery issues.
Buyers often face rough finishes, tolerance mismatches, and miscommunication. I’ll explain what casting parts are, how each process works, and how Prime helps clients in North America, Europe, and beyond succeed.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Casting Part?
- Common Types of Casting Parts
- Choosing the Right Casting Material
- Casting Process Comparison
- Industrial Applications
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Contact Prime
What Is a Casting Part?
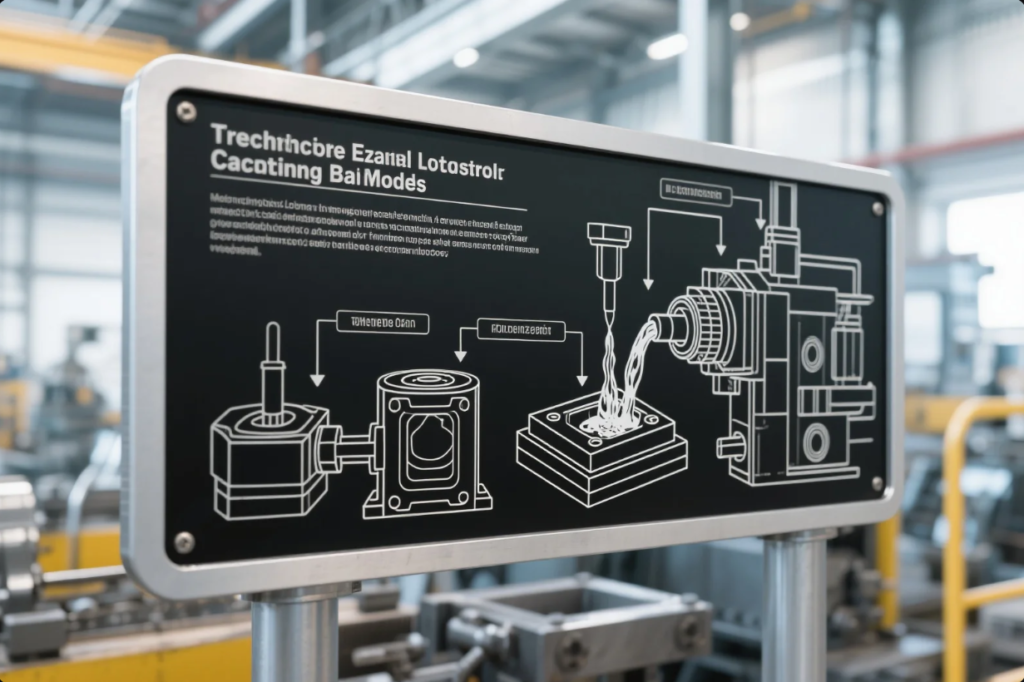
Casting is one of the oldest and most flexible manufacturing methods. It remains foundational in modern production due to its shape versatility and material savings.
A casting part forms when molten metal flows into a mold and solidifies. It can produce intricate shapes and hollow forms with limited post-processing. This is why foundries use casting for components like engine blocks and turbine blades.
- See definitions on Wikipedia: Casting
- Inspect global standards at ISO Casting Standards and ASTM Casting Specifications
Common Types of Casting Parts

Each casting method has distinct characteristics that suit different project requirements.
| Casting Type | Key Benefit | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Low cost, large parts | Found in pump housings and crankcases |
| Die Casting | High volume, smooth finish | Vehicle components, consumer parts |
| Investment Casting | High precision, detailed items | Aerospace parts, surgical instruments |
| Centrifugal Casting | Dense, defect-free cylinders | Pipes, sleeves, high-pressure rings |
More at Thomasnet – Types of Casting Processes and EngineeringClicks comparison guide
Choosing the Right Casting Material
Material choice deeply influences properties like weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost.
| Material | Strength | Weight | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Very High | Heavy | Moderate | Crane parts, construction machinery |
| Iron | High | Heavy | Low | Engine blocks, heavy equipment casings |
| Aluminum | Medium | Light | High | Aerospace, automotive, marine components |
| Zinc | Low | Light | Moderate | Small fittings, precision hardware |
Further reading:
Casting Process Comparison

Understanding trade-offs is essential in choosing the right process.
| Process | Tooling Cost | Speed | Tolerance | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Low | Medium | ±0.5–2 mm | Rough |
| Die Casting | High | Very Fast | ±0.1–0.3 mm | Smooth |
| Investment Casting | Medium–High | Slow | ±0.05–0.2 mm | Very Smooth |
| Centrifugal Casting | Medium | Medium | ±0.1–0.3 mm | Medium |
For guidelines:
Industrial Applications of Casting Parts

Industry demands shape choices and materials.
Automotive
Die-cast aluminum and iron parts appear in engines, suspension systems, and housings. SAE material specs
Aerospace
Investment casting of aluminum and titanium yields precise and light parts. FAA approved materials and NASA metallurgy database
Heavy Machinery
Iron and steel castings are found in mining, pump, and gear systems. EngineeringToolbox offers technical data.
Marine
Aluminum and bronze parts resist corrosion in flanges, fittings, and propellers. For standards, see NACE corrosion standards and ISO/TC 8 submersible valves
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What’s the best method for my product?
It depends on volume, geometry, and finish needs. Choose from sand, die, investment, or centrifugal. For details see EngineeringClicks guide.
2. How tight are tolerances?
We achieve ±0.05 mm on investment cast parts. CNC can add precision post-casting. GD\&T Basics gives guidance.
3. Suitable materials for marine use?
Opt for anodized aluminum or bronze for corrosion resistance. See Total Materia marine alloys and NACE standards.
4. Are you ISO certified?
Yes, we follow ISO 9001. Reports include CMM, PPAP, SGS inspections. Learn more on ISO.org.
5. How long is lead time?
Typically 15–30 days. We support expedited air or sea freight. See Incoterms 2020.
6. Do you support finishing options?
Yes: coating, heat treatment, anodizing, painting, plating. Check NADCA zinc finishing guide.
Contact Prime

We help global buyers succeed by delivering ISO-certified parts, fast lead times, and expert guidance.
Contact us now:
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com
We offer:
- Free quote and DFM review in 24 hours
- Full packaging and inspection services
- Support across North America, Europe, Middle East, Australia
Why Choose Prime for Casting Parts?
- ISO 9001 certified factory since 1993
- 10 production lines covering all casting types
- Over 20 years of one-stop metal parts experience
- Ability to customize to tight specs and branding needs
- Reliable logistics and packaging for bulk international shipping
Let Prime deliver your next casting project with precision, speed, and peace of mind.