TEMPLATE_START
What Metals Are Used in Human Body Parts?

Modern medicine uses metals revolutionarily to repair and replace damaged body parts. We manufacture medical-grade metals that meet strict ASTM and ISO standards for implants.
Snippet paragraph: Common implant metals include titanium (hip replacements), stainless steel (bone screws), cobalt-chrome (dental crowns), and nitinol (stents) - chosen for biocompatibility and mechanical strength similar to natural bone.
Let's examine how specific metals function inside the human body.
LOOP_START
What Metals Are Used in Orthopedic Implants?
Bone replacements require metals that can withstand years of mechanical stress without causing immune reactions.
Snippet paragraph: Orthopedic surgery primarily uses titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V) for joint replacements, cobalt-chrome for load-bearing surfaces, and surgical steel for temporary fixation devices like plates and screws.
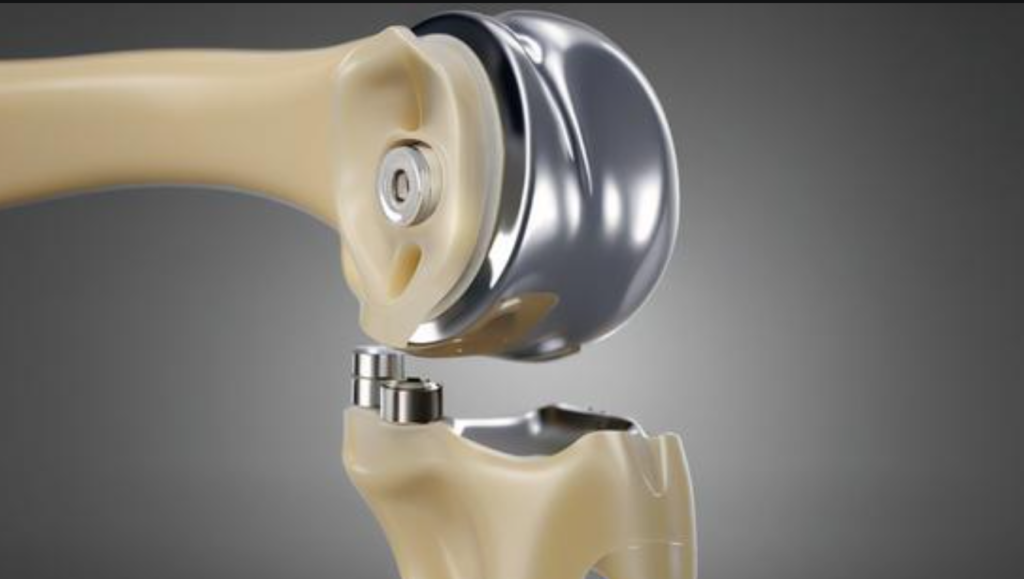

Major Orthopedic Metal Applications
Joint Replacement Materials
- Porous titanium for femur stems
- Ceramic-coated cobalt for ball joints
- UHMWPE plastic for socket lining
Mechanical Properties Comparison
| Metal | Yield Strength | Elastic Modulus | Osseointegration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 830 MPa | 110 GPa | Excellent |
| CoCrMo | 600-1500 MPa | 230 GPa | Moderate |
| 316L Steel | 290-690 MPa | 200 GPa | Poor |
Manufacturing Considerations
- Precision CNC machining for articular surfaces
- Electropolishing to reduce bacterial adhesion
- Plasma spray for porous coatings promoting bone growth
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What Metals Are in Dental Implants?
Tooth replacements require corrosion-resistant metals that bond well with jawbone while supporting chewing forces.
Snippet paragraph: Modern dentistry uses grade 4 titanium for implant posts, zirconia for visible abutments, and gold alloys for crowns - balancing biocompatibility with aesthetic requirements in oral environments.
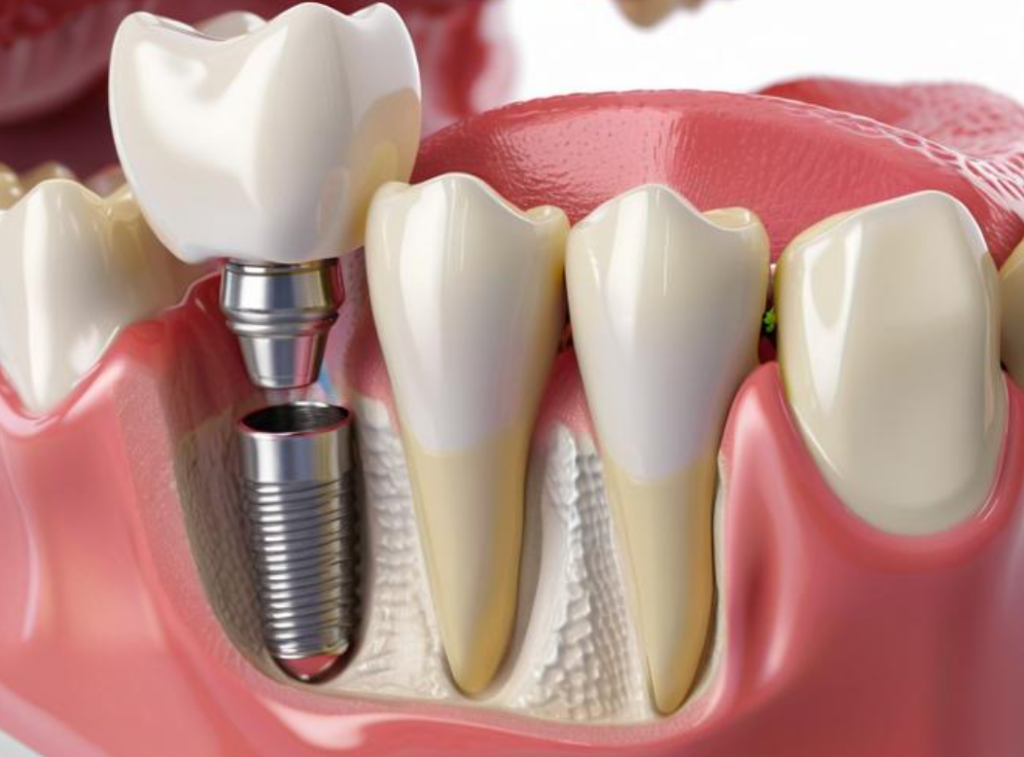
Dental Metal Composition Details
Implant System Components
| Part | Material | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Fixture | CP Ti Grade 4 | 98.9% Ti, 0.5% O₂ |
| Abutment | ZrO₂ (zirconia) | Tooth-colored |
| Crown | Au-Pd alloy | Wear resistance |
Mechanical vs. Biological Requirements
| Requirement | Titanium Solution | Traditional Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Bone bonding | TiO₂ oxide layer | PMMA cement |
| Load bearing | 4.5mm diameter | Natural tooth ~3mm |
| Gum contact | Machined collar | Porcelain margin |
Emerging Technologies
- 3D-printed lattice structures for better osteogenesis
- Nanotextured surfaces with 20-100nm features
- Antimicrobial silver coatings
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What Smart Metal Alloys Are Used in Medicine?
Shape-memory and superelastic metals enable minimally invasive procedures with remarkable functionality.
Snippet paragraph: Nitinol (Nickel-Titanium alloy) dominates medical applications requiring shape memory or superelasticity - used in stents (55% Ni), orthodontic wires, and bone staples that adapt to body temperature.
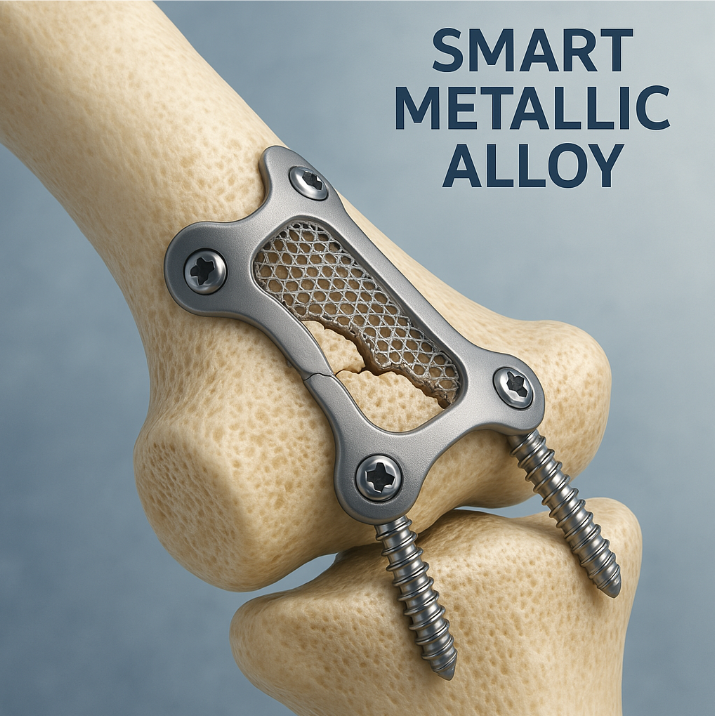
Nitinol Medical Applications
Vascular Devices
- Self-expanding stents (Af=25°C)
- Vena cava filters
- Embolization coils
Comparison with Traditional Materials
| Property | Nitinol | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Strain Recovery | 8% | 0.8% |
| MR Compatibility | Non-ferromagnetic | Causes artifacts |
| Chronic Outward Force | Sustained | None |
Precision Manufacturing Challenges
- Laser cutting of micro-patterns
- Electrolytic polishing to remove surface defects
- Thermal shape setting with ±2°C accuracy
LOOP_END
Conclusion
From titanium hips to "memory metal" stents, medical metals precisely replicate biological functions while meeting stringent safety standards.
TEMPLATE_END







