Choosing the Right Material for Metal Stamping Parts: Stainless Steel to Carbon Steel

Introduction: Why Material Choice Matters
Choosing the right metal stamping material impacts cost, strength, and performance. The wrong alloy can cause failures, delays, or high rework costs.
Smart buyers look beyond price—they consider corrosion resistance, conductivity, weight, and machinability. That’s how you protect margins and deliver consistent parts.
Stainless Steel vs. Carbon Steel: Performance vs. Cost
Stainless Steel
Stainless grades like 304 and 316 resist rust and chemicals. Great for food, marine, and outdoor parts.

Carbon Steel
Grades like SPCC and Q235 are low-cost and easy to stamp.
They are widely used in automotive brackets, enclosures, and industrial supports.
Quick Comparison
| Property | Stainless Steel | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High | Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Weldability | Fair | Excellent |
| Strength | High | Moderate |
| Common Use | Outdoor/medical | General brackets |
When to Select Aluminum, Copper, or Brass
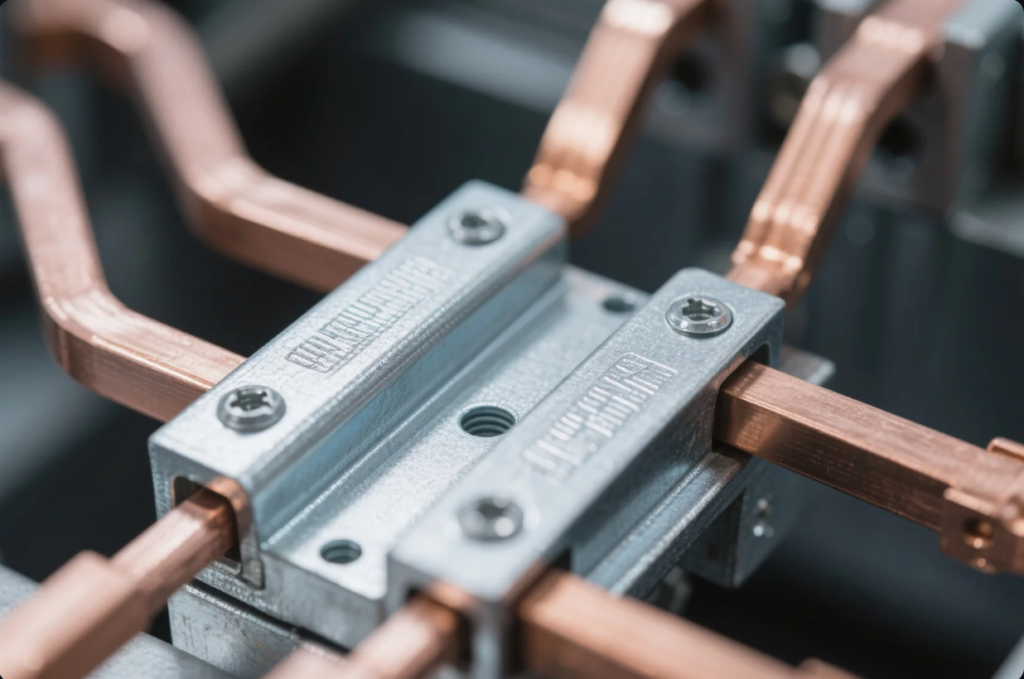
These metals offer unique benefits not found in steel:
- Copper: electrical
- Brass: decorative
- Aluminum: lightweight and corrosion-resistant
Use them when electrical conductivity or reduced weight is critical.
| Material | Strength | Use Case | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Medium | Housings, shields | Lightweight, conductive |
| Copper | Low | Sensors, busbars | Requires plating |
| Brass | Medium | Decorative, switches | Anti-rust, polishable |
Material Thickness & Tolerance: Impact on Production

Material thickness affects:
- Tool wear – thicker stock increases cost
- Flatness – thinner stock risks warping
- Forming – impacts bend radius and hole quality
- Tolerances – needs tighter press control for precision
Standard Thickness
- Steel: 0.5–3.0 mm
- Aluminum: 0.5–2.0 mm
- Brass/Copper: 0.2–1.5 mm
Tolerance Tip
Use CMM to verify ±0.05 mm tolerance. Tighter tolerances (±0.02 mm) require flatter coil stock.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Material Selection

Typical Errors
- Wrong alloy (e.g. using 316 when 304 would do)
- No finish requirement defined
- Tolerance too tight for material
- Unclear if plating is needed
- Specifying exotic alloys without confirming availability
Fixes
- Ask for a DFM review
- Confirm temper, coating, plating needs
- Match strength to function—not overkill
- Validate weldability and RoHS compliance
Prime’s Material Expertise and Support
Global Sourcing
We purchase from top mills like Baosteel, Thyssenkrupp, and Aurubis.
In-House Analysis
Our engineers test punch behavior, burr height, and wear. We simulate deep draw and progressive die flow using SolidWorks.
Certifications
We issue:
- Mill test reports (MTRs)
- REACH, RoHS statements
- Heat treatment certs
- Plating specifications (e.g. ASTM B633)
FAQs for Industrial Buyers
Q: What’s your min/max thickness?
A: 0.2–3.0 mm for metal stamping. CNC up to 25 mm.
Q: Can you advise on alloy substitution?
A: Yes. We recommend based on strength, price, and delivery.
Q: Do you support quick-turn prototyping?
A: Yes. Samples in 7–10 working days.
Q: What finishes can you provide?
A: Anodizing, nickel, tin, zinc, black oxide.
Q: Are your materials REACH and RoHS compliant?
A: Yes. All materials meet EU environmental requirements.
Conclusion & Contact Information
Choosing the right material helps you:
- Lower costs
- Reduce failure rates
- Improve delivery and quality
- Avoid rework and warranty issues
Prime helps global B2B buyers like you select smart alloys backed by mill certs and real results.
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com
Ask us for a free material consultation, quote, or sample analysis. We respond in 12 hours or less.