Complete Guide to Metal Surface Finishing Techniques for Custom Parts in 2025?

Introduction to Chemical, Mechanical, and Electrochemical Finishes
I needed clean, durable custom parts. I struggled with inconsistencies. I then studied full finishing methods. I learned how each finish works and why it matters.
In 2025, surface finishing evolves with green chemistry and digital controls.
Now, three main methods are widely used:
- Chemical Finishes: Including passivation, phosphating, conversion coatings.
- Mechanical Finishes: Such as polishing, blasting, tumbling.
- Electrochemical Finishes: Like plating, anodizing, electropolishing.
These methods change surface properties differently. As a custom stamping parts supplier, I use them daily. I base choices on metal type, end use, and spec.
Read further to see benefits, impact on tolerance, and metal matching advice.
Benefits of Surface Finishing for CNC, Stamping, and Casting Parts
I once ordered casting parts without finishing. They came rough. I lost time and money reworking them. I switched to finished parts. Production now runs smoother.
Snippet
Surface finishing boosts corrosion resistance and wear life. It also improves appearance and functionality.
For CNC precision machining parts, finishing gives smooth edges and tight tolerance.
For custom stamping parts, finishing removes burrs and sharp edges.
For ISO certified casting parts manufacturer, finishing removes sand and porosity.
Key Benefits
- Corrosion Protection: Coatings like plating or anodizing provide barriers.
- Improved Wear Resistance: Polishing and electropolishing reduce micro-scratches.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Decorative finishes serve consumer products and hardware.
- Better Functionality: Reduced friction, smoother fit, lower tolerance variation.
- Easier Cleaning: Finishes seal pores and restrict surface contamination.
Each product type sees distinct benefits:
- CNC Parts: Finishing removes heat-affected zones and micro-specks.
- Stamping Parts: Finishes reduce burrs and improve safety during assembly.
- Casting Parts: Surfaces become smooth and visually consistent.
Finishing helps in certifications too. For example, passivation of stainless steel helps meet FDA standards. Learn more at Passivation on Wikipedia.
How Surface Roughness and Tolerance Are Affected by Finishing
I once rejected parts because roughness exceeded spec. I realized finishing shapes roughness and tolerance significantly. Understanding this saves costs and avoids rework.
Snippet
Each finishing method changes surface roughness (Ra) and part tolerance. Removal methods like polishing and electropolishing smooth surfaces but may remove material. Conversion coatings add thickness. Balancing roughness and tolerance is key.
Dive-Deeper
Surface Roughness (Ra)
- Polishing & Electropolishing: Reduce Ra to <0.1 µm.
- Blasting: Leaves Ra = 1–3 µm.
- Anodizing: Adds 10–25 µm oxide.
- Powder Coating: Adds 50–150 µm, with texture.
Dimensional Tolerance
| Process | Material Change | Impact on Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Polishing | Removes 5–20 µm | Risk for tight specs |
| Electropolishing | Removes 2–5 µm | Safer for ±0.02 mm parts |
| Anodizing | Adds 10–25 µm | Offset needed |
| Zinc Plating | Adds 5–25 µm | Adjust machining required |
| Powder Coating | Adds 50–150 µm | Significant surface shift |
Best Practices
- Design with finish in mind.
- Allow tolerance buffer.
- Communicate roughness and plating needs clearly.
- Use quality checks post-finishing.
Choosing the Right Finish Based on Metal Type: Aluminum, Steel, Brass
I worked on parts in different metals. Each metal needed a tailored surface finish approach. This guide helps you decide finish per metal.
Snippet
Metal type determines applicable finishes.
Aluminum suits anodizing and powder coat.
Steel fits plating, passivation, or phosphating.
Brass benefits from polishing and lacquer.
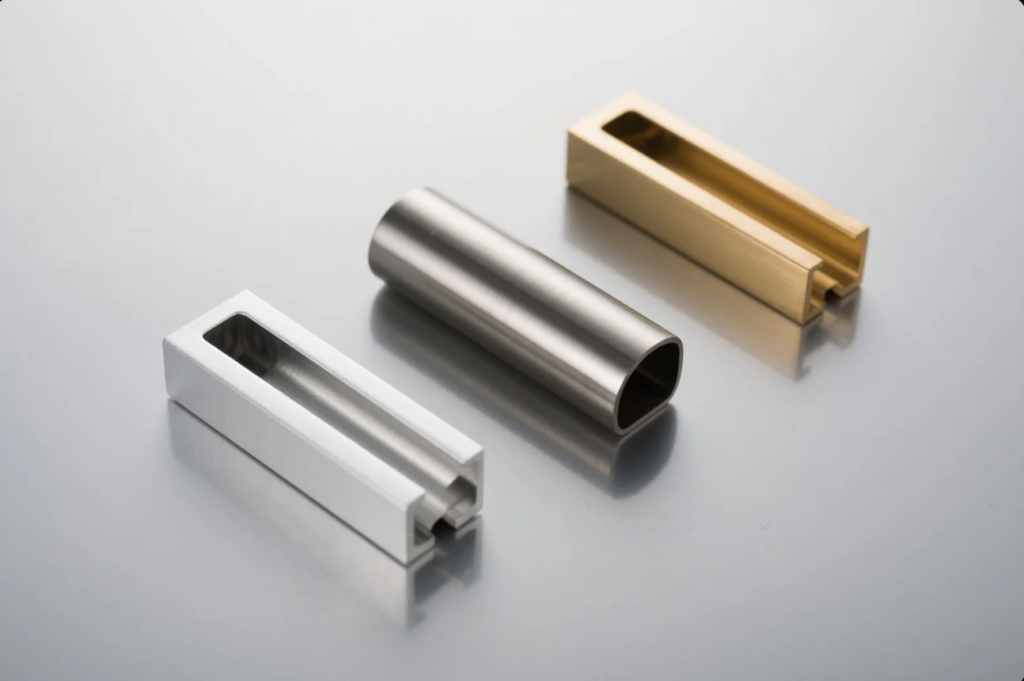

Finish Options
Aluminum
- Hard Anodizing: Adds 10–25 µm, boosts wear.
- Decorative Anodizing: Dyed for branding or appearance.
- Electropolishing: Smooths burrs, ideal for CNC parts.
- Powder Coating: Protects from outdoor corrosion.
Steel
- Zinc Plating: Great for industrial use.
- Zn‑Ni Plating: Strong salt resistance.
- Phosphating: Primer layer before painting.
- Powder Coating: Popular for tools and outdoor fixtures.
Explore Galvanization on Wikipedia
Brass
- Polishing: Gives clean reflective surface.
- Nickel/Chrome Plating: Adds strength and shine.
- Lacquering: Prevents tarnish, keeps luster.
| Metal | Common Finishes | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Anodize, Electropolish, Powder Coat | Aerospace, Electrical, Auto |
| Steel | Zn/Zn-Ni, Powder, Phosphate | Tools, Frames, Fasteners |
| Brass | Polish, Nickel, Clear Coat | Decorative, Fittings, Locks |
FAQs
Q1: Which finish is eco-friendly?
Powder coating uses no solvents and minimal waste.
Q2: Will plating affect tight dimensions?
Yes. Plate adds 5–25 µm. Use offsets or mask areas.
Q3: Why use electropolishing?
Smooths micro peaks, improves corrosion resistance.
Q4: Can finishing alone prevent rust?
Not fully. Duplex systems offer best protection.
Q5: How do I specify surface finish?
Add Ra, method, and tolerance to drawing. e.g., Ra ≤ 0.8 µm, anodized 15 µm.
Q6: Does Prime offer export-ready packaging?
Yes. Foam, desiccant, sealed bags, crates — all included.
Conclusion & Contact
The right finish improves every part.
Use finishing to protect, enhance, and precision-tune metal parts.
From CNC to stamping to casting — finishing transforms good into excellent.
Get in Touch with Prime
We’re a B2B ISO-certified custom parts factory with 10 production lines.
We offer fast lead times, flexible customization, and stable quality.
📞 Website: https://primecustomparts.com/
📧 Email: [email protected]
Let’s create reliable, beautiful metal parts together.