Custom Metal Forgings: What Types Benefit Machinery and Energy Fields Most?

Weak or incorrectly forged metal components often lead to equipment failure1 and expensive downtime. Without clarity on metal forging options2, selecting the right parts becomes challenging, putting your productivity at risk.
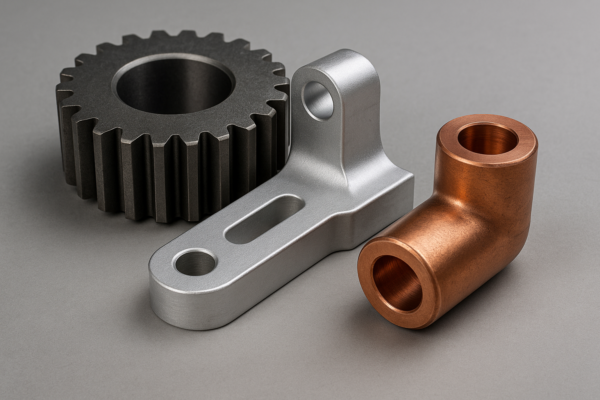
Custom metal forgings produce robust, durable components tailored for machinery and energy fields. Popular methods include free forging, rolling forging, and precision forging1, each offering distinct advantages. Steel, aluminum, and copper are common forging materials, each suited to specific industrial applications.
This guide provides clear insights on forging methods, materials, and quality certifications1. With this information, you’ll easily determine the optimal custom forgings2 for your machinery or energy equipment.
Free Forging vs Rolling Forging: Which Method Fits Large Shafts & Gears?
Production often halts unexpectedly1 due to failures in large shafts and gears. Choosing the wrong forging method2 can intensify these costly issues.
Free forging involves shaping metal with open dies, suitable for large, custom shafts. Rolling forging uses rotating dies, ideal for uniform, precise gears. Choose free forging1 for flexibility, and rolling forging2 when accuracy is paramount.
Dive Deeper: Pros and Cons of Free vs Rolling Forging
Both free forging1 and rolling forging2 have strengths and limitations. Here’s a direct comparison:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Free Forging1 | Flexible, great for large components | Less precise, generates more waste |
| Rolling Forging2 | High precision, minimal material waste | Higher setup costs, limited shapes |
In my experience, free forging1 worked exceptionally well for large shafts where customization mattered. On the other hand, rolling forging2 proved essential for producing multiple gears requiring precise dimensions. Ultimately, your selection depends on balancing flexibility versus accuracy.
Precision Forging for Energy Equipment: Ensuring Corrosion Resistance & Durability?
Corrosion and wear frequently damage energy equipment parts1, leading to frequent downtime and increased maintenance costs. Using standard forged parts2 can exacerbate these problems.
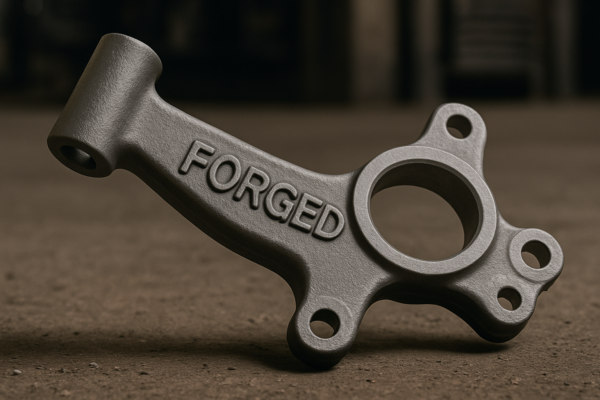
Precision forging creates dense, highly accurate components resistant to corrosion and wear. These forgings are ideal for energy equipment1 like turbine blades, valves, and fittings, significantly extending operational life and reliability.

Dive Deeper: Key Benefits of Precision Forging for Energy Equipment
The following factors illustrate how precision forging1 enhances the performance of energy-related equipment2:
- Dimensional Accuracy1: Ensures tight fits and optimal performance.
- Enhanced Strength: Withstands harsh operational conditions.
- Superior Corrosion Resistance2: Reduces equipment failures and downtime.
| Energy Component | Recommended Forging Material | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Turbine Blades | Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel1 | Corrosion-resistant, high strength |
| Valves | Carbon Steel, Copper Alloys2 | Precise dimensions, durability |
| Pipe Fittings | Aluminum Alloys, Stainless Steel | Lightweight, resistant to corrosion |
When I encountered repeated corrosion issues1 in turbine blades, shifting to precision forging2 offered an immediate improvement. Precision forgings lasted significantly longer, reducing maintenance costs dramatically.
Material Guide: Steel, Aluminum & Copper Forgings for Industrial Use?
Choosing incorrect forging materials1 is a costly mistake, often causing unexpected equipment failures2 and downtime.
Steel forgings1 offer exceptional strength, perfect for heavy machinery. Aluminum forgings2 provide lightweight durability ideal for automotive or aerospace parts. Copper forgings offer superior conductivity, essential for electrical applications.
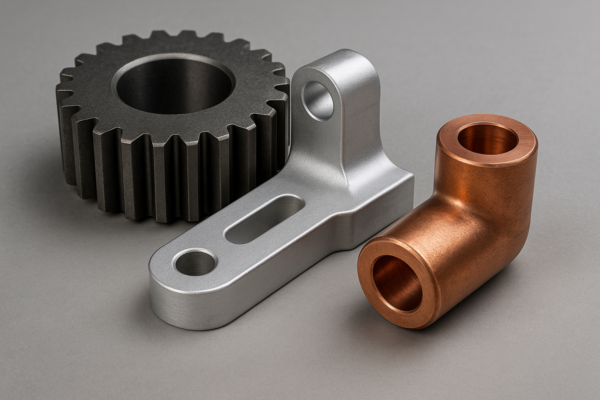

Dive Deeper: Selecting the Right Forging Material
Each material brings unique advantages1 and limitations. The table below guides your decision-making2:
| Material | Ideal Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Shafts, gears, heavy machinery | Strength, toughness | Heavy, can rust without coating |
| Aluminum | Aircraft parts, automotive | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant1 | Lower strength, higher cost |
| Copper | Electrical connectors2, fittings | Excellent conductivity, durable | Lower strength, costly |
I previously faced downtime using aluminum forgings1 for heavy gearboxes. Switching to steel2 dramatically improved equipment reliability, making it essential to match materials carefully to application requirements.
Why ISO-Certified Custom Forged Parts Drive Buyer Confidence Globally?
Without ISO certification1, suppliers frequently deliver inconsistent quality2 and delays, damaging your global competitiveness.
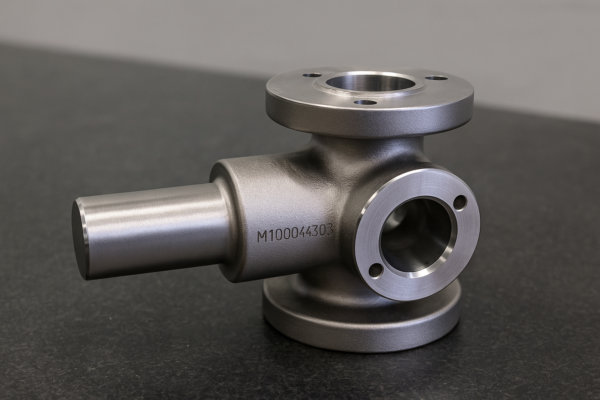
ISO-certified custom forging suppliers1 ensure consistent quality, precise dimensions, reliable deliveries, and transparency. Buyers worldwide prefer ISO-certified manufacturers2 for greater trust and minimal risk.

Dive Deeper: Benefits of ISO-Certified Suppliers
ISO certification1 brings tangible advantages2 to buyers, as shown clearly here:
| Certification Advantage | Buyer Benefit |
|---|---|
| Consistent Quality1 | Reduced defects, better reliability |
| Clear Traceability | Documented production processes |
| Worldwide Recognition2 | Accepted international quality standard |
| Effective Communication | Easier discussions, accurate orders |
After shifting to ISO-certified suppliers1, I saw immediate improvements in product consistency2, reducing returns and improving customer satisfaction significantly.
FAQs on Custom Metal Forging
What is custom metal forging?
Custom metal forging1 shapes metal components under controlled pressure for specific machinery or equipment requirements, offering enhanced durability2 and strength.
Which forging material is best for corrosion resistance?
Stainless steel and aluminum alloys1 offer excellent corrosion resistance2, ideal for harsh industrial environments.
How does forging differ from casting?
Forging1 compresses metal under high pressure, creating stronger components. Casting2 pours molten metal into molds, suited for intricate shapes but less strength.
What industries rely heavily on custom forged parts?
Industries such as energy, automotive, aerospace, construction, and machinery depend significantly on custom forged components1 for durability and precision2.
How quickly does Prime deliver custom forged parts?
Prime offers quick delivery times due to our advanced manufacturing facilities and streamlined processes, typically ensuring timely shipments worldwide.
Choose Prime: Your Trusted Custom Forging Partner
Choosing the right forging supplier1 directly affects your equipment reliability2, productivity, and global competitiveness. Prime International offers:
- ISO-certified quality assurance1
- Precision forging expertise2
- Rapid delivery worldwide
- Flexible, customized solutions
Contact Prime today at our official website https://primecustomparts.com/ or email us at [email protected]. Receive professional consultation, tailored quotes, and solutions to optimize your industrial and energy equipment performance.
We look forward to driving your success through premium forged components.
Prime International: Ensuring Quality and Reliability Since 1993
Contact us now to experience firsthand how Prime sets the industry standard in custom metal forgings, reliability, and precision manufacturing.
https://primecustomparts.com/
[email protected]
-
Understanding ISO-certified quality assurance can enhance your knowledge of industry standards and improve your business practices. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Exploring precision forging expertise can provide insights into advanced manufacturing techniques that enhance product quality and efficiency. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩