How Custom Metal Molds Improve Efficiency in Industrial Production Lines?

Industrial manufacturers lose millions yearly from delays, rejects, and inefficient tooling. Poor mold design slows production and inflates costs.
Custom metal molds ensure repeatability, reduce cycle time, and improve process stability across industrial sectors.
This article explores how molds impact efficiency, which fabrication methods apply, and why choosing the right tooling pays off.
Why is tooling important?
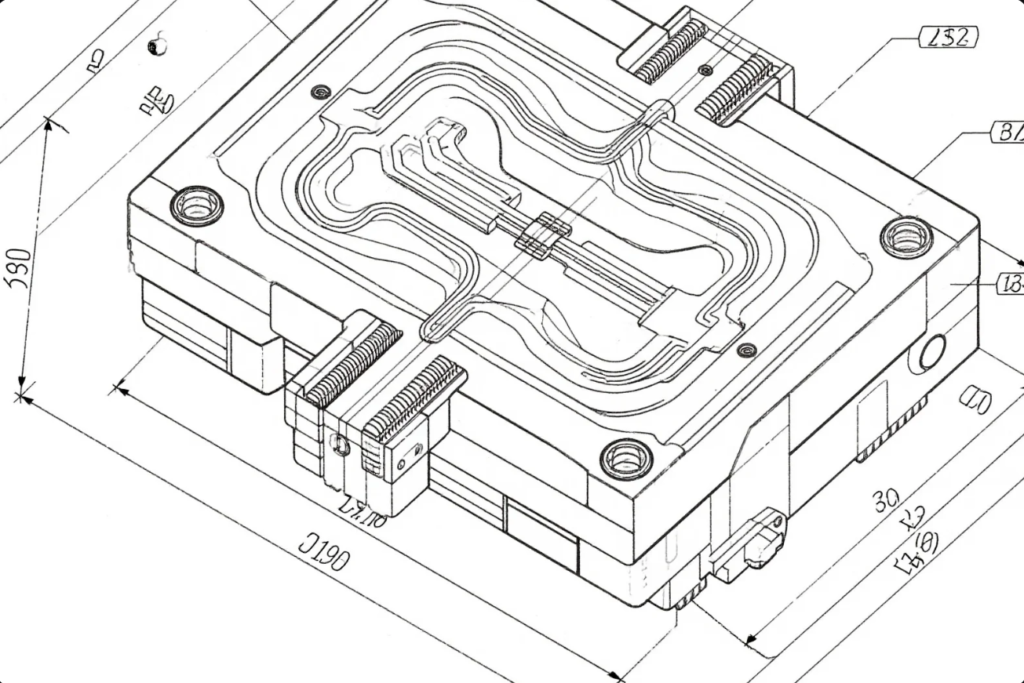
Tooling isn’t just about shaping material—it’s about controlling process, quality, and cost. In fast-paced industries, bad tooling halts the entire line.
Tooling determines precision, repeatability, uptime, and total cost of ownership in industrial production.
What Happens with Poor Tooling?
| Impact Area | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Rejects, customer complaints |
| Slow Cycle Time | Lower output, longer payback |
| High Maintenance | Downtime, spare part costs |
| Operator Fatigue | Inconsistent handling, ergonomic issues |
At Prime, we once redesigned a stamping mold for a European HVAC client. Output jumped 45%, and unplanned stoppages dropped to zero.
Learn more from Autodesk’s Tool Design Solutions and ThomasNet on Tooling.
Which moulding techniques used to manufacture a metal based component?

Not all metal parts are formed the same way. Selecting the right molding method depends on size, shape, volume, and alloy.
Main metal molding techniques include die casting, investment casting, and metal injection molding (MIM).
Common Molding Techniques
| Technique | Key Features | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High pressure, tight tolerance | Auto parts, connectors |
| Investment Casting | High detail, no flash | Valves, impellers, tools |
| Metal Injection Molding | Complex, micro-size, high-volume | Medical, electronics, defense parts |
Explore in-depth analysis from Engineering Product Design and Dynacast Molding Guide.
Prime offers all three mold types, with optimized cooling, ejection, and automation-ready formats.
What is the use of metal mould?

Metal molds are the backbone of modern industry. They’re more than just shapes—they define how parts behave in real-world use.
A metal mold is used to shape molten or powdered metal into a precise, repeatable component, often under high pressure or heat.
Industrial Uses of Metal Molds
| Sector | Component Examples |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Brackets, gear housings, transmission pins |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, sensor frames, casings |
| Medical | Implant housings, surgical tool parts |
| Power Systems | Connectors, shields, motor enclosures |
Learn more about die molds at Wikipedia – Die Casting, or dive into tooling design at Machine Design.
We helped one telecom client redesign their heat sink mold, which cut cycle time by 21%.
What are the 3 metal fabrication techniques?

Molded components are just one part of the industrial metalwork puzzle. Fabrication includes forming, joining, and subtracting material.
The three core fabrication methods are casting, welding, and CNC machining.
Fabrication Technique Comparison
| Method | Process Description | Typical Products |
|---|---|---|
| Casting | Molten metal poured into a mold | Large parts, near-net shapes |
| Welding | Metal fusing through heat or filler | Frames, structural assemblies |
| CNC Machining | Cutting/shaping using digital tooling | Precision shafts, housings |
To compare techniques, see The Fabricator’s Guide to Metal Processing or Xometry’s Fabrication Service Page.
At Prime, we integrate casting, CNC, and welding to deliver complete component packages—ready for industrial assembly.
FAQs
1. What mold life can I expect in industrial use?
P20 lasts \~300,000 shots. H13/NAK80 molds exceed 1,000,000 cycles under regular maintenance.
2. Can you analyze my existing mold for optimization?
Yes. We offer DFM + moldflow reports to improve part cooling, cycle time, and gate balance.
3. Do you handle international shipping?
We ship to 50+ countries with ISPM-15 wooden crates and CE/ISO documents.
4. What CAD formats are accepted?
STEP, IGES, DXF, and SolidWorks files. We can also correct poor models for free.
5. How long does a new mold take to make?
Prototype: 7–10 days. Full production tools: 15–30 days, including T1 trial.
Conclusion
Efficient molds equal efficient production. Prime helps you run faster, leaner, and smarter with precision metal molds.
✅ ISO-Certified Tooling
✅ High-Cycle Mold Longevity
✅ One-Stop CNC + Casting + Welding
📞 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com
Let’s optimize your production—one custom mold at a time.







