How to Cast with Aluminum? The Complete Foundry Guide for Beginners and Pros

Aluminum casting melts at just 660°C (1220°F), making it ideal for DIY and industrial projects. Compared to steel or iron, it’s safer to handle while producing lightweight, corrosion-resistant parts.
Snippet paragraph: Aluminum casting involves melting scrap or ingots (600-760°C), degassing with argon/table salt, then pouring into sand, plaster, or metal molds—producing parts with 85-95% as-cast dimensional accuracy when done properly.
Follow this technical guide to avoid common defects like porosity or oxide inclusions in your aluminum castings.
What Equipment Do You Need for Aluminum Casting?
A basic setup costs under $500 but scales to automated production.
Snippet paragraph: Essential tools include: crucible furnace (propane/electric), #8-10 silica sand with bentonite clay, steel flasks, thermocouple (650°C+ range), skimmer, tongs, and PPE (face shield/gloves). Optional: flux, degassing tablets.

Aluminum vs Other Metals: Equipment Differences
| Tool | Aluminum Specs | Iron/Steel Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace | Propane (650-800°C) | Induction (1200-1600°C) |
| Crucible | Clay-graphite (#6-10) | Silicon carbide |
| Mold Sand | Greensand (3-5% moisture) | Resin-bonded (dry sand) |
| Pouring Temp | 730±20°C (optical pyrometer) | 150-200°C above melting |
Warning: Never use galvanized steel tools—zinc fumes are toxic when heated.
How Do You Prepare Aluminum for Casting?
Impure metal causes 70% of casting defects.
Snippet paragraph: Clean scrap by removing paint/coatings (burn-off at 400°C), then pre-melt into ingots—add 1% flux (50% NaCl + 50% KCl) to separate aluminum from slag before final casting melt.
Aluminum Alloy Selection Guide
| Alloy | Melting Range | Best For | Scrap Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | 650-760°C | Structural parts | Bicycle frames, truck rims |
| A380 | 580-600°C | Thin walls | Engine blocks, gearboxes |
| 1100 | 640-660°C | Artistic casts | Drink cans, food trays |
| 4043 | 570-630°C | Welding rods | Window frames, pipes |
Pro Tip: Mix 80% scrap with 20% pure aluminum to maintain alloy consistency.
What’s the Optimal Mold Technique for Aluminum?
Different methods suit various project needs.
Snippet paragraph: For most DIY casts, use greensand molds rammed to 70-80 hardness (B-scale)—ensure 1-3° draft angles on patterns. Permanent metal molds work best for >100 identical parts.

Mold Type Comparison
| Type | Surface Finish | Dimensional Accuracy | Cost | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greensand | ±150 Ra | ±0.5mm per 25mm | $ | Prototypes, large parts |
| Plaster | ±50 Ra | ±0.2mm per 25mm | $$ | Art pieces, jewelry |
| Die Cast | ±25 Ra | ±0.1mm per 25mm | $$$$ | Mass production |
| Investment | ±15 Ra | ±0.05mm per 25mm | $$$ | Aerospace, medical |
Key Metric: Aluminum shrinks 1.3-1.5% during solidification—scale patterns accordingly.
How Do You Pour Aluminum Safely?
Turbulence causes oxide contamination.
Snippet paragraph: Preheat molds to 100-150°C, pour at 730±20°C in a steady stream (10 sec/kg), keeping ladle within 2cm of sprue—degas with 0.3% argon tablets 2 minutes before pouring.
Pouring Defects & Solutions
| Defect | Cause | Prevention | Repair Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold shuts | Pouring too slow/cold | Increase temp by 30°C | Re-melt and recast |
| Gas porosity | Moisture in mold | Bake sand at 120°C for 2hrs | Epoxy impregnation |
| Inclusions | Oxide/slag entry | Use ceramic foam filters | Grinding/welding |
| Shrinkage | No risers | Add 150% feeding volume | Machining allowance |
Safety: Always have a CO2 fire extinguisher—water reacts explosively with molten aluminum.
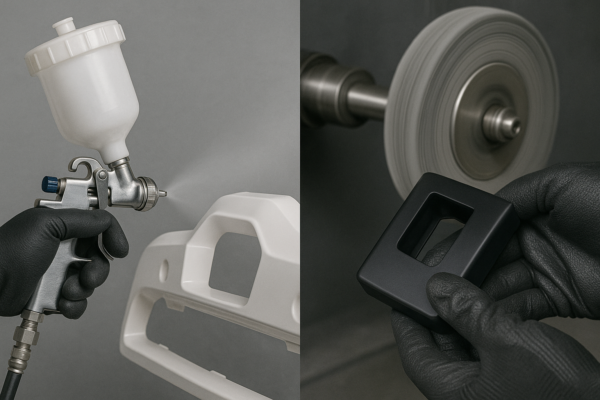
How Do You Finish Aluminum Castings?
Post-processing improves functionality and appearance.
Snippet paragraph: After 24hr cooling, remove gates with bandsaws (±1mm cut lines), sandblast with 80-120 grit alumina, then optionally polish to 600-grit for mirror finishes—anodizing increases corrosion resistance.
Finishing Options Table
| Process | Equipment Needed | Surface Ra | Cost | DIY Friendly? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sanding | Belt sander (60-600 grit) | 3.2-25 μm | $ | Yes |
| Tumbling | Rotary tumbler + media | 1.6-6.3 μm | $$ | Yes |
| CNC Machining | Vertical milling center | 0.4-1.6 μm | $$$$ | No |
| Anodizing | DC power supply, acid bath | 0.2-0.8 μm | $$$ | Advanced |
Inspections: Check for hidden voids with ultrasonic testing if parts bear structural loads.
Conclusion
Successful aluminum casting requires clean metal, proper mold design, controlled pouring, and thorough finishing—master these steps to produce everything from replacement parts to custom sculptures.