How to forge metal parts and what tools do you need to get started?

Forging is one of the oldest and strongest ways to shape metal—but it requires heat, pressure, and proper process control.
Forging metal involves heating it to a malleable state and shaping it with force—ideal for strong, durable parts.
Here’s how forging works, from home setups to industrial processes.
LOOP_START
How do you forge metal?
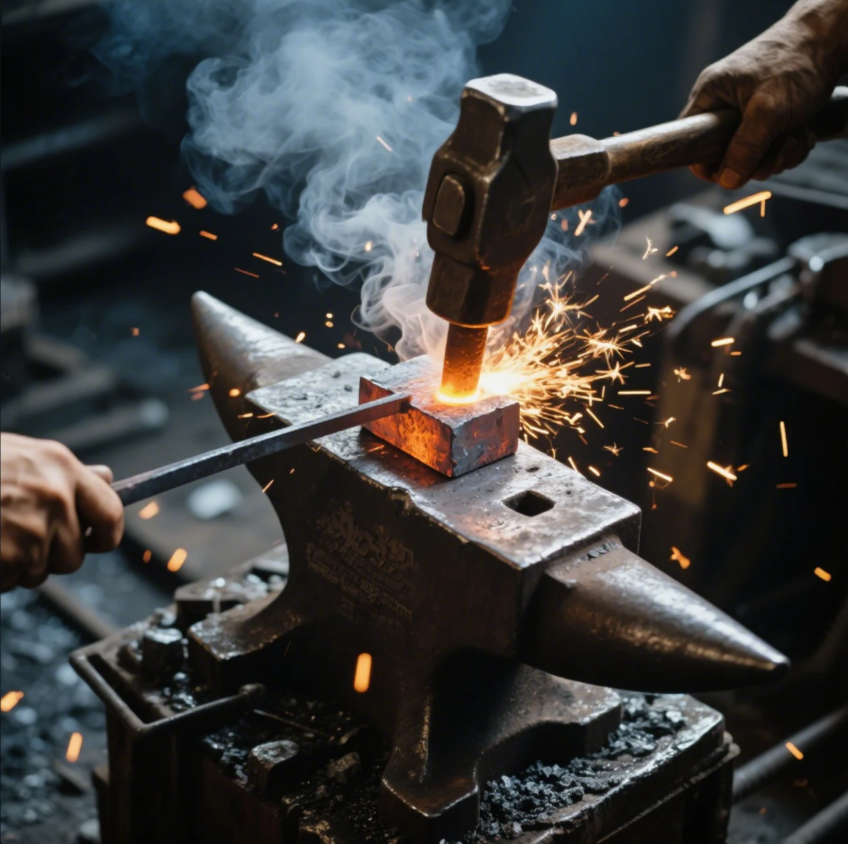

Forging isn’t just hitting hot metal—it’s a carefully controlled process to achieve exact shapes and properties.
To forge metal, you heat it until it’s malleable, then hammer or press it into the desired form using dies or hand tools.
Key steps in metal forging
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating | Metal is brought to 1,100–1,300°C depending on type |
| Shaping | Force is applied with hammers, dies, or hydraulic presses |
| Trimming | Extra material (flash) is removed |
| Cooling | Controlled cooling helps relieve stress |
| Finishing | Parts may be ground, machined, or heat treated afterward |
How Prime supports forged parts
At Prime, we offer open-die and closed-die forged components in steel, aluminum, and copper. For one EU automotive client, we supplied forged brackets with 4x the fatigue strength of comparable cast parts—ready for rough terrain use.
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
Can you forge steel at home?
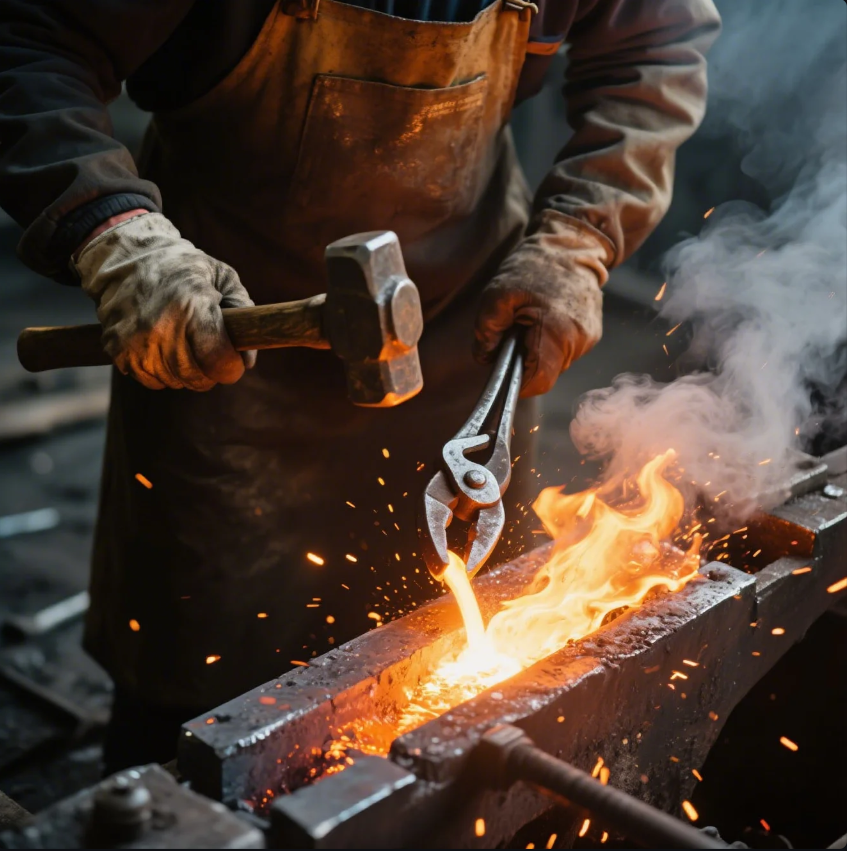

With the right tools, even beginners can forge basic shapes at home—safely and affordably.
Yes, you can forge steel at home using a propane forge, anvil, hammer, and proper safety gear.
Home forging equipment list
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Propane Forge | Heats steel to forging temperature (~1,200°C) |
| Anvil | Provides a hard shaping surface |
| Hammer (Cross-peen) | Applies impact to shape metal |
| Tongs | Holds hot workpiece securely |
| Quench Tank | Cools and hardens part after shaping |
| Safety Gear | Gloves, goggles, apron, and ventilation |
Safety tips from Prime
Always forge in a well-ventilated outdoor space. Use high-carbon or mild steel to start—avoid unknown scrap, as it may crack or not forge properly. Wear full protection—metal can shatter, and hot scale can cause injury.
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What are the various 5 steps in the forging process?

Each step in forging affects the metal’s shape, strength, and internal structure.
The 5 main steps in the forging process are heating, preforming, forging, finishing, and cooling.
Breakdown of the 5 steps
| Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
| 1. Heating | Brings metal to a malleable temperature |
| 2. Preforming | Rough-shapes metal before final forming |
| 3. Forging | Applies pressure to form the metal into its final design |
| 4. Finishing | Trimming flash, grinding, or adding surface treatments |
| 5. Cooling | Controlled cooling to avoid cracks and control grain structure |
Our industrial forging sequence
At Prime, we use hydraulic presses with in-die preforming, allowing faster cycles and better shape control. This is how we forged high-precision drive shafts for a North American machinery OEM, cutting post-machining by 35%.
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
How do you forge two pieces of metal together?
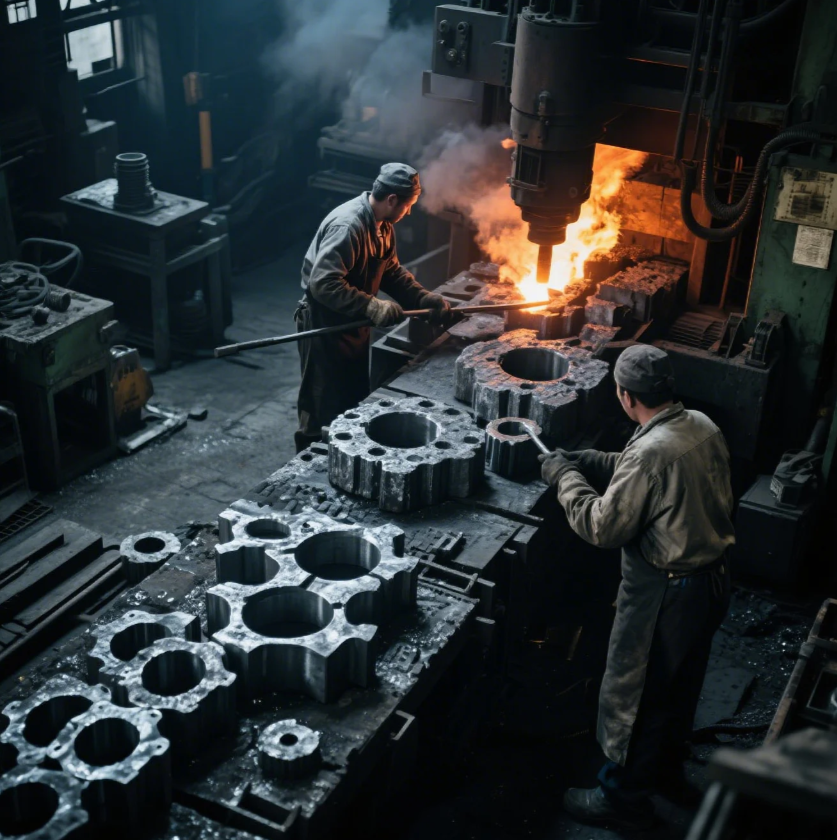

Joining metals by forging creates incredibly strong bonds—but only if done properly.
To forge two metal pieces together, you heat both to forging temperature and hammer them under pressure until they fuse into a single unit.
What’s needed to forge-weld metal
| Requirement | Role in Joining |
|---|---|
| Correct Temperature | Ensures grain structure blends without melting |
| Clean Surfaces | No oxidation or scale between joint areas |
| Force Application | Pressure must be high enough to displace metal at boundary |
| Flux (optional) | Used to prevent oxidation in some traditional forge welding |
Prime’s approach to joined forgings
While traditional forge welding is less common in industry today, we use closed-die multi-piece forging to pre-assemble complex parts. In one project, we produced joined tool holders that passed 200,000-cycle torque tests with no weld separation.
LOOP_END
结论
Forging shapes metal into stronger, denser forms—at home or in industry, it delivers unmatched toughness and durability.
Need custom-forged parts for your project? Contact Prime today for a free consultation, fast tooling, and ISO-certified forged components—trusted globally in automotive, energy, and industrial markets.