The Complete Guide to Custom Sheet Metal Parts: From Material to Finish
Whether you’re building precision enclosures, structural components, or high-performance brackets, custom sheet metal parts are the backbone of countless industries—from automotive and aerospace to medical and electronics.
This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of the custom sheet metal process, from material selection to fabrication techniques, surface treatments, and how to work with suppliers to get accurate, fast quotes.

Choosing the Right Material: Steel, Aluminum, Copper, or Brass
Selecting the correct base material is the first and most critical step in sheet metal design. Each material offers different benefits in strength, formability, conductivity, weight, and corrosion resistance.
🔩 Steel
- ✅ Strong, durable, affordable
- ⚠️ Prone to rust unless coated
- Ideal for: structural brackets, automotive frames, machine panels
✈️ Aluminum
- ✅ Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, non-magnetic
- ⚠️ Softer, must be carefully formed to avoid cracking
- Ideal for: aerospace parts, electronics enclosures, heat shields
🔋 Copper
- ✅ Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity
- ⚠️ Expensive and soft
- Ideal for: power systems, busbars, electronics terminals
🎖️ Brass
- ✅ Good corrosion resistance, formable, aesthetic finish
- ⚠️ Less common for structural applications
- Ideal for: decorative components, marine hardware, precision fasteners

📘 Learn more: Matmatch – Compare Sheet Metal Materials
Overview of Fabrication Processes: Laser Cutting, Punching, and Welding
Sheet metal manufacturing includes several stages. Here’s how the most common processes work:
🔥 Laser Cutting
- Precision cutting using focused laser beam
- Ideal for intricate patterns or tight tolerances
- Works with all metals including stainless, aluminum, copper
- Extremely clean edges, low distortion
🥊 CNC Punching
- Turret press punches standard holes and slots
- Fast and cost-effective for repeatable shapes
- Best for medium-thickness steel and aluminum parts
- May require deburring after
🔧 Bending & Forming
- Performed on a press brake
- Requires bend allowance, K-factor, and springback compensation
- Precision forming critical for enclosures and brackets
🔩 Welding
- Joins metal components permanently
- MIG and TIG are most common
- Stainless and aluminum require experienced welders
- Welding distortion must be managed
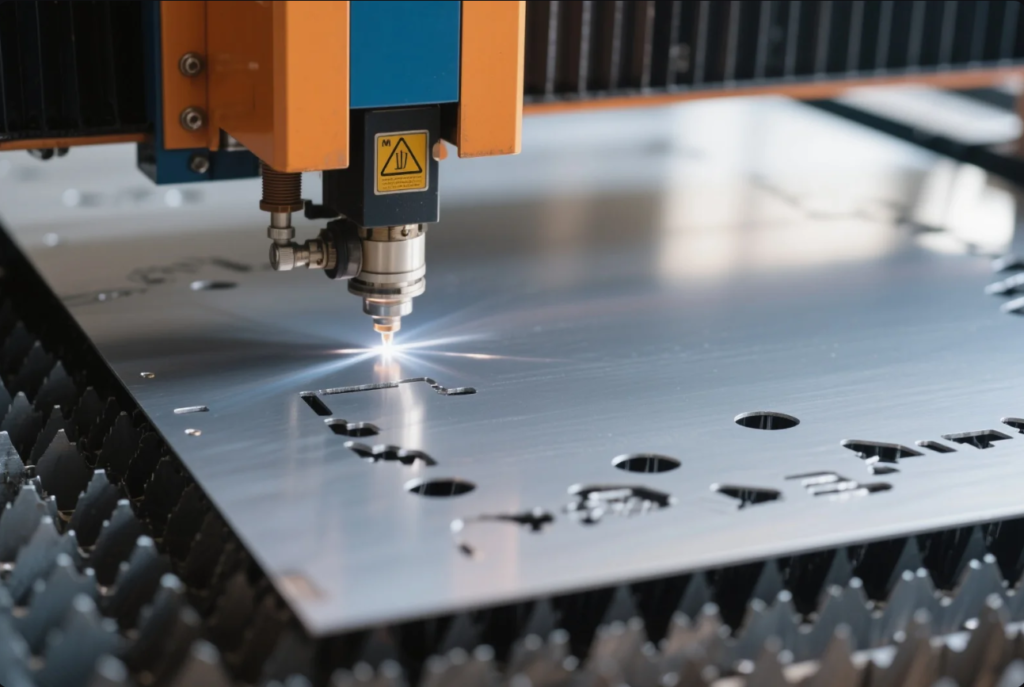

More on laser cutting: Trumpf Technologies
Surface Finishing Options: Powder Coating, Plating, and Anodizing
Once the metal part is fabricated, it’s time for finishing. This improves:
- Corrosion resistance
- Surface smoothness
- Aesthetics and branding
- Conductivity (in special applications)
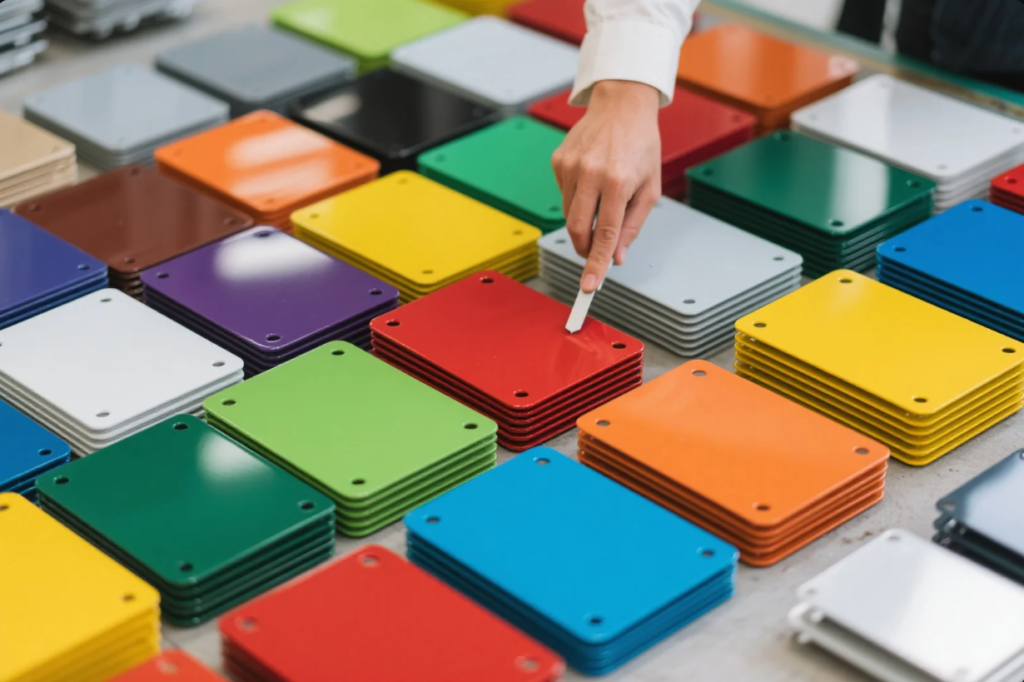
🎨 Powder Coating
- Electrostatic application of colored resin
- Cured under heat for durable finish
- Available in various colors and textures
- Common in consumer electronics, appliances, signage
🧪 Electroplating
- Adds a thin layer of metal (e.g., zinc, nickel, chrome)
- Improves corrosion resistance and appearance
- Typically applied to steel components
- Can be combined with passivation
⚡ Anodizing (for Aluminum Only)
- Converts aluminum surface into a corrosion-resistant oxide layer
- Can be dyed in various colors
- Maintains conductive properties
- Common in aerospace, medical, and electronics

How to Submit Drawings and Get Fast, Accurate Quotes from Suppliers
To get accurate sheet metal quotes fast, follow these best practices:
📝 File Types
- Provide 2D DXF or DWG for flat patterns
- Provide 3D models in STEP, IGES, or SLDPRT
- Include PDF with dimensions, tolerances, material spec, finish type
📐 Include Design Intent
- Mark critical dimensions
- Highlight bend lines and direction
- Specify surface finish, if required
📦 Clarify Order Volume & Delivery
- Include quantity (prototype or production)
- Delivery location and preferred lead time
- Request DFM feedback before final release
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the same design for both laser cutting and CNC punching?
A: You can, but laser supports more intricate shapes. For CNC punching, use round/square patterns and standard tooling.
Q2: What’s the minimum sheet thickness you can work with?
A: Typically 0.5 mm for aluminum and up to 6 mm for steel. Thinner materials risk warping during cutting or bending.
Q3: Can I get samples before mass production?
A: Yes! At Prime, we offer prototypes with fast turnaround before committing to volume production.
Q4: Is finishing required for all parts?
A: Not necessarily. For indoor applications or budget projects, raw metal may suffice. For corrosion-prone environments, finishing is strongly recommended.
Contact Us
Ready to create high-performance custom sheet metal parts?
📧 Email us: [email protected]
🌐 Visit our site: https://primecustomparts.com
At Prime, we provide ISO-certified, one-stop sheet metal solutions including stamping, bending, welding, cutting, and finishing—with fast, accurate quotes and on-time delivery to clients worldwide.