The Ultimate Guide 2025: Which Metal Fasteners Are Best for Your Project Needs?

If you choose the wrong fastener, you risk costly failures1. Let’s solve your fastener selection2 challenges right now.
Choosing between stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel fasteners is a key step for every industrial project. Each type has different properties, advantages, and limitations. In this ultimate guide, I share a complete comparison of materials, corrosion resistance1, price, applications, and sourcing best practices. I also offer insight based on my 20+ years of experience at Prime, an ISO-certified, globally trusted fastener supplier2.
Your fastener choice1 affects your product’s lifetime, safety, costs, and your company’s reputation. You might have faced issues like poor material quality2, missed delivery dates, and unclear supplier specs. Here, you’ll find real answers based on practical experience. Stay with me to avoid common mistakes and make sure you select fasteners that fit your exact needs. This guide aims to provide everything you need in one place so you don’t have to search elsewhere.
What Are Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, and Alloy Steel Fasteners? How Do Their Properties Compare?
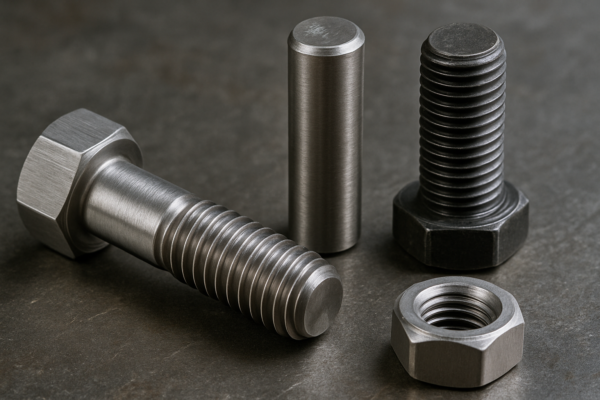

Many buyers find fastener material choices1 overwhelming. You may hear confusing grades, numbers, and claims from suppliers. Sometimes, engineers or procurement teams don’t have time to dig into the differences, which causes mistakes in sourcing. In my years at Prime, I have helped hundreds of clients choose the correct fastener2 for each application.
Stainless steel fasteners1 are known for corrosion resistance and a clean finish. Carbon steel fasteners2 are affordable and strong. Alloy steel fasteners deliver high strength, excellent for heavy loads. Each type has a unique chemical composition, and that directly impacts its performance and price.
To make your choice easier, let’s compare these three materials1 side by side using simple language2.
Material Comparison Table
| Material | Main Elements | Mechanical Strength1 | Corrosion Resistance2 | Typical Application | Customization Level | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Iron, Chromium (>10%) | Medium | Excellent | Food, marine, medical, outdoor | High | \$\$\$ |
| Carbon Steel | Iron, Carbon (0.05-2%) | Low-High | Poor (unless coated) | Auto, construction, machines | Very High | \$ |
| Alloy Steel | Iron, Cr/Mo/Ni/V/etc | Very High | Good (with coating) | Bridges, cranes, mining | High | \$\$ |
In my daily work, clients often ask about the differences between grades like 304, 316, or 8.8, 10.9 bolts. Stainless steel fasteners (such as 304 or 316) offer corrosion resistance but cost more. Carbon steel (like grade 8.8) can be very strong but may rust if not coated. Alloy steel, with extra elements such as chromium or molybdenum, delivers top strength for demanding jobs but needs protective coating.
A buyer from North America once ordered carbon steel fasteners1 for an outdoor marine project. After six months, rust appeared, causing costly replacements. If he had chosen stainless steel 3162, the fasteners would have lasted for years. Mistakes like this are common but can be avoided with the right knowledge.
When sourcing, always ask for complete chemical composition1 and mechanical test reports. At Prime, I always include ISO certificates2 and test data for every shipment to help you verify quality.
Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel Fasteners: Are They Best for Tough Environments?

Industrial buyers often worry about rust, especially if their products are exposed to moisture, chemicals, or salt. Many people believe all stainless steel1 is “rust-proof2,” but there are many types and grades, each with a different resistance level.
Stainless steel fasteners1 resist corrosion better than carbon steel and most alloy steels. Their chromium content forms a thin, strong oxide film that stops rust and resists acids and salts. 304 stainless2 works for most environments. 316 stainless, with added molybdenum, resists even harsh marine and chemical exposures.

Corrosion can ruin projects, cause safety risks, and lead to returns. I have seen many clients pay high replacement costs because they chose the wrong material or were misled by non-expert suppliers. Prime often supplies stainless fasteners1 for food equipment, medical devices, and outdoor constructions where corrosion risk2 is high.
Real World Corrosion Resistance Comparison
| Grade | Corrosion Resistance1 | Suitable For2 | Cost Level | Common Surface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless 304 | Very High | General outdoor, food | Medium | Polished |
| Stainless 316 | Superior | Marine, chemical plants | High | Polished |
| Carbon Steel (Zn) | Medium (coated) | Indoor machines, tools | Low | Plated |
| Alloy Steel (coated) | Good (if coated) | Heavy-duty, engines | Medium | Plated |
Why Stainless Steel Performs Better
- Chromium creates a self-healing oxide layer1.
- 316 grade2 adds molybdenum for salt/acid resistance.
- No coating needed, so maintenance is easy.
I recommend stainless steel1 for projects in coastal, food, medical, and public outdoor areas. For even better performance, you can choose passivated or electropolished finishes2. If you want technical advice, I offer free consultation and samples at Prime to help you test and select the right grade.
Carbon Steel Fasteners: What Is the Cost–Benefit, and Where Are They Used?

Cost is a top concern for most buyers. When budgets are tight, carbon steel fasteners1 are often the first choice. However, it is important to match the application and protect against rust2.
Carbon steel fasteners provide strong performance at the lowest cost. They can be easily manufactured in all shapes and sizes. With proper surface treatment1, like zinc plating or black oxide, they last longer indoors. However, in humid, salty, or chemical environments, they will rust and lose strength quickly.

For bulk orders and non-critical applications, carbon steel1 is often the best choice. At Prime, our clients in automotive, machinery, and construction prefer carbon steel1 for internal assembly2, frames, and machines.
Carbon Steel Cost–Benefit Analysis
| Feature | Carbon Steel | Stainless Steel | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Cost1 | Lowest | Highest | Medium |
| Lead Time | Short | Medium | Medium |
| Customization | Easy | Medium | Easy |
| Minimum Order | Low | Higher | Medium |
| Rust Resistance2 | Poor (unless coated) | Excellent | Good (with coating) |
Main Applications
- Indoor machinery and assembly1
- Construction frameworks
- Automotive bolts and nuts (non-exposed)
- Large-scale manufacturing lines2
If you want to save costs, use carbon steel1 for indoor applications and consider surface treatments2 for extra life. At Prime, I help clients choose the right coating and package to protect the parts during transport and storage. We also do strict quality checks to avoid defects or dimension problems.
A client once ordered bulk carbon steel fasteners1 for a factory line, specifying only “zinc-plated bolts2.” After delivery, some parts rusted during storage because the plating thickness was too thin. Now, we always review client specs and suggest correct coating levels.
If you are unsure about coatings1 or want to optimize your cost, reach out to Prime for material and treatment suggestions2.
Strength Advantage of Alloy Steel Fasteners: How Do You Choose the Right High-Strength Fastener?

Strength is vital in heavy equipment, bridges, cranes, and machinery subject to shock or vibration. Many buyers get confused about the differences between “alloy steel1,” “hardened steel2,” or “heat-treated” fasteners.
Alloy steel fasteners1 are designed for top strength and toughness. They contain elements like chromium, molybdenum, nickel, or vanadium. With heat treatment, they achieve high tensile strength2, fatigue resistance, and can handle extreme loads. But they must be coated to prevent corrosion, as the high-strength alloys can rust.
If you want to build safe, reliable infrastructure or machinery, choose certified alloy steel fasteners1. At Prime, we manufacture bolts, nuts, and special parts that pass ISO, DIN, ASTM2, and other international standards.
High-Strength Fastener Comparison Table
| Fastener Type | Max Load | Fatigue Life1 | ISO Certified | Corrosion Resistance2 | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Steel (10.9/12.9) | Highest | Excellent | Yes | Needs coating | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Medium | Good | Yes | Excellent | High |
| Carbon Steel | Low-Med | Moderate | Yes | Poor | Low |
Application Examples
- Heavy machinery joints and frame bolts1
- Mining, oil and gas equipment2
- Bridges, towers, and steel structures
- Automotive engines and drive parts
I often work with global clients building new plants or transport systems. Once, a buyer needed high-strength bolts1 for a Middle Eastern oil refinery. Using Prime’s ISO 898-1 class 10.9 alloy steel bolts2 with proper coating, the project passed all inspections and has run safely for over five years.
For high-strength fasteners, always request material certificates1, test data, and proof of surface treatment. Prime can supply PPAP, 3.1/3.2 certificates, and traceable production records2.
If you want fast delivery, we keep large stocks of standard alloy steel fasteners1, and we offer express production2 for custom items.
How to Select the Right Fastener for Your Application? Step-by-Step Guide
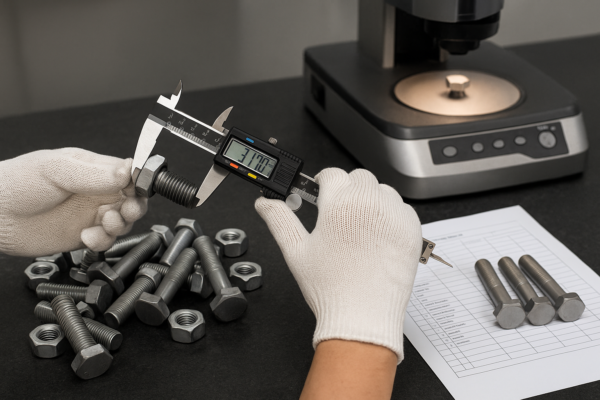

Selecting the right fastener1 is not only about the material. You must also consider size, thread, coating, and compliance with relevant standards2.
The best approach is a step-by-step evaluation. First, define the application and environment. Then, set your strength and corrosion needs1. Next, choose a certified supplier2 with a proven track record. Finally, request samples and inspect all documents.
Fastener Selection Checklist
- Confirm the working environment (indoor, outdoor, marine, chemical).
- List all load and vibration requirements.
- Set lifespan and maintenance expectations.
- Check international standards required1 (ISO, DIN, ASTM, etc).
- Choose the right material (stainless, carbon, alloy steel).
- Decide on coating, plating, or finishing.
- Request certificates, test data, and samples from your supplier.
- Compare total cost, not just unit price2.
- Check packaging and logistics solutions to avoid damage.
- Always confirm supplier’s ISO quality system and experience.
My Real-World Sourcing Tips
- For outdoor use, pick 316 stainless steel1 for the best corrosion resistance.
- For heavy loads, use ISO-certified alloy steel2, but insist on good coatings.
- For cost-sensitive, indoor use, carbon steel with zinc or phosphate is a good choice.
- For food, medical, or visible locations, choose stainless steel for a clean finish and safety.
- For large projects, always test samples before bulk order.
At Prime, I offer free consulting and fast prototype sampling for new clients. I believe open communication is key. Many problems can be avoided if you share your actual application, drawings, and quality requirements.
How to Avoid Common Fastener Sourcing Pitfalls?

Global buyers often run into problems such as delays, wrong materials, or poor packaging. The key is to work with experienced, ISO-certified suppliers1 who understand export standards2.
Avoiding sourcing mistakes1 saves money, time, and reputation. Always request quality documents2, agree on packaging, and use clear communication channels.
Typical Sourcing Issues and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Prime’s Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Rusted fasteners on delivery1 | Poor coating, bad pack | Strict QC, sealed anti-rust packing |
| Wrong material shipped | Supplier error | Full traceability, batch samples |
| Delayed shipment2 | Poor planning, overload | Ten production lines, flexible dates |
| Damaged packaging | Weak or cheap boxes | Custom export-grade packaging |
| Miscommunication on specs | Language gap, no drawing | 24h English service, sample proofing |
At Prime, our workflow includes three rounds of inspection, barcode tracking1, and export-standard packaging. I always advise clients to share drawings and samples before order confirmation. For urgent projects, our rapid-response team2 can ship samples in 3-7 days.
If you are buying from overseas, insist on full documentation1 and don’t settle for vague answers. My team and I handle each inquiry personally, and we respond within 12 hours, including technical questions2 or logistics tracking.
FAQs About Metal Fasteners
Q1: What is the difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel fasteners?
A: 316 contains molybdenum, which gives it better corrosion resistance1 in marine and chemical environments. Use 316 for harsh conditions, and 304 for general use.
Q2: Can I use carbon steel fasteners outdoors?
A: Only if they have a high-quality coating, but even then, rust may appear over time. Stainless steel is the safer option for outdoor or wet environments.
Q3: Are alloy steel fasteners always stronger than stainless steel?
A: Yes, alloy steel fasteners (especially grades 10.9 or 12.9) have much higher tensile strength2, but they need protective coating to avoid rust.
Q4: How can I confirm the fastener quality before shipment?
A: Ask for ISO certificates1, mechanical test reports, material analysis, and real photos. At Prime, I always provide these documents for every order.
Q5: What packaging options can prevent fastener damage in transit?
A: We offer double-layer cartons2, custom pallets, moisture-proof bags, and barcode labels. You can request export-specific packaging for maximum protection.
Q6: How quickly can you deliver custom fasteners?
A: For standard items, we ship in 3-7 days. For custom CNC parts, the lead time is usually 10-15 days. We also provide urgent delivery service for large projects.
Q7: Does Prime support logo engraving or custom shapes1?
A: Yes. We provide flexible customization, including logo laser marking2, unique packaging, and non-standard shapes as per your drawings.
Q8: How do I request a quote or sample?
A: Contact us at [email protected] or use the inquiry form on our website. Send us your drawings or requirements, and I will reply with a detailed quote and lead time.
Q9: What countries do you export to?
A: Prime exports to North America, Europe, the Middle East, Australia, and over 50 countries worldwide.
Q10: What quality standards do you follow?
A: We follow ISO 90011, DIN, ASTM, and other international standards2. We also meet clients’ special testing or compliance needs.
Conclusion
The right fastener1 saves money and boosts your project’s quality. Choosing Prime means you always get fast, reliable service and ISO-certified quality2.
Contact us today for a fast quote, expert consultation, and free sample analysis.
We deliver quickly, support custom projects, and guarantee stable quality.
Send your inquiry now for a professional solution you can trust.
Website: https://primecustomparts.com/
Email: [email protected]
-
Understanding the importance of the right fastener can enhance your project’s quality and cost-effectiveness. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Exploring ISO certification can help you ensure that your products meet high standards of quality and reliability. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩







