Top 10 Questions to Ask Before Ordering a Custom Metal Mold?

Ordering the wrong mold can delay production, increase costs, and damage your brand reputation.
Before investing in a custom metal mold, it’s critical to understand the process. Key factors include mold type, metal selection, design accuracy, tolerance, and supplier capability. This guide covers the most important questions to ask to ensure you’re getting the right mold for your production needs.
With insights from over 30 years of experience at Prime, this article provides a detailed breakdown of everything you must know before placing an order.
1. What is the purpose of the mold?
Mold design must match your part’s end-use.
If your mold will produce structural parts, you’ll need durable materials and close tolerances. If the mold will make decorative parts, high polish and precise finishes matter more.

| Application | Mold Priority |
|---|---|
| Structural Parts | Strength, precision |
| Consumer Plastics | Surface finish, speed |
| High-Temperature Use | Thermal stability |
2. What are the two types of molds used in metal casting?
You must choose between expendable and permanent molds.
Expendable molds are made of sand, plaster, or ceramics. They’re used once. Permanent molds are made of metal and reused for thousands of cycles.
| Type | Material | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Expendable | Sand, plaster | Prototypes, large castings |
| Permanent | Steel, iron | High-volume production |
3. What is the casting process sequence?
The full sequence includes 8 critical steps.
Understanding the metal casting process helps you design better parts and avoid costly defects.
Steps:
- CAD Design — 3D models created from client drawings.
- Mold Creation — CNC or EDM tooling made.
- Metal Melting — Furnace heats aluminum, zinc, or steel.
- Pouring — Controlled pouring into mold cavity.
- Cooling — Mold remains closed to solidify metal.
- Shakeout — Casting is removed from mold.
- Cleaning — Flash, sprue, and gates removed.
- Inspection — CMM or X-ray to verify dimensions.
4. What metal will be used, and why?
Different metals behave differently in molds.
Each metal has a unique shrink rate, flow speed, and surface finish. Choosing the right one avoids cracking, voids, and poor part quality.

| Metal | Best For | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace | Lightweight, fast cooling |
| Zinc | Consumer goods, electronics | Precise detail, low melting point |
| Steel | Industrial machinery | Strong, but hard to cast |
5. What is the easiest metal to mold?
Zinc and aluminum are the easiest to work with.
They have low melting points, good flowability, and short cycle times. That’s why they’re ideal for high-volume casting.
| Metal | Melting Temp | Flowability | Mold Lifespan Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc | \~420°C | Excellent | Low wear |
| Aluminum | \~660°C | Very good | Medium wear |
| Steel | \~1370°C | Poor | High wear |
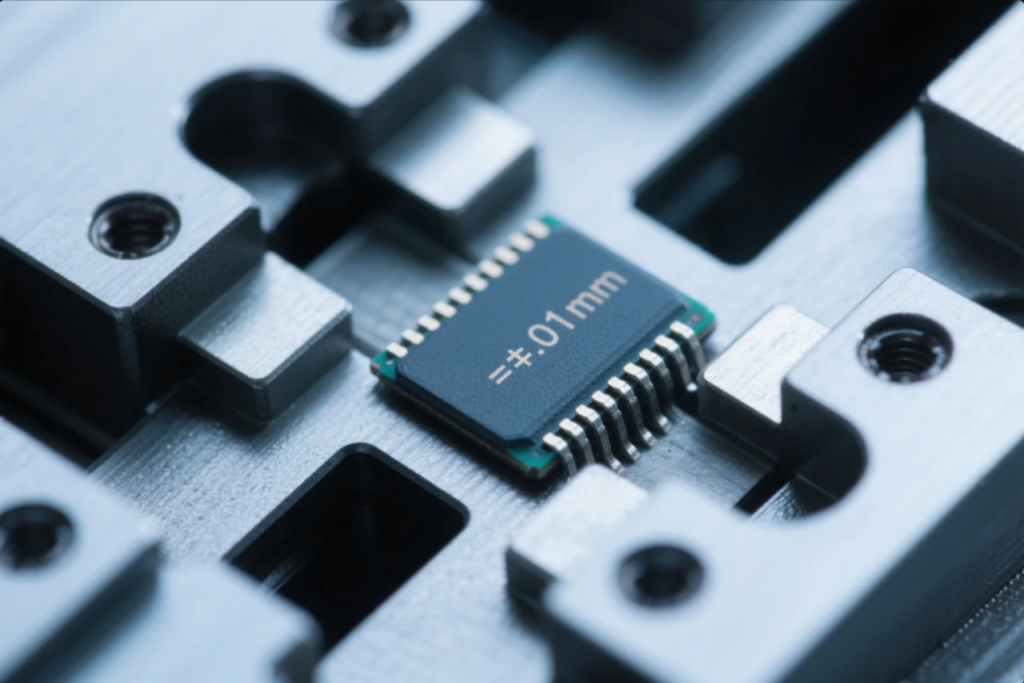
6. What tolerance is required for the part?
Tighter tolerances increase both precision and cost.
We define tolerances to prevent part misalignment during assembly. Prime achieves ±0.01mm with 5-axis CNC machining.
7. What is it called when you pour metal into a mold?
That’s called “casting,” or “metal pouring.”
It’s a critical step in the metal casting process. Bad pouring leads to cold shuts, porosity, and misruns.
At Prime, we simulate flow paths before tooling is made. This ensures even metal distribution and full mold fill.
8. What tooling is required?
Tooling defines the mold base, inserts, ejectors, and core pins.
At Prime, every mold includes:
- CNC-machined mold cavities
- Hardened steel inserts
- Ejector pins and lifters
- Cooling and venting channels
Tooling is fully customizable based on volume and part geometry.
9. What is the estimated mold lifespan?
It depends on material and production frequency.
| Mold Type | Material | Shot Life |
|---|---|---|
| Prototype Mold | Aluminum | 10,000–20,000 |
| Standard Mold | P20 Steel | 100,000–200,000 |
| High-Volume Mold | H13 Steel | 500,000+ |
We also provide preventative maintenance to extend your tool life.
10. Is the supplier ISO-certified and experienced?
Certification ensures repeatability. Experience prevents problems.
Prime is ISO 9001:2015 certified and has exported to over 30 countries since 1993.
We serve automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial machinery sectors.
FAQs
What 3D formats should I provide for mold design?
.STEP, .IGES, or native SolidWorks files are preferred.
How fast can Prime make a mold?
Simple molds: 2–3 weeks. Complex tools: 4–6 weeks.
Can I visit your factory in China?
Yes. We welcome site audits and provide online tours.
Do you provide sample runs?
Yes. All projects include First Article Inspection (FAI).
What are common casting defects to avoid?
Porosity, shrinkage, misruns, hot tears, and cold shuts.
What is the difference between molding and die casting?
Molding includes plastic or low-pressure metals. Die casting uses high pressure for metals like aluminum or zinc.
Conclusion
Asking the right questions ensures your custom mold project meets its goals—on time and within budget.
📩 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Visit: https://primecustomparts.com
Contact Prime for free consultation, rapid quotes, and expert engineering support. We help you avoid risks, reduce lead time, and ensure long-term mold performance.