Top 5 Inspection Methods to Ensure Quality in Custom Metal Molds?

Even the most advanced mold-making machine can’t compensate for poor inspection.
Thorough inspection is essential to ensure that a custom metal mold meets dimensional accuracy, material strength, and surface finish requirements. From visual checks to first article testing, every step in the inspection process helps prevent costly rework, part failure, and production delays.
This article explains the top 5 most effective inspection methods used in the mold manufacturing industry, based on international standards and Prime’s 30+ years of experience.
1. Visual Inspection for Surface Finish and Defects
Visual inspection is the first and most basic form of quality control.
It helps detect surface-level defects such as tool marks, burrs, discoloration, corrosion, scratches, or weld lines. Technicians use LED lamps and magnifying tools under controlled lighting to highlight inconsistencies.
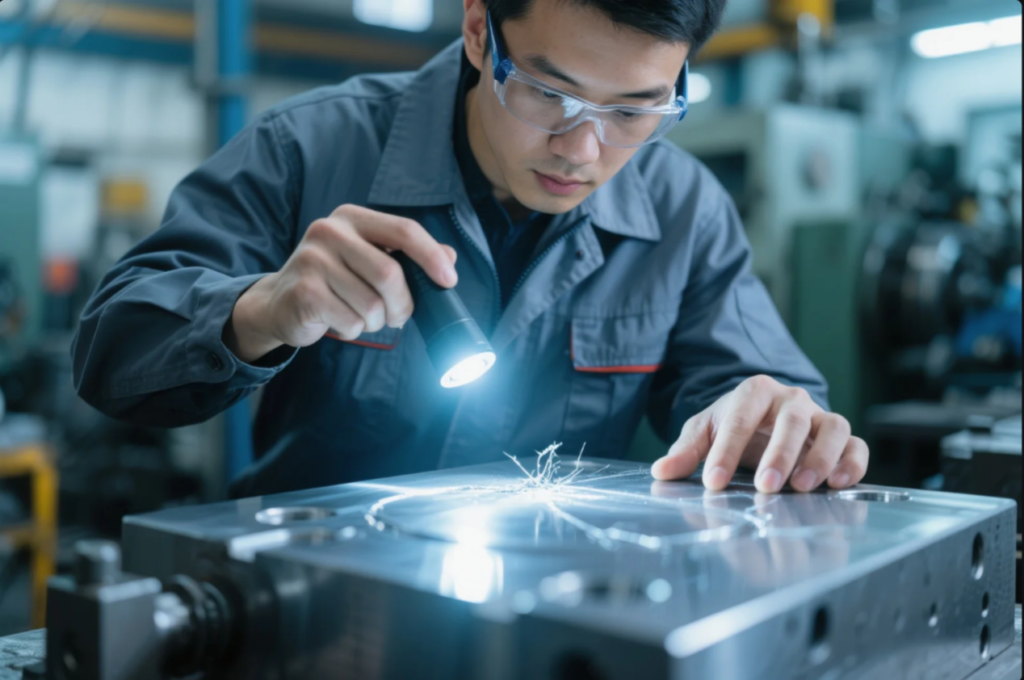

Visual inspection should follow guidelines from the ASME Y14.5 GD\&T Standard to assess geometric tolerances and surface flatness.
Common findings:
- Non-uniform polish
- Sharp transitions causing sink marks
- Poorly aligned ejector holes
- Residual burrs on parting lines
2. Dimensional Inspection with Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)
Precision molds require dimensional accuracy within ±0.005 mm, and that’s where CMMs come in.
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are used to verify cavity dimensions, core depths, flatness, hole positions, and alignment between inserts and plates.

Standard checks include:
| Feature | Acceptable Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Cavity length/width | ±0.01 mm |
| Hole-to-hole distance | ±0.005 mm |
| Core height | ±0.01 mm |
| Parallelism/Flatness | <0.02 mm |
At Prime, all molds include a CMM inspection report following the ISO 10360 standard and GD\&T rules.
3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): X-ray & Ultrasonic
Not all defects are visible. That’s why non-destructive testing (NDT) is critical to detect internal flaws.
NDT methods are used to reveal:
- Internal porosity
- Shrinkage voids
- Cracks from heat treatment or welding
Techniques include:
- X-ray radiography: Detects hidden cracks and voids
- Ultrasonic testing (UT): Identifies lamination or inclusions in thick sections
- Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI): Finds near-surface fatigue cracks in hardened steel
Prime follows ASNT Level II NDT Certification Standards for all ultrasonic and radiographic testing on H13, P20, and S136 mold components.
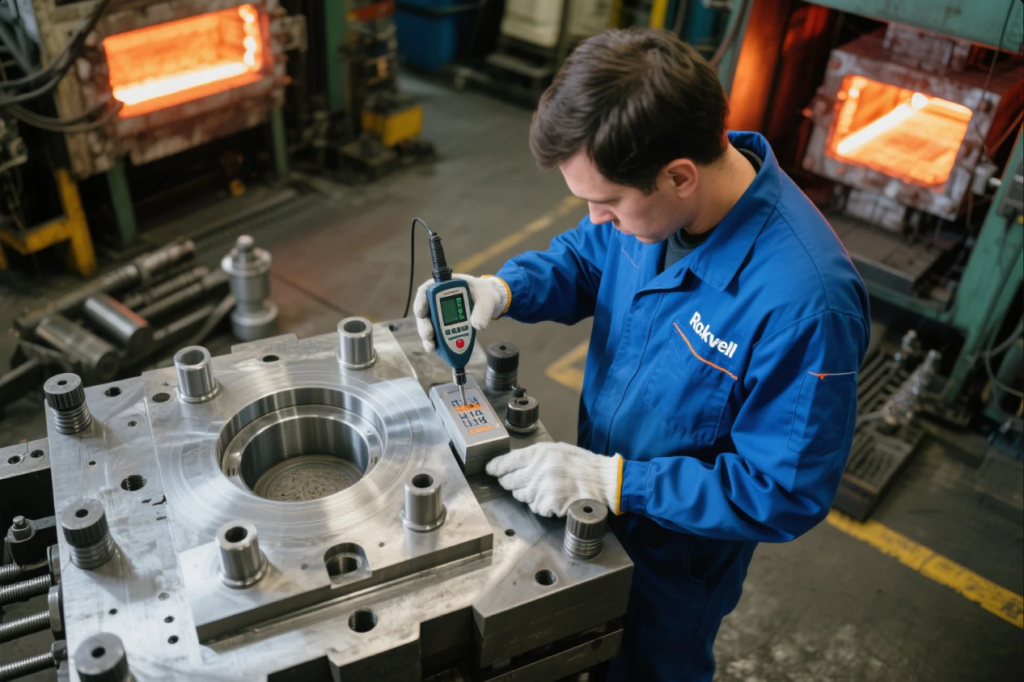
4. Hardness and Material Verification
Material selection and heat treatment determine mold lifespan. Incorrect hardness can result in early failure.
Tests include:
- Rockwell Hardness (HRC): To confirm proper heat treatment
- Vickers Test: For thin or polished areas
- Optical Spectroscopy: To verify alloy composition

Typical hardness values:
| Material | Hardness (HRC) |
|---|---|
| P20 Prehardened Steel | 28–32 |
| H13 Tool Steel | 48–52 |
| S136 Stainless Steel | 50–55 |
| BeCu Copper Alloys | 38–42 |
All material certificates at Prime conform to ASTM A681 Tool Steel Standard.
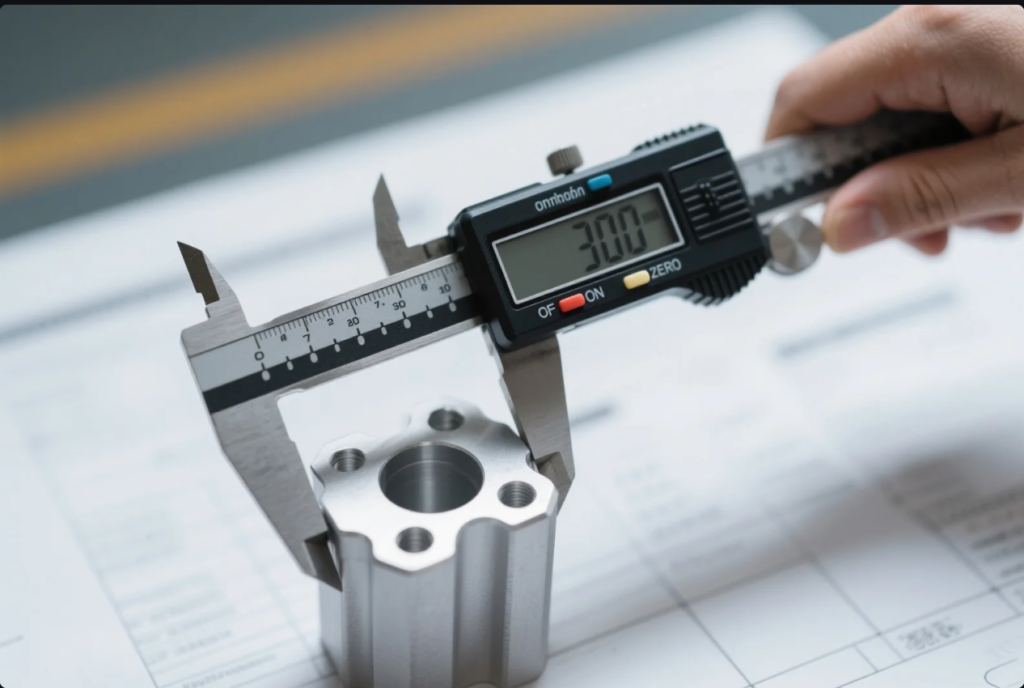
5. Functional Mold Trial and First Article Inspection (FAI)
The final and most important quality check is mold trial and part validation.
First Article Inspection (FAI) includes:
- Mounting the mold in an injection or die casting machine
- Producing 5–20 sample parts
- Measuring each part for dimensional compliance
- Evaluating surface quality, flash, warping, and shrinkage
- Compiling a complete FAI report with dimensional data and photos

Prime follows AIAG PPAP Level 3 FAI protocol and includes:
- Full dimensional report
- First part photos
- Mold trial video upon request
FAQs
Q: How do I check the quality of a casting mold?
A: Use a combination of CMM measurements, surface visual checks, NDT, and material hardness tests.
Q: What are metal product inspections?
A: Inspections include visual review, hardness verification, dimensional checks, NDT, and FAI validation.
Q: What is casting inspection?
A: It ensures the mold tool and the first molded or cast parts meet all dimensional, mechanical, and cosmetic requirements.
Q: Which processes use metal molds?
A: Die casting, plastic injection molding, and investment casting all rely on precision metal molds.
Conclusion
No custom mold is complete without a comprehensive inspection. Skipping even one step can lead to failures in production or downstream assembly.
📩 Need an expert QA-certified mold supplier? Email: [email protected]
🌐 Learn more or request a free quote at: https://primecustomparts.com
Prime ensures every mold we produce undergoes ISO-compliant inspection, documented FAI, and the industry’s highest quality assurance standards.







