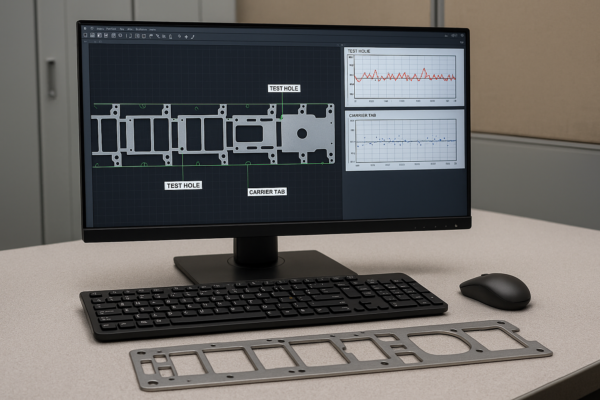
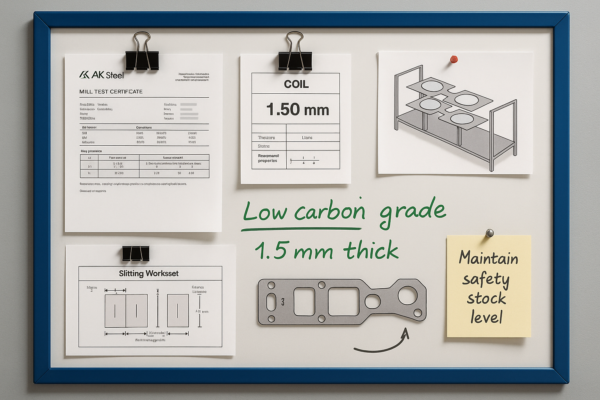
Top 5 Welding Methods for Precision Metal Parts?

Introduction
Many manufacturers struggle with weld strength and precision. They waste time and cost with poor weld choices. I saw this often on jobs. That inspired me to write this guide. It helps you select and apply optimal welding methods. You can reduce rework, save money, and ramp up output. Prime supports these goals with consistent, fast delivery.
Spot Welding vs Tack Welding: Key Differences
Spot welding and tack welding fulfill different roles in production. Spot welding uses pressure and current to fuse thin sheets at single points. Tack welding holds components in place before full welding.

Key Comparison
| Feature | Spot Welding | Tack Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Permanent metal join | Alignment for full weld |
| Heat Input | High, localized | Low, intermittent |
| Best For | Sheet metal ≤6 mm | Thick plates or big parts |
| Equipment | Resistance welder | MIG/TIG/stick welders |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate |
Practical Tips
- Keep surfaces clean for consistent welds.
- Use heavy-duty clamps during tack welding.
- Space tack welds evenly to prevent distortion.
In chassis manufacturing, spot welding dominates bracket joining. Meanwhile, we use tack welds in structural assemblies to maintain frame straightness within 0.3 mm.
Learn about electrode pressures and time control from the AWS Technical Library:
AWS Technical Resources
Benefits of MIG, TIG, and Stitch Welding
I regularly apply MIG, TIG, and stitch welding across diverse parts. Each method suits different materials and production requirements.

MIG Welding
Advantages
- Rapid deposition
- Simple training
- Cost-effective for steel
Drawbacks
- Forms spatter
- Hard to control heat on thin sheets
MIG Welding Introduction – WeldingTipsAndTricks
TIG Welding
Advantages
- Clean, aesthetic welds
- Precise heat input
- Ideal for corrosion-resistant alloys
Drawbacks
- Lower deposition rate
- Needs skilled operators
TIG Welding Explained – The Fabricator
Stitch Welding
Advantages
- Limits heat distortion
- Good for long joints
- Helps maintain flatness
Drawbacks
- Slower than continuous weld
- Requires programming oversight
Stitch Welding Strategies – Engineering.com
Dive Deeper
| Method | Speed | Precision | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIG | High | Medium | Fabrication of steel support parts |
| TIG | Low | High | Equipment housings and panels |
| Stitch Welding | Med | High | Cabinets and sheet enclosures |
We once welded HVAC duct panels using stitch welding to minimize warping. That lowered scrap by 18%.
Further reading:
Choosing Fuse Welding for Steel and Stainless
Fuse welding melts adjacent metal without filler. I use it where full metallurgical bond and corrosion resistance are essential.

Advantages
- Seamless joint without additives
- Retains alloy integrity
- Strong and corrosion-resistant
Limitations
- Tight tolerances needed
- Not ideal for thick sections
- Specialized equipment required
Dive Deeper
| Requirement | Recommended Practice |
|---|---|
| Edge Cleanliness | Grind and degrease before welding |
| Fit Gap | Less than 0.1 mm for stainless parts |
| Post-weld Testing | Use NDT methods like ultrasonic scan |
For medical device components, fuse welding gave us zero porosity and full corrosion control. See ASME guidance for alloy selection:
ASME Material Standards
Best Practices in Plug and Seam/Fillet Welding
Plug welding fills a drilled hole with weld material to join two metal layers. Seam and fillet methods create edge welds along lap joints.
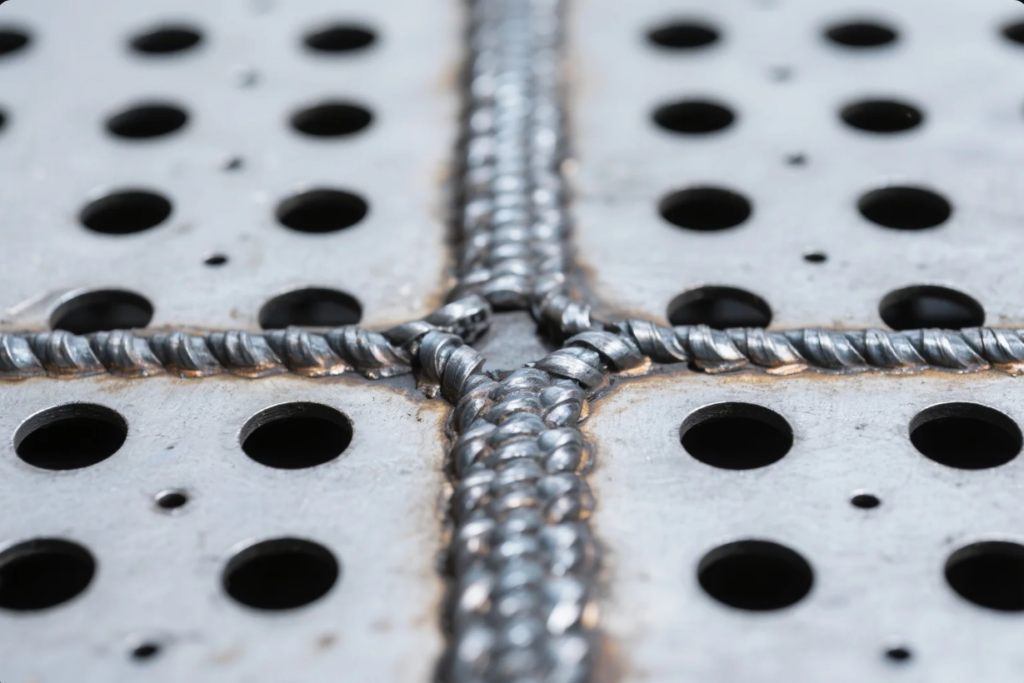
Plug Welding Tips
- Match hole diameter to wire size
- Fill hole completely
- Grind flush to match surface
Seam/Fillet Welding Tips
- Maintain consistent travel speed
- Overlap passes by 25–30%
- Use tack welds to reduce shrinkage
Fillet Welding Procedure – AWS Standard
Dive Deeper
At our plant, plug welding helps mount brackets with consistent placement. For seam welds, we test strength via ASTM A370. We document results to meet OEM specs.
Key references:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Which method is best for thin stainless?
TIG welding offers best finish and minimal distortion. -
Can fuse welding be done on mild steel?
Yes. But clean edges and shielding gas are essential. -
How do I reduce distortion on long welds?
Use stitch welding or back-step sequence and allow cool-down periods. -
What tests verify weld quality?
Use ultrasonic, liquid‑penetrant, or radiographic testing. -
Which welding standards apply?
Commonly: AWS D1.1, ISO 3834, and ASME IX. -
What industries use Prime’s welding?
Aerospace, automotive, agriculture, HVAC, and medical devices. -
How fast is Prime’s lead time?
Typically 15–30 days based on volume and complexity.
Contact Prime for Custom Welding Solutions
If you need ISO‑certified, precision welding at scale, Prime is ready.
We offer fast global delivery, consistent quality, and flexible customization.
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com/
Request a free quote, technical review, or design consultation today.