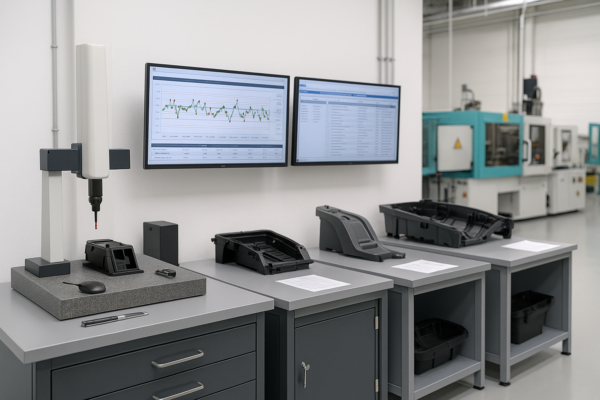
Top Applications of Custom Metal Molds in Automotive Manufacturing 2025?
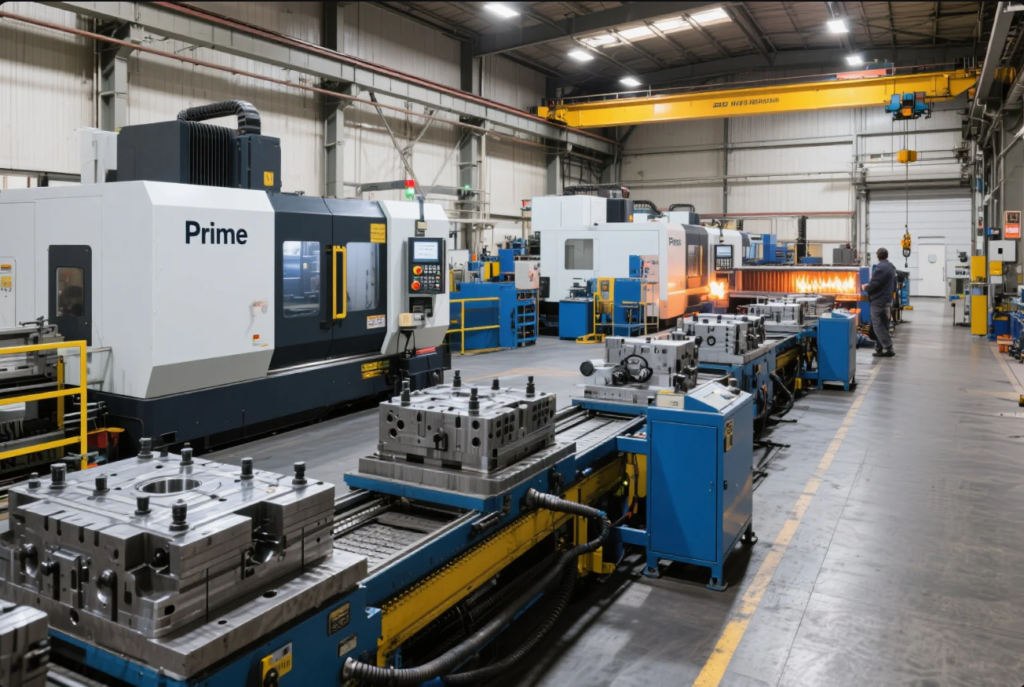

Automotive manufacturers demand lightweight, durable, and precision-fit parts. Inconsistent molds lead to misalignment, waste, and costly recalls.
Custom metal molds ensure dimensional accuracy, repeatability, and strength across key automotive systems. In 2025, their role is more vital than ever.
This guide explains how metal molding technologies like MIM, die casting, and CNC contribute to the automotive supply chain.
What is the future of metal injection molding?
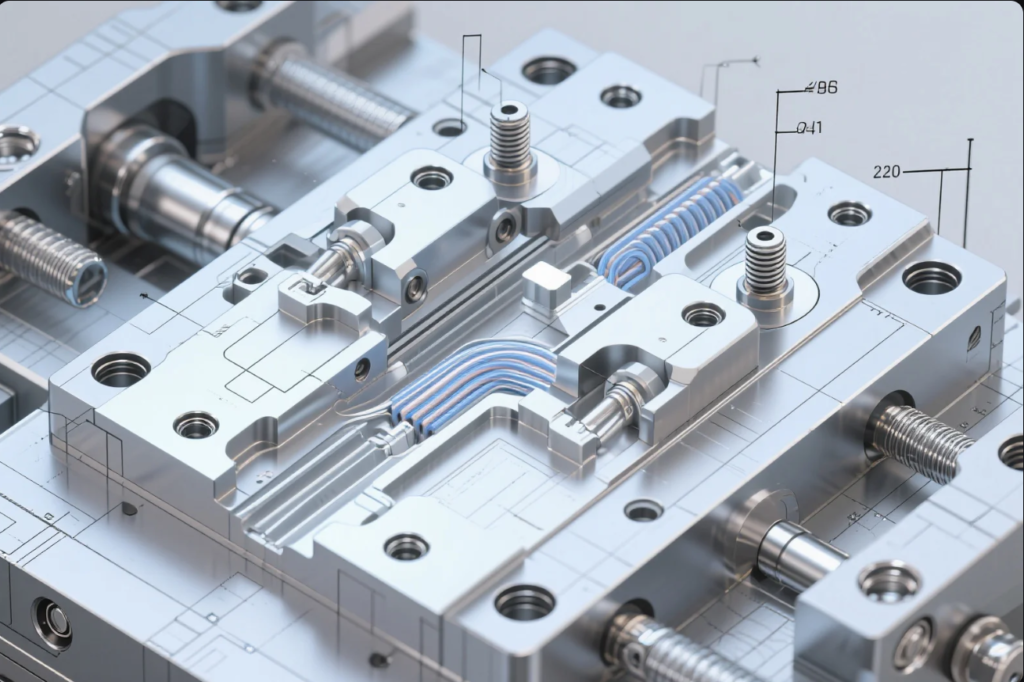
Metal injection molding (MIM) is revolutionizing small, complex part production for automotive electronics and safety systems.
By 2025, MIM adoption in automotive has expanded due to EV trends, part miniaturization, and performance demands.
Why MIM Will Lead Automotive Micro-Components
| Feature | Benefit in Auto Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| High Detail Tolerance | Ideal for gears, latch pins, micro-axles |
| Near-Net Shaping | Reduces machining, waste |
| Alloy Flexibility | Works with stainless steel, titanium, alloys |
| Scalable Volumes | From 1000 to millions with consistent quality |
We’ve built MIM-ready custom steel molds for EV battery housing clips, drive-by-wire system parts, and turbocharger micro-levers. MIM allows designs that are impossible with CNC alone.
Want to explore MIM further? See Wikipedia – Metal Injection Molding
What is the process of metal molding?
Whether you’re casting or injecting, metal molding transforms raw metal into functional shapes—repeatably and accurately.
The typical metal molding process includes mold design, pre-processing, forming, sintering (for MIM), and finishing.
Key Steps in Metal Molding
- CAD Part Design – Optimized for molding tolerance and shrinkage
- Mold Tooling – CNC/EDM-built metal cavities from P20, H13, etc.
- Feedstock Prep (MIM) – Metal powder + binder compound
- Injection/Die Casting – High-pressure shaping inside mold
- Debinding & Sintering – Burn off binders, fuse powder
- Post-Processing – Heat treatment, surface finish, QC
We follow this process at Prime for metal injection mold projects, especially in drivetrain electronics and structural sensor components.
For full manufacturing process flow, refer to Autodesk’s guide to injection mold design
What are the four types of metal casting?
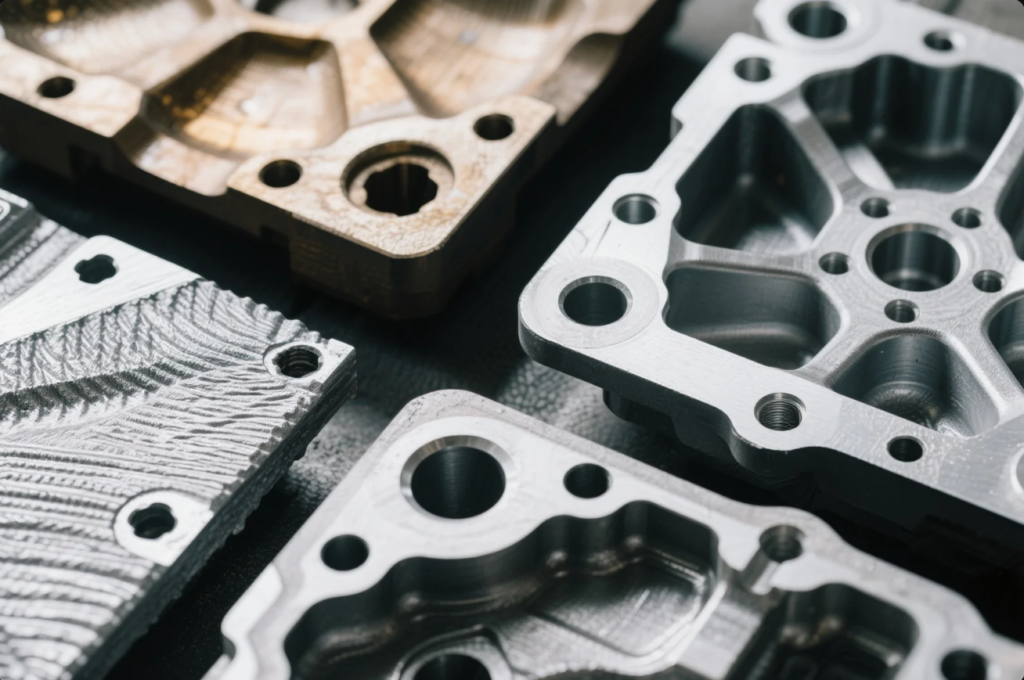

In automotive, casting helps create strong yet intricate parts—engine blocks, mounts, and gearbox housings rely heavily on casting molds.
The four main types of metal casting are sand casting, die casting, permanent mold casting, and investment casting.
Casting Method Comparison for Automotive Use
| Casting Type | Ideal For | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Engine blocks, differential cases | Low tooling cost, rougher finish |
| Die Casting | Transmission housings, connectors | High volume, precise, fast cycle |
| Permanent Mold | Suspension parts, brake housings | Better surface finish, reusable |
| Investment Casting | Valve parts, turbine wheels | Extreme precision, slower process |
At Prime, we use die casting molds and permanent steel molds for long-run auto part programs. We also supply casting molds to clients across Europe and the U.S. for aftermarket systems.
Visit Engineering Choice – Types of Casting for a deeper dive.
What is the MIM industry?
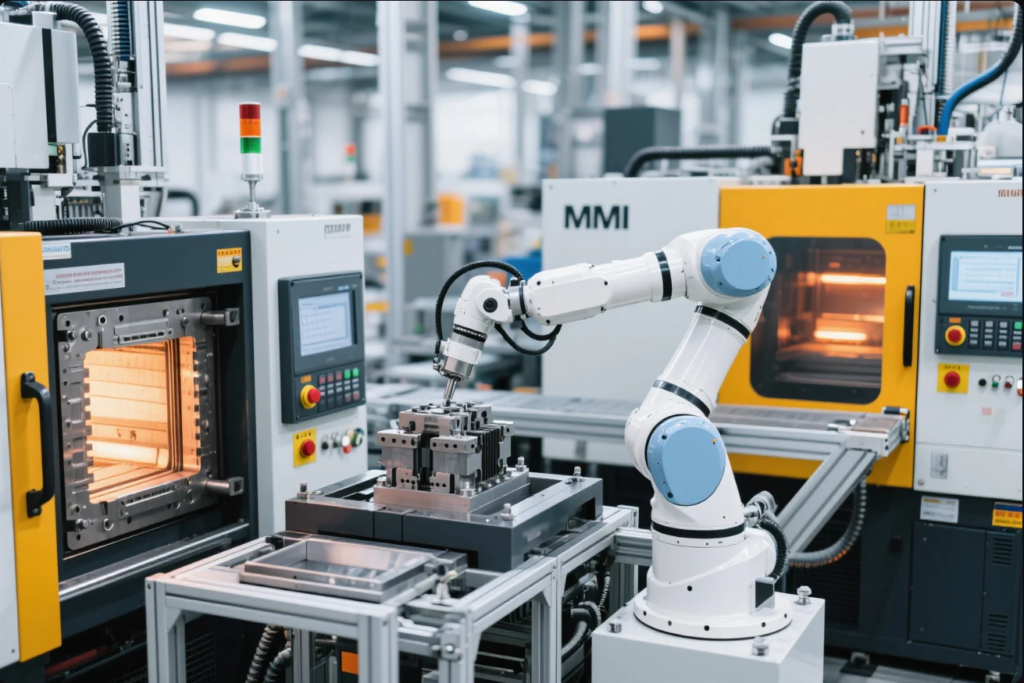

The MIM industry combines metal forming and plastic injection tech to enable compact, durable, high-precision parts.
It serves automotive, aerospace, defense, and med-tech, with growing applications in e-mobility and autonomous driving systems.
MIM in Automotive: 2025 Snapshot
| Application Area | MIM Part Examples |
|---|---|
| EV Motors | Rotor shafts, magnet retainers |
| Steering Systems | Yoke pins, sensor brackets |
| Safety Devices | Airbag components, seatbelt locks |
| Interior Electronics | Volume control, vent flow regulators |
We see 20–25% YoY demand growth in automotive MIM molds at Prime. Customers benefit from parts that need no secondary machining, reducing cost and time-to-market.
For industry data, see Grand View Research – MIM Market Forecast
FAQs
1. What mold steel is best for automotive MIM?
H13 and maraging steel offer excellent durability and heat resistance for high-shot applications.
2. Can I combine casting and CNC in one part?
Yes. We offer hybrid processes—cast and then CNC-machine critical features (holes, threads).
3. Do you support IATF 16949 requirements?
We follow strict quality protocols and can supply PPAP, FAI, and traceable process records.
4. What’s the average lead time for custom auto molds?
7–15 days for CNC molds; 20–30 days for multi-cavity MIM tools, including validation.
5. Do you export to Tier 1 or OEM suppliers?
Yes. Our automotive clients include Tier 1s and regional OEMs in Germany, USA, and the Middle East.
Conclusion
Custom metal molds are the backbone of modern automotive manufacturing—supporting lightweight designs, higher tolerances, and zero-defect production.
Prime helps clients lead in 2025 with ISO-certified, precision-engineered molds—ready for EVs, ADAS, and beyond.
📞 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com
Let’s drive the future together—mold by mold.







