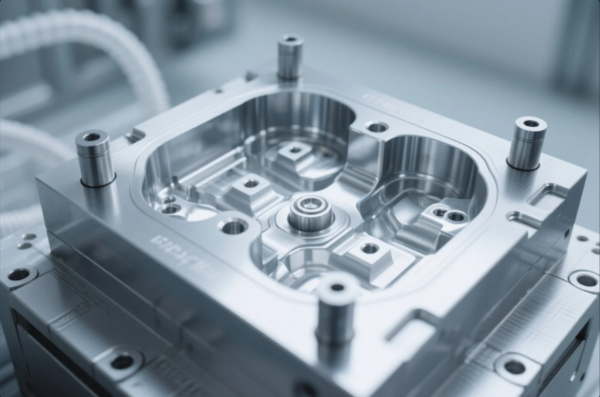
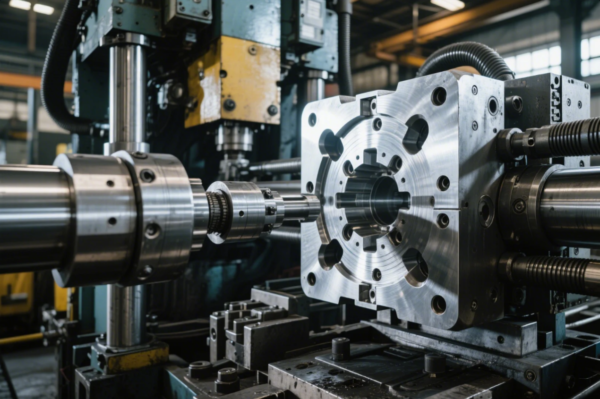
Top Custom Mold Makers for Precision Metal Components: 2025 Guide to Choosing the Right Partner
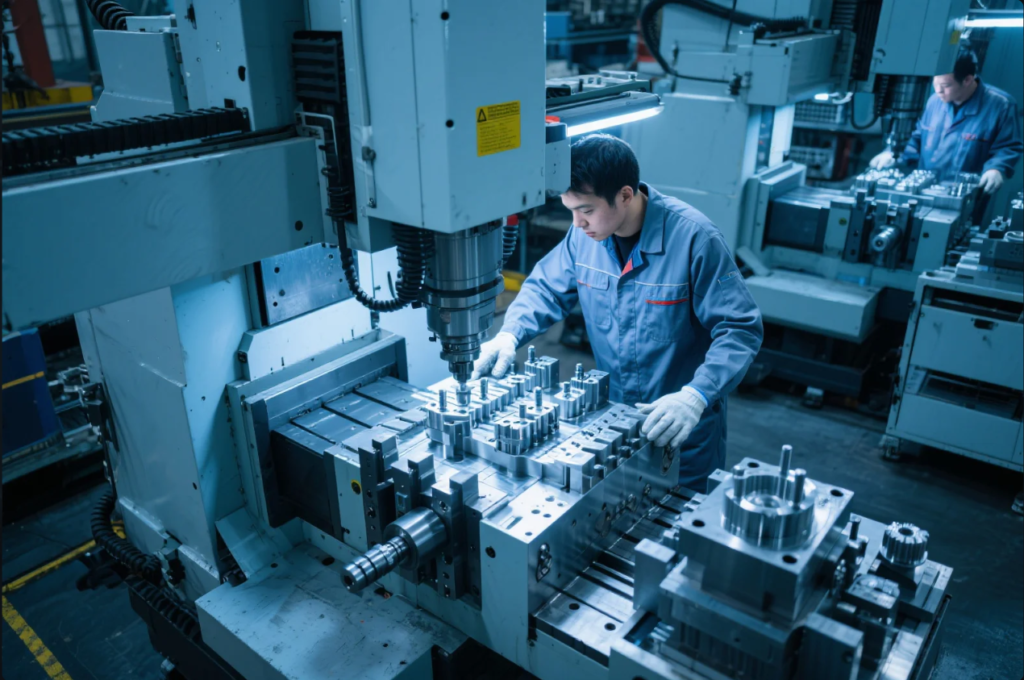

Poor mold quality can destroy even the best design. In 2025, finding a skilled and reliable mold maker is more critical than ever.
This guide introduces the top custom mold makers for precision metal components, and helps you understand what a custom mold is, how mold makers operate, and what to look for when outsourcing tooling globally.
Whether you need metal injection molds, die casting tools, or precision stamping dies—this article gives you the insights to choose a partner with confidence.
Table of Contents
- What is a custom mold?
- How to become a mold maker?
- Are mold makers in demand?
- What is mold fabrication?
- FAQs
- Contact Information
What is a custom mold?
A custom mold is not a one-size-fits-all tool—it’s engineered for your exact part design, production volume, and material.
A custom mold is a precision-engineered tool used to shape metal or plastic components. It’s built to exact specifications, usually with CNC machining, EDM, and grinding processes, and tailored to the customer’s geometry, alloy, and production needs.
Types of Custom Molds for Metal Parts
| Mold Type | Application | Material Commonly Used |
|---|---|---|
| Die Casting Mold | Aluminum, zinc parts | H13 or SKD61 tool steel |
| Metal Injection Mold | Small, detailed stainless parts | 420 SS or S7 tool steel |
| Stamping Die | Sheet metal components | D2 or SKD11 high-speed steel |
| Sand Casting Pattern | Prototypes, large iron parts | Aluminum, wood, or resin |
At Prime, we specialize in building custom molds using ISO-certified processes and customer-provided 3D models.
For more, read Wikipedia’s definition of mold making.
How to become a mold maker?
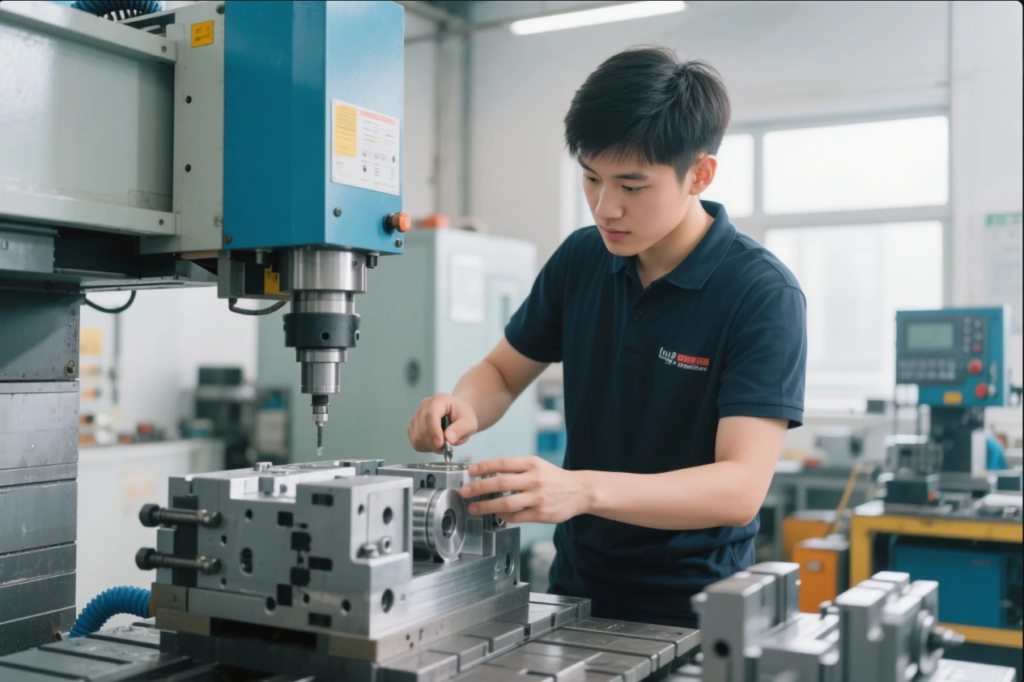

Mold making is a mix of mechanical skill, CAD/CAM design, and material science.
To become a mold maker, you need training in mechanical engineering, CAD software, and hands-on experience with CNC machines, EDM, polishing, and inspection tools. Apprenticeships and vocational schools are the usual path into this skilled trade.
Steps to Become a Mold Maker
- Study mechanical drawing and manufacturing basics
- Get formal training in CNC, mold assembly, and CAD/CAM
- Complete an apprenticeship or internship at a mold shop
- Learn materials like tool steels, aluminum, and coatings
- Develop attention to detail and problem-solving skills
See the NTMA training programs to learn more about moldmaker education in North America.
At Prime, our lead mold designers have 15+ years of experience and are certified in both ISO 9001 and automotive PPAP requirements.
Are mold makers in demand?
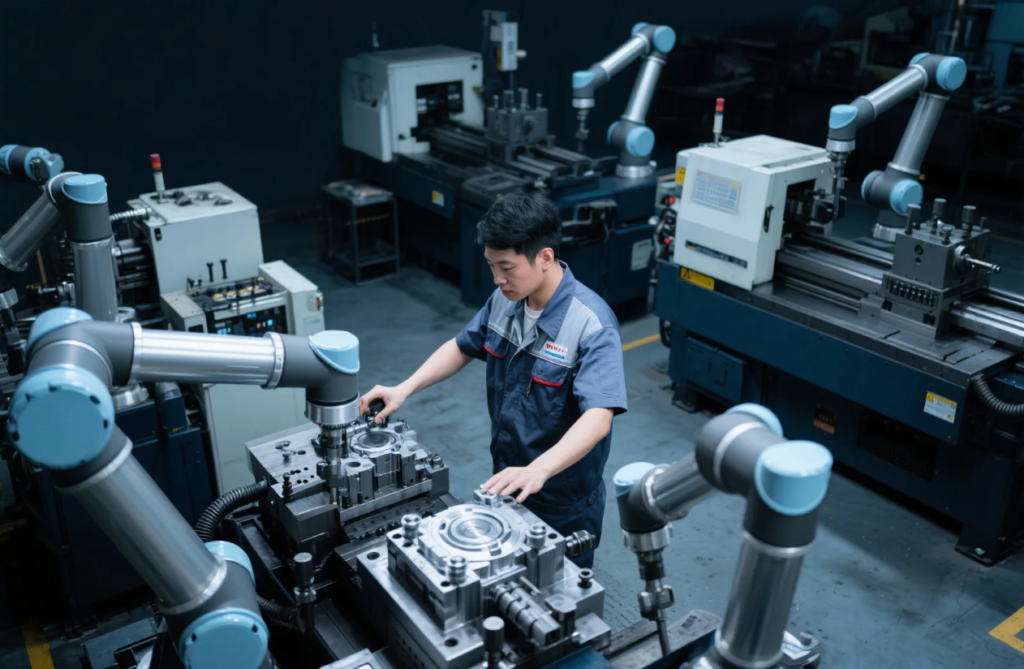

In 2025, demand for mold makers is rising—especially in high-tech and industrial sectors.
Yes, mold makers are in high demand due to growing needs for precision parts in EVs, medical devices, automation, and aerospace. As older mold technicians retire, a new generation is urgently needed.
Industries That Rely on Mold Makers
| Industry | Type of Mold Required | Key Growth Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Die casting, injection molds | EV and lightweight metal integration |
| Medical Devices | MIM, micro molds | Miniaturized instruments and implants |
| Aerospace | Investment molds, jigs | Titanium and high-temp metal shaping |
| Electronics | Insert molds, stamping dies | High-speed, automated assembly |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics – Mold Tool Technicians Outlook
Prime continues to expand its mold workshop team and offers in-house training to meet growing global mold demand.
What is mold fabrication?
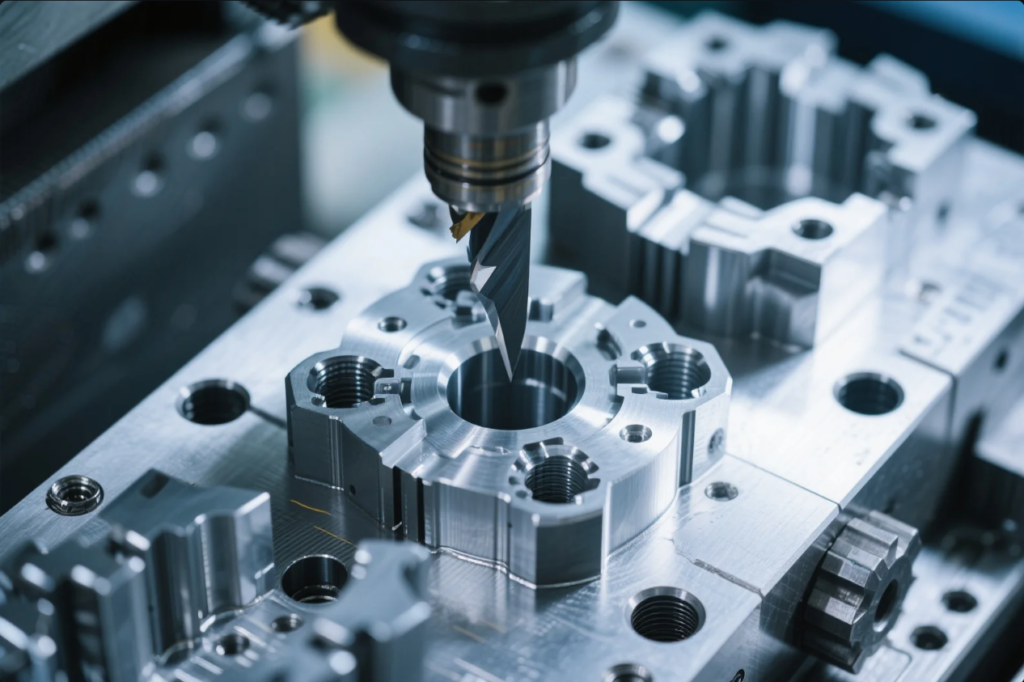

Mold fabrication isn’t just building a block—it’s precision manufacturing at every level.
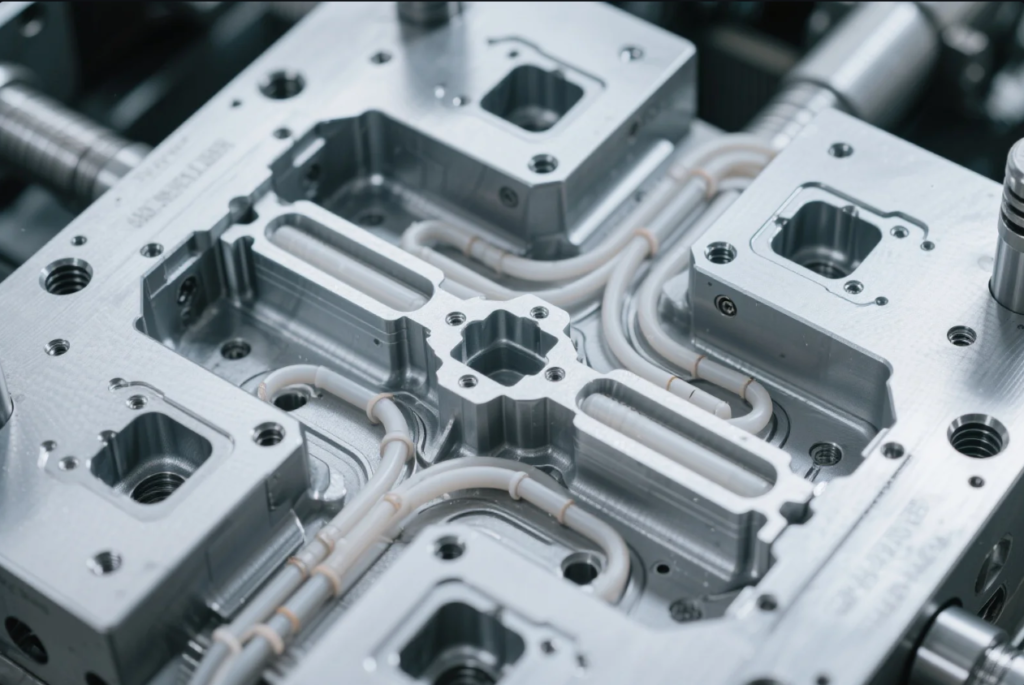
Mold fabrication is the process of making the components that form a mold, including cores, cavities, base plates, guide systems, cooling lines, and ejector mechanisms. It involves CNC machining, EDM, grinding, polishing, and inspection.
Mold Fabrication Process at a Glance
- Receive CAD model and part spec
- Design mold with cooling, venting, and gating
- Machine base plates, cores, and cavity blocks
- Apply EDM for detailed and hardened features
- Assemble and test mold with sample shots
Prime uses CMM inspection, 5-axis machining, and mirror polishing for ultra-tight tolerances. Our average mold tolerance: ±0.01 mm.
Explore Wikipedia’s page on mold manufacturing for deeper insights.
FAQs
Q1: What materials are used to make molds?
A1: Tool steels (H13, P20, S7), aluminum (7075), beryllium copper, and hardened stainless steels (420).
Q2: How long does a custom mold last?
A2: Depends on material and usage—steel molds can last over 1 million shots; aluminum molds about 100,000.
Q3: Can Prime build multi-cavity molds?
A3: Yes. We support 2–64 cavity molds for both metal and plastic parts.
Q4: Do you provide mold drawings and 3D files?
A4: Yes, upon request. We deliver full 2D technical drawings and editable STEP/IGES files.
Q5: Can I modify my mold later?
A5: Yes. We offer mold modification services including insert swap, layout change, and cooling system upgrade.
Contact Information
Looking for a top-tier mold maker for your next metal parts project?
- 🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com
- 📧 Email: [email protected]
Our Services Include:
- Custom mold design for metal injection, die cast, and stamping
- Tool steel selection and optimization advice
- Fast turnaround on prototypes and production tooling
- Full documentation, QA, and global delivery
Trust Prime for custom molds that drive precision, durability, and speed.
With 20+ years of experience and global tooling expertise, Prime is your partner for high-performance metal molds—on time and on spec.