Understanding Metal Clips: A Comprehensive Guide?
Line stoppages1, rattles, and corrosion2 often trace back to the wrong clip. I clarify types, standards, and tests so you can specify once and launch on time.
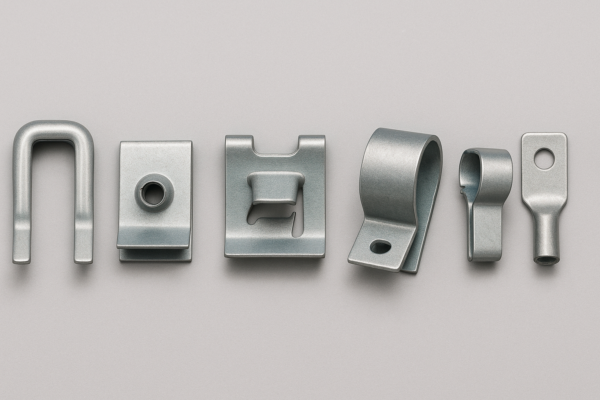
Metal clip fasteners are spring-formed parts that clamp, retain, or align components without loose nuts/bolts. Common types include U-clips1, speed nuts, snap-in panel clips, edge clips, hose/tube clips, and electrical contact clips. Selection depends on substrate thickness, load direction, environment, assembly method, and measurable insertion/retention force targets.
I’ll map choices to your use case, show tolerances and finishes, and outline test plans1 that de-risk PPAP2 and field performance.
Different Types of Metal Clip Fasteners?
Vague “clip” specs cause jams and warranty returns. Start with function, then choose geometry, material, and coating1.
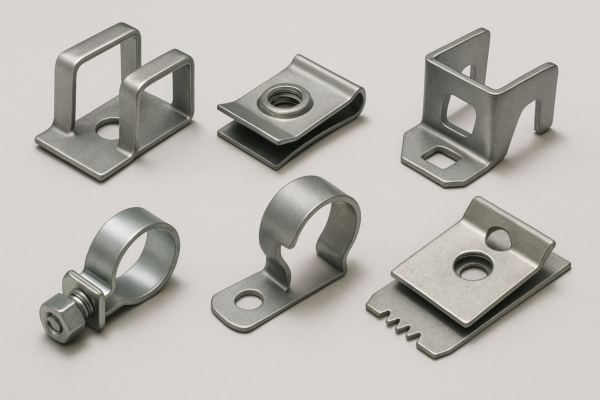
**Core types: U-clips/speed nuts1 for sheet-metal joints; snap-in panel clips for trims; edge/trim clips for flanges; hose/tube clips for round parts; contact clips for conductive spring force. Typical materials: 1074/1075 spring steel2, 301/304 stainless, phosphor bronze. Finishes: zinc, zinc–nickel, phosphate-oil, black oxide, or stainless passivation (per
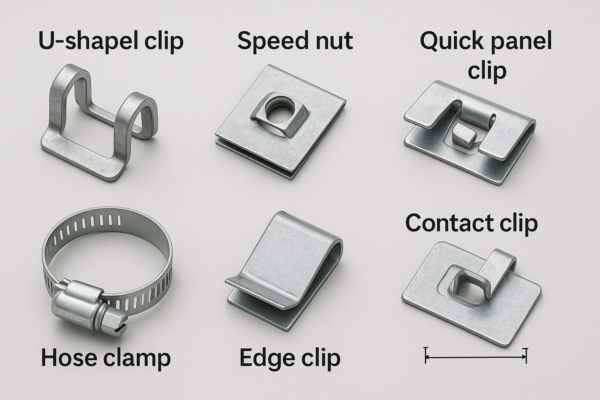
U-clips and speed nuts1 combine alignment with thread capture (machine or thread-forming screws). Snap-in panel clips use spring legs and barbs sized to the panel thickness/hole tolerance; add felt to reduce NVH. Edge clips grip a flange without holes; serrations or acrylic adhesive pads help on oily steel. Hose/tube clips wrap the circumference and must meet a clamp-force window across temperature. Electrical contact clips2 need conductivity and low stress relaxation; phosphor bronze or 301 stainless temper control is common.
As Prime (China, founded 1993; ISO-certified1; 10 production lines), I combine stamping, coining, forming, heat treat, plating partnerships, and inspection (FAI/CMM) to deliver consistent clips. Send your drawing for 24-hour DFM2 and quote.
Practical checkpoints buyers should verify
- Panel or edge thickness window (e.g., 0.8–1.2 mm / 0.031–0.047 in).
- Retention force target and test direction1 (pull-out vs. shear).
- Free-state leg gap and elastic deflection margin2 at install.
Quality & packaging notes buyers care about
- Heat-treat certs with multi-point HRC readings1.
- Coating thickness (μm) and salt-spray hours on the cert.
- VCI bags, partitioned trays; 5-ply cartons ≤25 kg (55 lb).
| Factor | Option A | Option B | What it means for cost/lead time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material/Grade | AISI 1075 | AISI 301 (½–¾ hard) | 1075 is economical; needs heat treat. 301 costs more; skips quench. |
| Strength/Hardness | HRC 44–50 | Work-hardened temper | Higher hardness boosts spring force but raises brittleness risk. |
| Corrosion Resistance1 | Zn 8–12 μm | Zn–Ni 12–20 μm | Zn–Ni often reaches ≥480–720 h B117; plating queue can extend. |
| Tolerance Feasibility | ISO 2768-m | ISO 2768-f | Tighter tol. increase tool polish and maintenance time. |
| Surface Finish2 | Phosphate-oil | Black oxide | Phosphate reduces squeak; black oxide is cosmetic, low salt life. |
| Testing/Reports | FAI + salt spray | FAI + CMM + fatigue | More tests increase confidence and calendar days. |
Upload your drawing for 24-hour DFM advice1 and quote; I’ll confirm type, material, finish, and realistic tolerances2.
Choosing the Right Metal Clip Fastener?
Too many catalog shapes slow decisions. Tie geometry to load, substrate, and environment.
**Choose by five inputs: substrate thickness/stack-up1, load path (pull-out, shear, cyclic), environment (humidity, salt, chemicals), assembly method (push-on, slide-over, screw-assisted), and service temperature. Verify insertion/retention forces, vibration, and corrosion to standards2 like
I begin with the joint style: edge, hole, or round feature. For indoor appliances (0.6–1.0 mm), 1074/1075 + Zn 10 μm typically meets life; target insertion ≤50 N (11.2 lbf) and retention ≥100 N (22.5 lbf). For coastal/under-hood environments, select 301/304 stainless or Zn–Ni with sealers; avoid hexavalent chromate to align with the EU RoHS Directive.
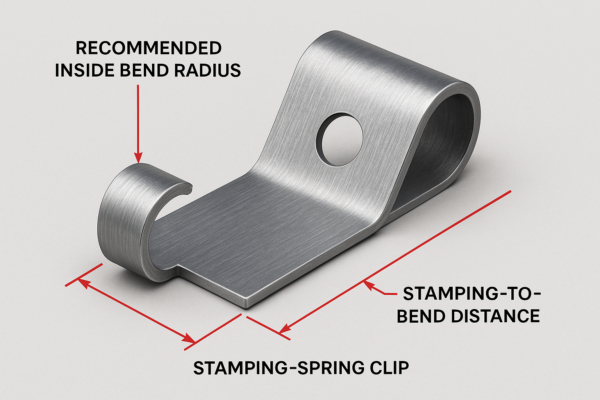
Tolerance strategy: use slots where stack-ups vary; call burr height ≤0.05 mm (0.002 in). If using thread-forming screws with speed nuts, match screw property class from ISO 898-1; validate torque-to-failure and prevailing torque.
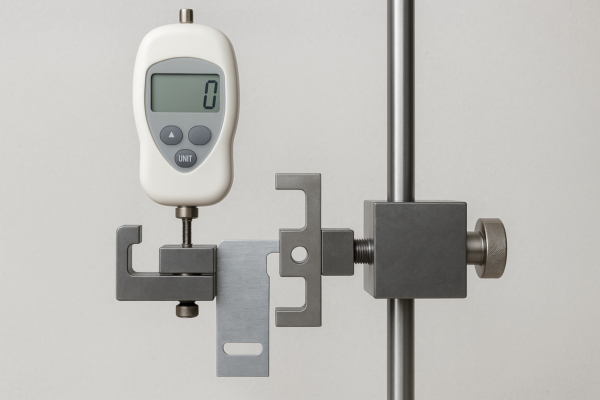
Test methods: define fixtures and speeds (e.g., 50 mm/min) for insertion/retention. Confirm on coated panels—paint/e-coat adds thickness. For corrosion, state exposure hours and red-rust criteria, then function-check after test. For vibration, run amplitude-swept testing and measure retention loss.
Ergonomics and safety: one-hand push ≤60 N (13.5 lbf), chamfered lead-ins for blind assembly, and edge radii to protect paint/harnesses.
At Prime, I provide DFM simulations, prototype tools, capability studies, and PPAP Level 2–3 on request. Packaging plans include dividers to prevent spring set and barcode labeling for line accuracy.

Practical checkpoints buyers should verify
- Document insertion/retention fixtures and test rate.
- Specify substrate hardness/coating; coupons match production stack-up.
- Confirm grain direction vs. bend to prevent cracking.
Quality & packaging notes buyers care about
- CMM on barb height, leg width, and free-state gap.
- Functional gauges (go/no-go) for panel coupons.
- Carton labels: PO, part, lot, quantity, CoO, RoHS mark.
| Factor | Option A | Option B | What it means for cost/lead time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material/Grade | 1075 + Zn 10 μm | 301 SS + passivation | SS raises unit cost \~20–40%; reduces coating steps. |
| Strength/Hardness | HRC 46 target | ¾-hard temper | Comparable spring energy via different routes (heat vs. work). |
| Corrosion Resistance1 | 240 h B117 | 720 h B117 | Higher hours require Zn–Ni or stainless; longer validation. |
| Tolerance Feasibility | ±0.10 mm | ±0.05 mm | Tight tol. increase tool cost and maintenance. |
| Surface Finish2 | Phosphate-oil | Zn–Ni + sealer | Sealers cut friction/whitening; add piece cost. |
| Testing/Reports | FAI + PPAP 2 | PPAP 3 + run-at-rate | Deeper studies improve confidence; extend calendar. |
Upload drawings for a 24-hour DFM1 and quote—I’ll translate your environment and loads into a measurable, testable spec2.
Metal Clip Fasteners: Types and Uses?
Use cases vary by industry. Map features to assembly pain points to avoid field issues.
U-clips and speed nuts simplify sheet-metal joints1; snap-in clips secure trims; edge clips hold harnesses on flanges; hose clips clamp tubes; contact clips deliver conductive spring force2. Match to panel thickness, vibration profile, exposure, and tool access to balance cost, ergonomics, and durability.

HVAC/appliances (0.6–1.2 mm): U-clips align panels1 and accept machine or thread-forming screws, eliminating loose nuts and reducing takt time. Interiors: snap-in clips with felt patches prevent buzz/squeak/rattle; phosphate-oil reduces insertion friction2 and NVH. Body-in-white: edge clips route harnesses without drilling; serrations plus acrylic adhesive pads help on oily or painted steel. E-mobility/battery: phosphor bronze or 301 stainless contact clips control resistance (mΩ) and force after thermal cycling; specify stress-relaxation limits and resistance rise. Marine: 316 stainless plus passivation per
Documentation: FAI/CMM packs, control plans1, and PPAP2 available; I support logo marking, color dots, and kitting with mating screws where required.

Practical checkpoints buyers should verify
- Complete substrate stack-up including paint/e-coat thickness1.
- Insertion path clearance and tool access at the station.
- Vibration profile and post-vibration retention measurement.
Quality & packaging notes buyers care about
- Passivation/plating certs tied to lot and thickness records.
- Carton drop testing without leg deformation.1
- Mix-prevention: color dots or unique barcodes per part variant.2
| Factor | Option A | Option B | What it means for cost/lead time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material/Grade | Phosphor bronze | 304/316 stainless | Bronze excels electrically; 316 for marine chloride resistance. |
| Strength/Hardness | 350–600 MPa yield | 700–1,000 MPa yield | Higher yield increases retention; requires tighter forming control. |
| Corrosion Resistance1 | Passivated stainless | Zn–Ni + sealer | Stainless avoids chipping; Zn–Ni fits carbon-steel economics. |
| Tolerance Feasibility | Hole ±0.10 mm | Slot ±0.05 mm | Slots add adjustability; tighter slots slow stamping. |
| Surface Finish2 | PTFE-like low-friction coat | Phosphate-oil | PTFE lowers insertion force; phosphate reduces squeak. |
| Testing/Reports | Salt spray 240 h | Salt spray 720 h + vibration | Longer tests validate durability; extend qualification time. |
Upload your drawing for a 24-hour DFM1 and quote—I’ll align clip type2, finish, packaging, and tests to your real environment.
Conclusion
Choose clip type by function and environment, lock tolerances and coatings to standards, validate forces and corrosion, then send your drawing for a 24-hour DFM quote.