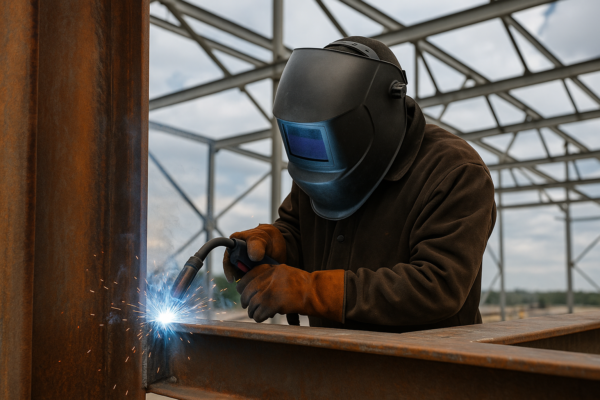
Welding Defects and How to Avoid Them in Precision Metal Parts
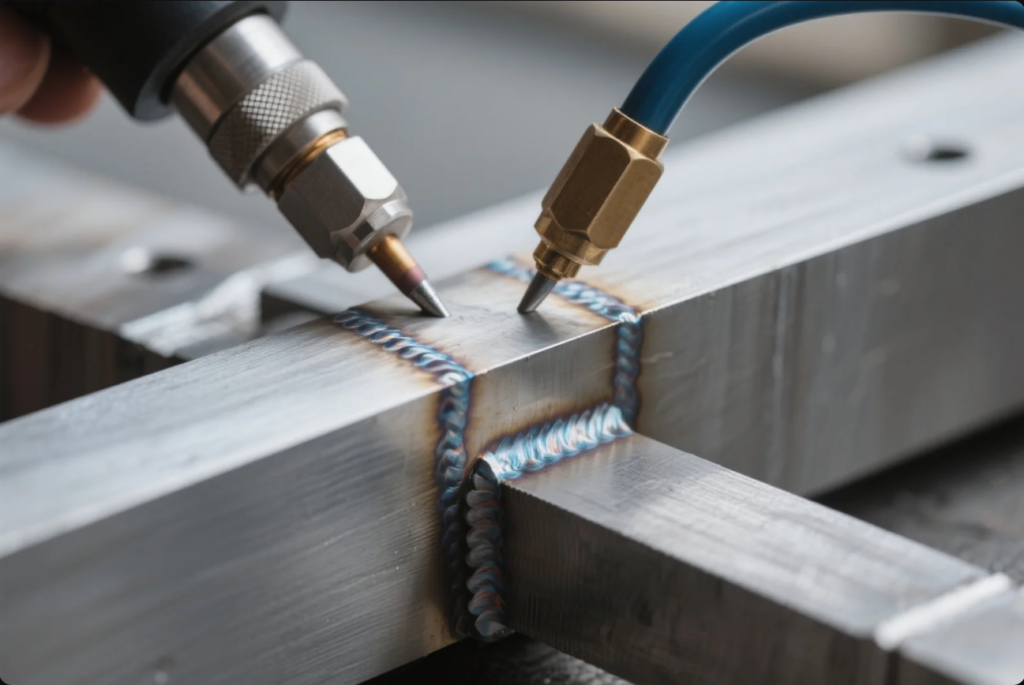

I used to face defects that ruined precision welds. Then I learned how to spot and prevent them early. This guide helps you understand, inspect, and avoid typical welding problems in metal parts.
Common Weld Defects: Cracks, Porosity, and Undercuts
I once found cracks in high‑stress components. Then I learned the defect patterns. Understanding defect origins helped me avoid them.
Snippet paragraph:
Cracks risk structural failure. Porosity reduces strength. Undercuts weaken load-bearing surfaces. Knowing what to look for helps prevent them.
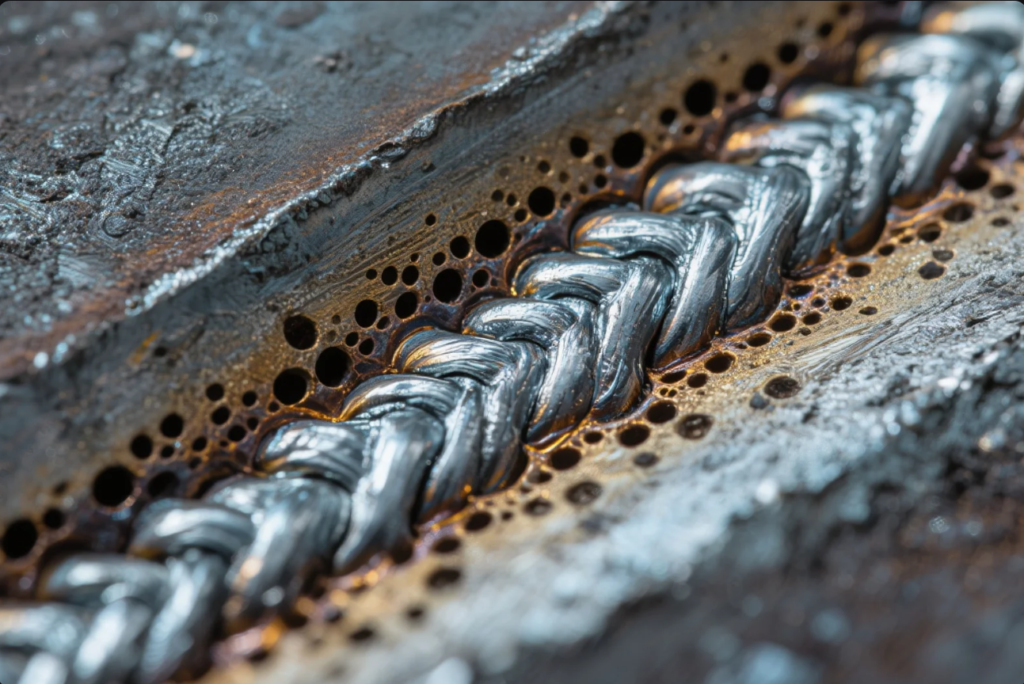

Types of Common Defects
Cracks
- Hot cracks occur during weld cooling.
- Cold cracks form after weld due to residual stress or hydrogen.
- Appear along the heat‑affected zone or root area.
- Caused by too fast cooling, high restraint, or moisture.
Porosity
- Gas pockets trapped in the weld metal.
- Look like pinholes or cavities.
- Caused by moisture, rust, lubricant, or shield gas loss.
Undercuts
- Melted grooves at weld toe.
- Reduces effective weld area.
- Caused by excessive current, incorrect torch angle, or high travel speed.
Why They Matter
- Structural integrity is compromised—hot cracks can cause catastrophic failure. According to NACE corrosion studies, cracks foster corrosion.
- Porosity decreases tensile strength by up to 30% per American Welding Society.
- Undercuts act as stress risers, doubling fatigue crack growth rate—see ISO fatigue standards.
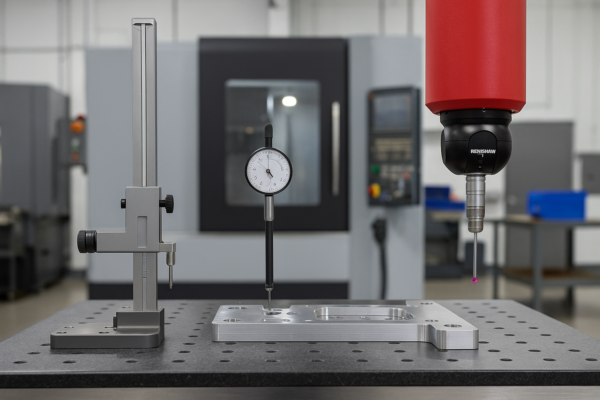
How to Inspect and Test Welded Metal Assemblies
I learned that detection without delay matters. I use both visual and advanced tests to catch hidden defects early.
Snippet paragraph:
Start with simple visual checks. Then apply ultrasonic, X‑ray, dye‑penetrant, hydro‑tests, or sectioning to ensure full weld integrity.
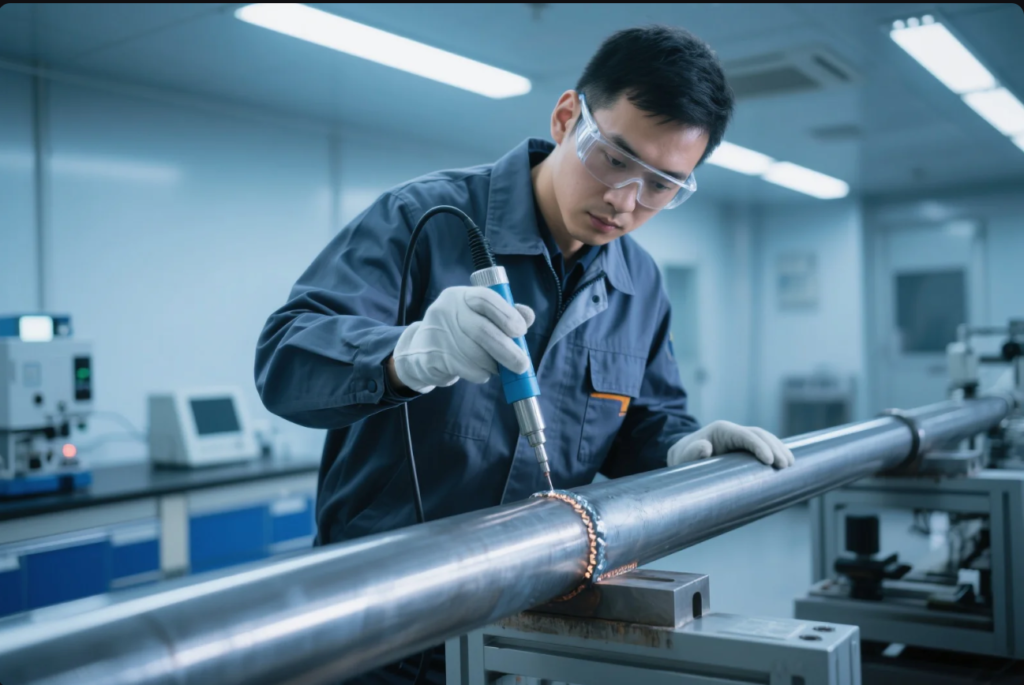

Inspection Methods
-
Visual Testing (VT)
- Inspect bead shape, undercuts, cracks with penlight or magnifier.
-
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
- Reveals surface-breaking defects per ASTM E165 guidelines.
-
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
- Works on ferrous metals; finds subsurface defects per ASTM E709.
-
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
- Detects internal flaws using sound waves as per ASME Section V.
-
Radiographic Testing (RT)
- Uses X‑ray or gamma rays. Standard in aerospace per NADCAP.
-
Hydrostatic Pressure Test
- Checks seals and strength in pressure vessels.
-
Macro‑etching & Sectioning
- Cuts weld for microstructure confirmation under magnification.
🔗 More inspection detail at The Fabricator.
Importance of Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS)
I once dismissed WPS. Then I saw it failed everything as welders guessed settings. A proper WPS avoids that.
Snippet paragraph:
A WPS outlines critical variables: materials, heat, weld technique, and test methods. Following it ensures consistency and controls defect rates.
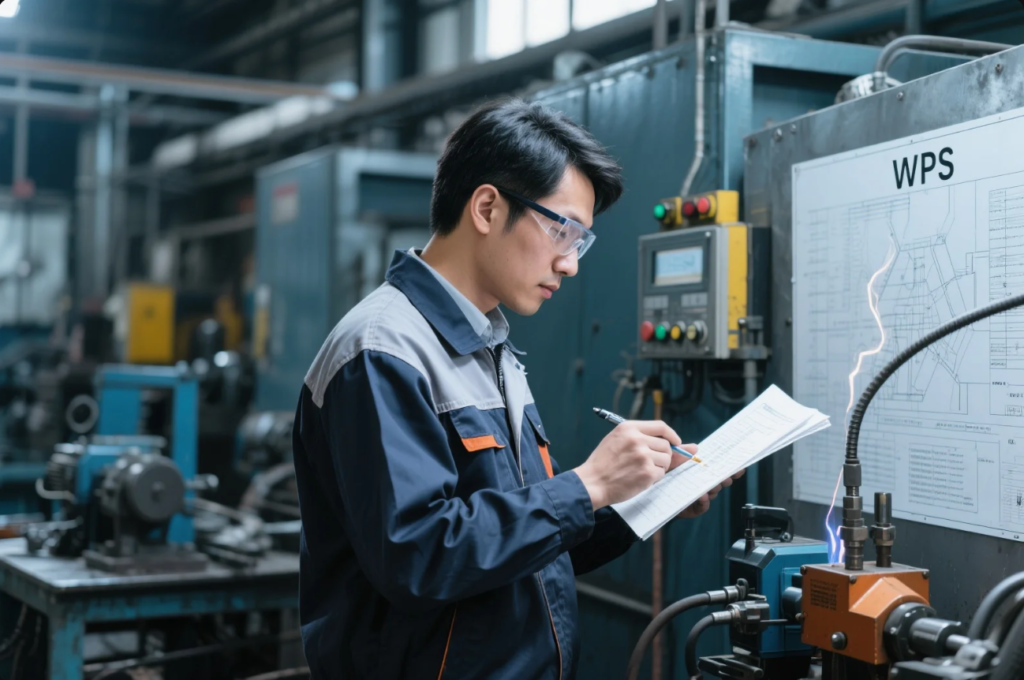

Key WPS Components
- Base and filler metal details
- Joint type and groove geometry
- Welding method (MIG/TIG) and parameters
- Preheat and interpass temperature ranges
- Shield gas type and flow
- WPS must reference AWS D1.1 or ISO 15614 standards.
When welder drifted from WPS, we saw undercuts increase by 50%. Strict adherence cut that to nearly zero.
How PrimeCustomParts.com Ensures Zero‑Defect Weld Quality
At PrimeCustomParts.com, we claim zero defects—and we prove it daily. Here’s how we deliver consistently flawless welds:
Snippet paragraph:
We use certified procedures, climate-controlled booths, inline inspection, and rigorous testing before and after welding. Zero defect isn’t an ideal—it’s our baseline.

Prime’s Commitment
| Stage | What We Do |
|---|---|
| Certified WPS | Aligned with AWS, ISO, and NADCAP requirements |
| Qualified Welders | Certified per ISO 9606, retested every 6‑12 months |
| Controlled Environment | Temperature/humidity control prevents porosity |
| Inline Monitoring | Cameras detect bead shape and heat issues live |
| 3rd‑Party Testing | SGS or Intertek perform UT, RT, and MT |
| Full Traceability | Every weld tied to part and welder record |
| Continuous Improvement | Defect triggers root cause investigation |
Our defect rate remains <0.05%, better than industry average. That why OEMs trust us.
FAQs
Q: Can porosity be completely prevented?
A: Yes. With dry weld surfaces, clean gas shielding, and controlled environment, we eliminate porosity.
Q: How often must welders be requalified?
A: Requalification is required every 6–12 months or after WPS changes, per AWS/ISO.
Q: Do all parts need radiographic testing?
A: No. Only critical parts (pressure vessels, aerospace) need RT. We use UT for most.
Q: Does digital WPS help reduce errors?
A: Yes. It enforces correct settings and records each weld for audit.
Q: How soon can we get test results after inspection?
A: Visual & PT drop results in minutes. UT/RT takes a few hours to complete.
Q: Do you include test documentation with shipments?
A: Absolutely. We supply full test certificates, WPS, welder logs, and inspection data with each delivery.
📞 Contact Prime
Want precision welded parts with guaranteed zero defects? Talk to us.
Website: https://primecustomparts.com
Email: [email protected]
Conclusion
Weld defects like cracks, porosity, and undercuts threaten performance. You stop them with proper inspection, strict WPS, trained welders, and defect avoidance systems. PrimeCustomParts.com brings these together to deliver precision welds in every project—without compromise.