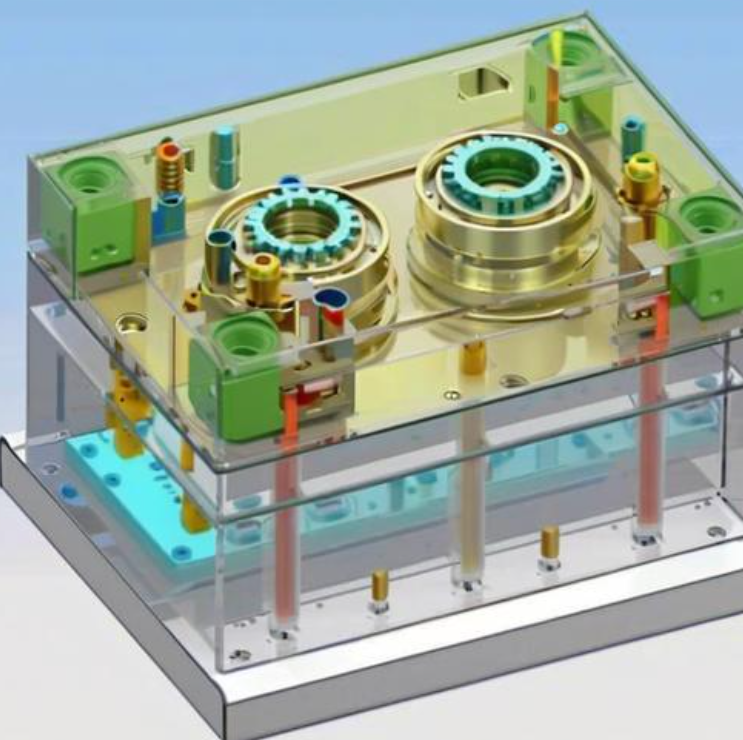
What Are the Structures of Molds?
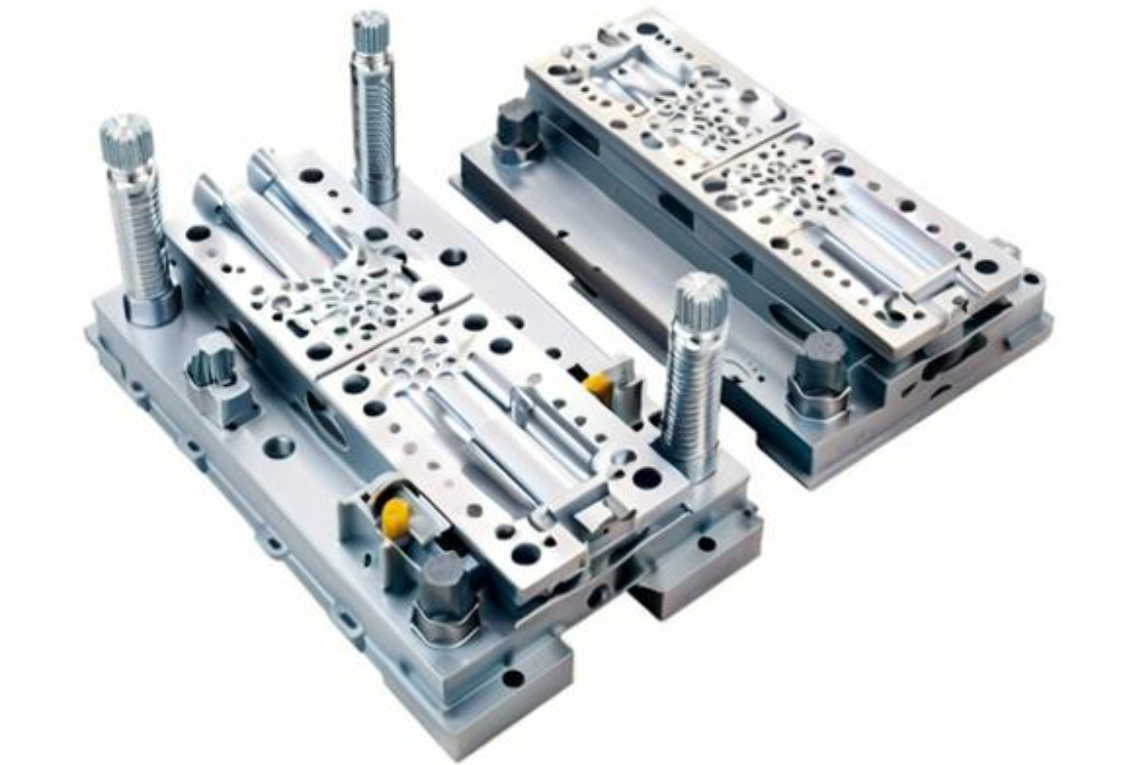

Ever wondered what makes molds work? The structure of a mold directly impacts its functionality and the quality of the final product.
Molds typically consist of two main parts: the core and the cavity. These components work together to shape the material into the desired form, ensuring precision and consistency in manufacturing.
Dive deeper to explore the essential components of molds and how they function in various manufacturing processes.
What Are the Core and Cavity in Molds?
What roles do the core and cavity play in molding? They are the heart of the mold’s structure.
The core and cavity are the primary components of a mold, with the cavity forming the outer shape of the product and the core creating internal features, ensuring accurate and detailed designs.
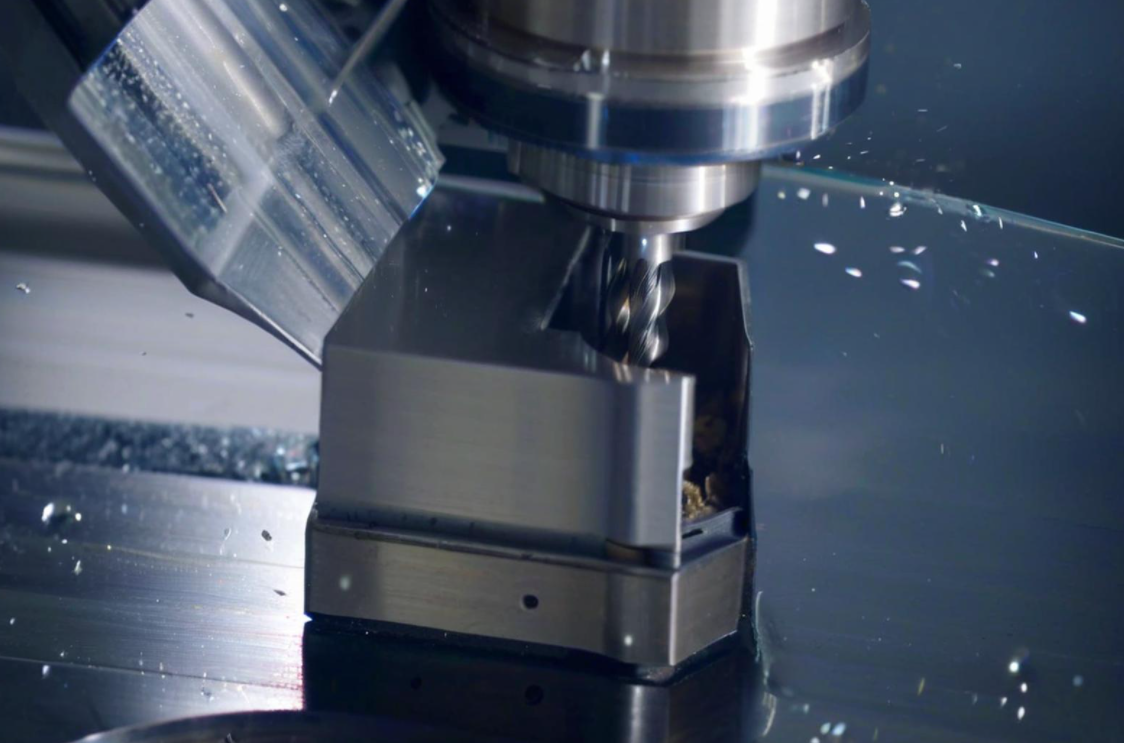

Functions of the Core and Cavity
- Cavity: Shapes the external surface of the product.
- Core: Defines internal features like holes or recesses.
Key Considerations
| Component | Function | Design Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Cavity | External shaping | Smooth surface finish, precise dimensions |
| Core | Internal features | Detail accuracy, ease of removal |
Materials Used
The core and cavity are typically made from durable materials like:
- Steel: High strength and wear resistance.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and cost-effective.
- Beryllium Copper: Excellent thermal conductivity.
What Are the Different Types of Mold Structures?
What are the common mold designs? Each type serves specific purposes.
Molds can be single-cavity, multi-cavity, or family molds, with each type offering unique advantages based on production needs and complexity.

Single-Cavity Molds
Single-cavity molds produce one part per cycle.
Advantages
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplicity | Easy to design and maintain |
| Cost-Effective | Lower upfront investment |
Multi-Cavity Molds
Multi-cavity molds produce multiple identical parts per cycle.
Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher production rates |
| Consistency | Uniform quality across parts |
Family Molds
Family molds produce different parts in a single cycle.
Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Versatility | Suitable for complex assemblies |
| Cost Savings | Reduces production time and costs |
Comparison of Mold Structures
| Type | Parts Per Cycle | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Cavity | 1 | Simple, cost-effective | Lower production efficiency |
| Multi-Cavity | Multiple | High efficiency, consistent quality | Higher initial cost |
| Family | Multiple (different) | Versatile, reduces assembly time | Complex design and maintenance |
What Are the Key Components of a Mold?
What other parts are essential in a mold’s structure? They ensure smooth operation.
Beyond the core and cavity, molds include components like runners, gates, ejector pins, and cooling systems, which facilitate material flow, part ejection, and temperature control.
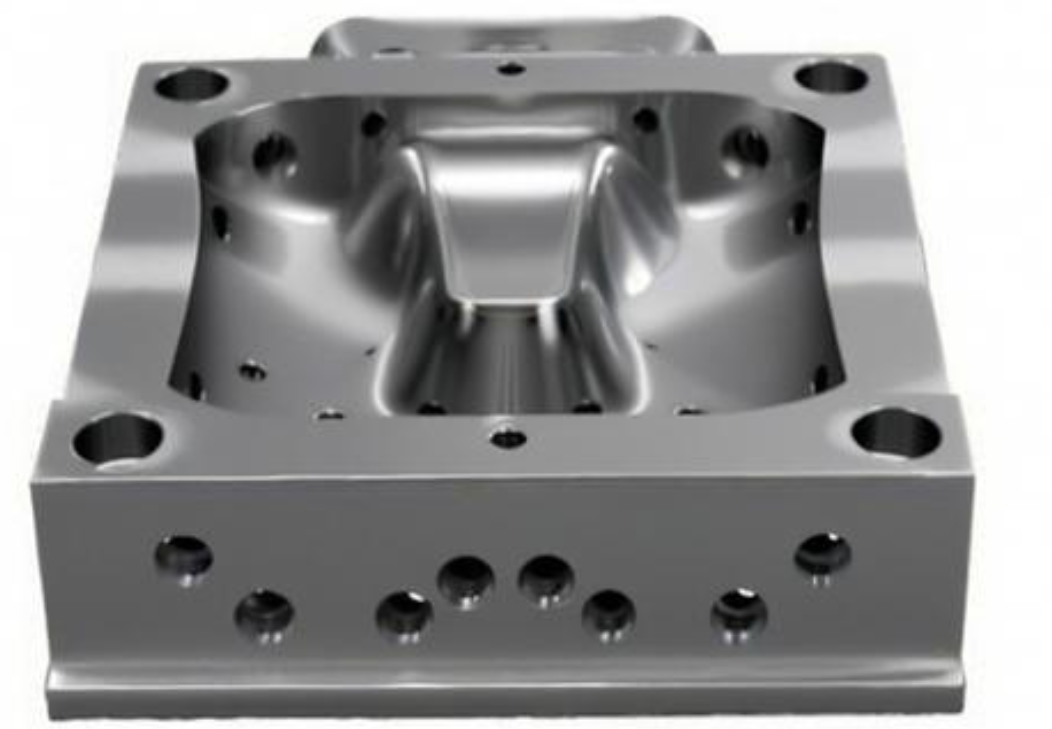

Runners and Gates
Runners and gates guide the material into the mold cavity.
Functions
- Runners: Channels that carry material to the cavity.
- Gates: Entry points where material enters the cavity.
Ejector Pins
Ejector pins help remove the finished part from the mold.
Key Points
- Placement: Strategically located to avoid damage.
- Material: Durable to withstand repeated use.
Cooling System
The cooling system regulates the mold’s temperature.
Importance
- Cycle Time: Reduces cooling time for faster production.
- Quality: Prevents defects like warping or shrinkage.
Components of a Mold
| Component | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Runners | Material flow channels | Ensures even distribution |
| Gates | Entry points for material | Controls flow rate and pressure |
| Ejector Pins | Part removal | Prevents damage during ejection |
| Cooling System | Temperature control | Improves cycle time and part quality |
How Does Mold Structure Affect Product Quality?
Why is mold structure critical for quality? It directly impacts the final product.
A well-designed mold ensures consistent dimensions, surface finish, and structural integrity, while poor design can lead to defects like warping, shrinkage, or incomplete filling.

Common Defects from Poor Mold Design
- Warping: Uneven cooling causes deformation.
- Shrinkage: Material contracts unevenly.
- Incomplete Filling: Insufficient material in the cavity.
Solutions to Improve Quality
- Precision Design: Accurate core and cavity dimensions.
- Efficient Cooling: Uniform temperature control.
- Proper Venting: Prevents air traps and incomplete filling.
Quality Assurance Checklist
| Aspect | Solution | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Design Accuracy | Precise core and cavity | Consistent dimensions |
| Cooling System | Efficient cooling channels | Prevents warping and shrinkage |
| Venting | Proper vent placement | Avoids air traps and incomplete filling |
How Does Prime Design and Manufacture Molds?
How does Prime ensure top-quality molds? Expertise and advanced technology are key.
Prime designs and manufactures molds with precision, using advanced CAD software and CNC machining for accurate dimensions and efficient production, ensuring high-quality results for every project.

Our Process
- Design: Using CAD software for precise specifications.
- Manufacturing: CNC machining for accurate components.
- Testing: Ensuring functionality and quality before delivery.
Why Choose Prime?
- Experience: Over 20 years in mold manufacturing.
- Technology: Advanced tools for precision.
- Quality: ISO-certified processes for consistency.
Success Stories
Prime has delivered high-quality molds for industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, earning recognition for innovation and reliability.
Conclusion
Mold structures, including the core, cavity, runners, and cooling systems, play a vital role in manufacturing. Prime leverages expertise and advanced technology to design and manufacture high-quality molds for diverse applications.