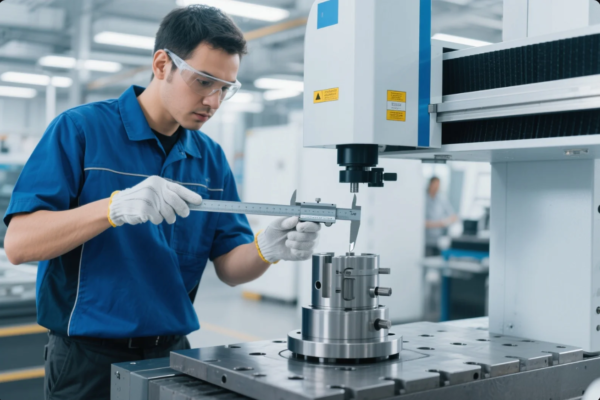
# What Does It Mean to Jog in CNC? Mastering Machine Movements
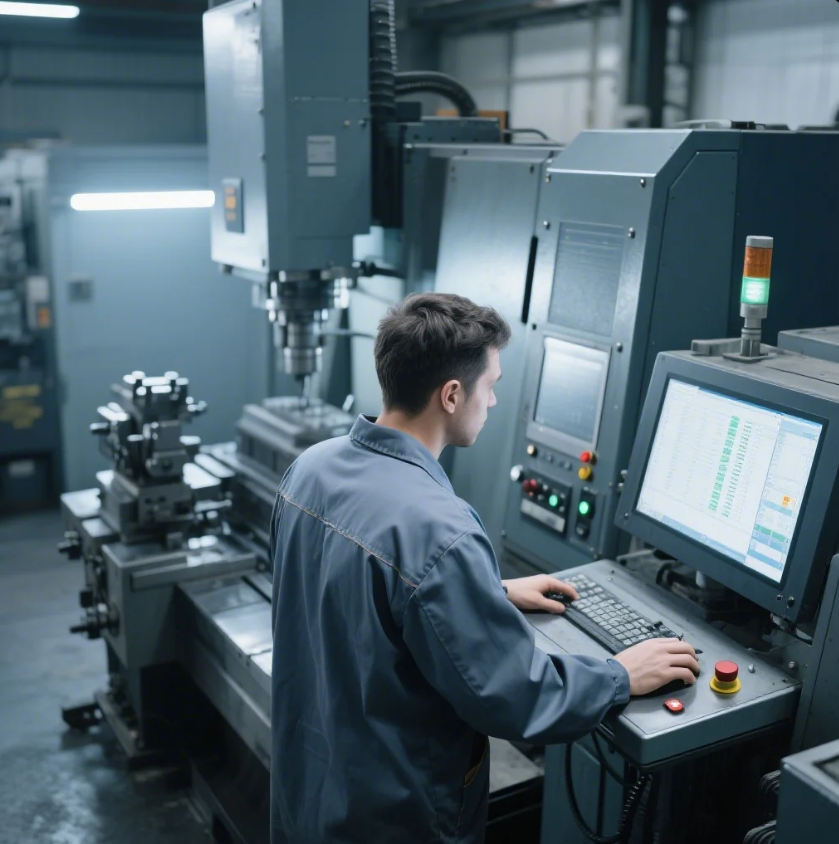

Leading paragraph: Confused about jogging vs running a CNC? Discover how this fundamental operation affects your machining workflow.
**Snippet paragraph: Jogging in CNC means manually moving axes using the control panel for setup, while 'Run' executes programmed G-code automatically - both critical for safe operation.**
Transition paragraph: Let's break down jogging mechanics and how it fits into production cycles.
## What Is Jog in a CNC Machine?
Leading paragraph: Jogging is your hands-on control method for precise machine positioning.
**Snippet paragraph: The jog function allows incremental axis movement (typically 0.001"-1.0" steps) using pendant controls or keyboard, essential for tool setup and workpiece alignment.**
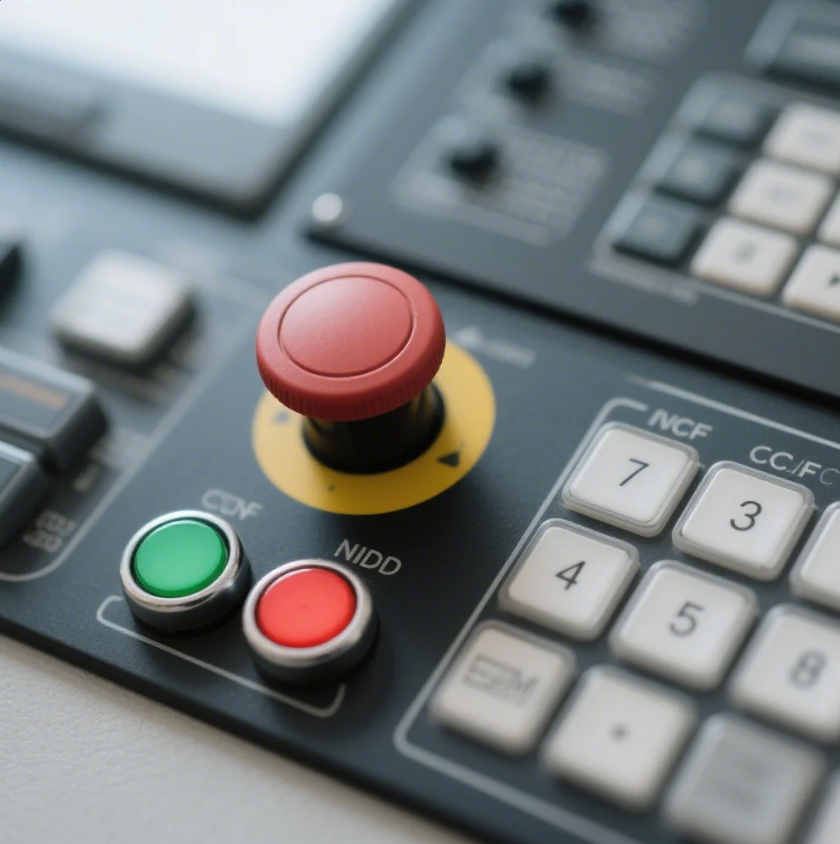

Dive-Deeper paragraph:
### Jogging Parameters in Industrial CNCs
#### Common Jog Increments
| Increment Size | Use Case | Button Color (Standard) |
|---------------|----------|-------------------------|
| 0.001" (0.02mm) | Final tool touch | Green |
| 0.010" (0.25mm) | Die alignment | Yellow |
| 0.100" (2.54mm) | Rapid positioning | Blue |
| Continuous | Long travel | Red |
#### Safety Protocols During Jogging
1. **Speed Limits**:
- X/Y Axes: Max 20% rapid rate
- Z Axis: Max 10% rapid rate
2. **Collision Avoidance**:
```plaintext
Jog Sequence:
1. Verify clearance in path
2. Select proper increment
3. Keep finger on Emergency Stop
4. Move smoothly, no sudden stops
```
**Prime's Practice**: Our operators complete 20-hour jog proficiency training before machine access.
## What Does It Mean to Jog a Machine?
Leading paragraph: Beyond simple movement - jogging is about controlled preparation.
**Snippet paragraph: Machine jogging involves manually positioning cutting tools or workpieces using variable feed rates, different from automated operation modes controlled by programs.**
Dive-Deeper paragraph:
### Jogging Application Matrix
#### Setup Procedures Requiring Jogging
| Task | Jog Method | Safety Check |
|--------------------|------------|--------------|
| Tool Length Offset | Z-axis micro | Spindle off |
| Work Coordinate Set | X/Y med. | Probe clear |
| Fixture Alignment | All axes | Clamps secured |
| Crash Recovery | Single-axis | E-stop ready |
#### Jog Speed Comparison Table
| Machine Type | Max Jog Speed | Resolution |
|--------------|---------------|------------|
| Vertical Mill | 100 IPM | 0.0001" |
| Lathe | 60 IPM | 0.0005" |
| Router | 300 IPM | 0.001" |
| EDM | 20 IPM | 0.00005" |
## What Does Run CNC Mean?
Leading paragraph: The transition from manual control to automated precision.
**Snippet paragraph: 'Run' mode executes the loaded G-code program at set feed rates, where the CNC machine autonomously performs all cutting operations without manual intervention.**

Dive-Deeper paragraph:
### Run Mode Execution Process
#### Program Verification Steps
1. **Dry Run**:
- Tools move without cutting
- 50% reduced speed
- Verify all coordinates
2. **Single Block**:
- Execute one line at a time
- Used for critical operations
3. **Full Run**:
- Normal production speed
- Requires first-piece inspection
#### Run vs Jog Performance Factors
| Factor | Jog Mode | Run Mode |
|---------------|----------|----------|
| Speed Control | Manual | Programmed F/S |
| Accuracy | ±0.002" | ±0.0005" |
| Repeatability | Low | High |
| Use Case | Setup | Production |
## What Are the Different Modes of CNC?
Leading paragraph: Your control panel's hidden workflow options revealed.
**Snippet paragraph: Modern CNCs offer 7 operational modes: Jog, MDI, Auto, Edit, Zero Return, DNC, and Emergency Stop - each serving specific phases of the machining process.**

Dive-Deeper paragraph:
### CNC Mode Selection Guide
#### Mode Functionality Matrix
| Mode | Access Level | Primary Use | Axis Movement |
|--------------|--------------|-------------|---------------|
| Jog | Operator | Setup | Manual |
| MDI | Programmer | Test code | Semi-auto |
| Auto | Production | Batch run | Full auto |
| Edit | Supervisor | Code modify | Locked |
| Zero Return | Maintenance | Calibration | Automatic |
#### Safety Interlocks by Mode
```plaintext
1. Jog Mode:
- Requires enabled drives
- Feed hold active
- Spindle interlock
2. Auto Mode:
- Door must close
- Tool offsets verified
- Work coordinates setPrime's Protocol: We implement mode-specific checklists to prevent operational errors.
Conclusion
Master jogging fundamentals to ensure safe, efficient CNC operation.
Need CNC Expertise? Prime's technicians can:
- Provide mode-specific training
- Offer custom jog speed configurations
- Program optimal run parameters
[Contact our CNC specialists] today for operational best practices tailored to your machines and applications.
SEO Keywords:
- "CNC jog vs run mode differences"
- "proper CNC machine jogging techniques"
- "industrial CNC operational modes explained"
- "CNC setup and production workflow"
- "safe CNC machine operation practices"
Image Alt Texts:
- CNC operator demonstrating proper jogging posture
- Close-up of jog increment selection buttons
- Directional jogging reference diagram
- CNC controller in program run mode
- Mode selector switch positions