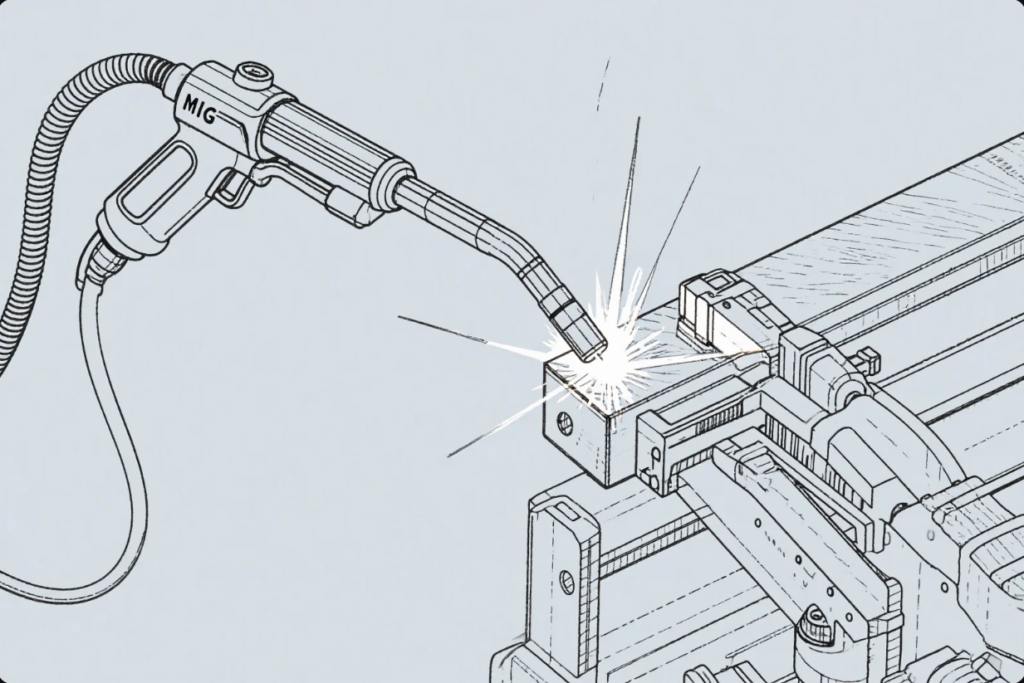
What does MIG stand for?
Many professionals hear "MIG" but aren’t sure what it means.
MIG stands for “Metal Inert Gas,” a core welding process used in modern fabrication. At Prime, MIG welding is a daily foundation for quality industrial manufacturing.
Understanding MIG welding—from gas types to applications—helps you source smarter, avoid costly mistakes, and ensure parts meet international quality standards.
📌 Table of Contents
- What is MIG Welding?
- Why MIG Welding Matters for B2B Buyers
- MIG Welding vs. Other Methods
- Real Use Cases in Prime Projects
- Technical Considerations in MIG Welding
- FAQs
- Contact Us
What is MIG Welding?
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding is a gas metal arc welding (GMAW) process. A continuously fed wire electrode joins base materials while a shielding gas protects against contamination.
Key Elements:
- Electrode: solid wire (typically ER70S-6)
- Shielding gas: argon or argon-CO₂ mix
- Power source: constant voltage (CV) supply
- Process type: semi-automatic or fully robotic
Prime applies MIG welding to steel, stainless steel, and aluminum with consistent quality.
Why MIG Welding Matters for B2B Buyers
For industrial procurement teams, MIG means efficiency and scalability.
- Speed: MIG can weld faster than TIG or SMAW.
- Repeatability: Suitable for batch production and robotic systems.
- Material compatibility: Works with a wide range of alloys.
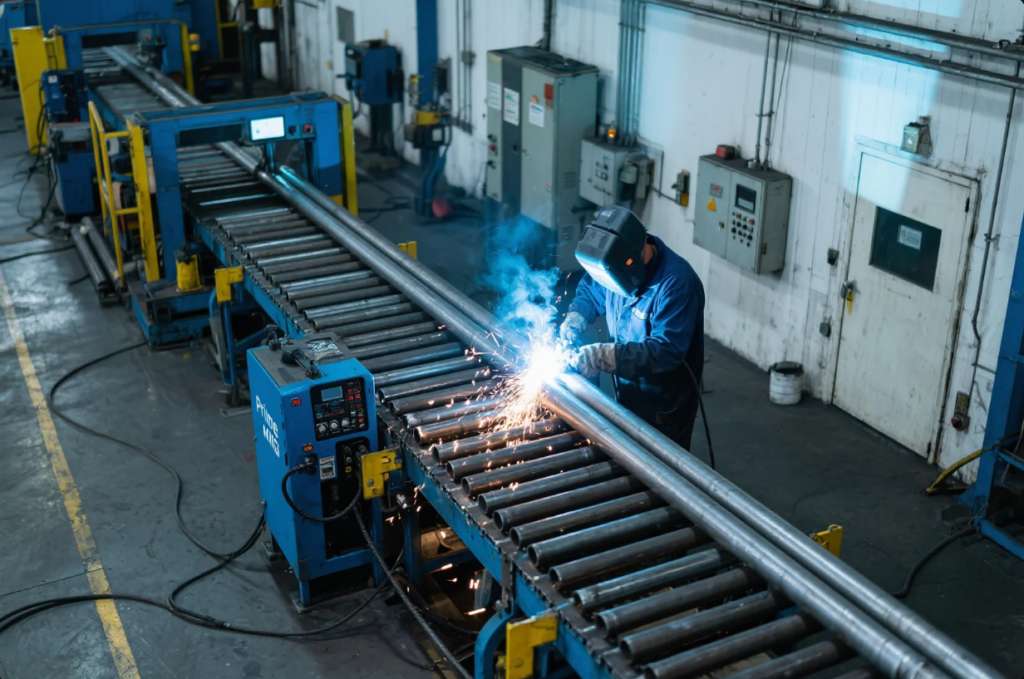

Use cases include:
- Enclosures for HVAC systems
- Brackets for automotive frames
- Load-bearing fabrication for construction
MIG Welding vs. Other Methods
| Welding Method | Gas Used | Speed | Skill Needed | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIG | Argon mix | High | Moderate | Mass production |
| TIG | Argon | Low | High | Precision joints |
| Stick (SMAW) | No gas (flux) | Medium | Low | Outdoor steel welding |
MIG strikes the balance for B2B needs—fast, adaptable, and clean.
Real Use Cases in Prime Projects
📦 HVAC Bracket Welding
A Chicago client requested 8,000 MIG-welded enclosures. Our robotic MIG line finished production in 16 days.
🛢️ Oil & Gas Skid Assemblies
For a Middle East client, we delivered dual-pass MIG welds with 100% X-ray tested joints.
🚗 Automotive Fixture Fabrication
A German Tier-2 supplier relied on Prime for 1,200 high-load fixtures with ±0.2 mm tolerance via MIG welding.

All reports passed ultrasonic inspection and conformed to AWS D1.1 structural code.
Technical Considerations in MIG Welding
1. Shielding Gas Types
Use argon-CO₂ mixes (75/25) for carbon steel; 100% argon for aluminum.
2. Wire Feed Speed
Adjust feed to match material thickness and travel speed.
3. Weld Positioning
Prime performs MIG in all positions: flat, vertical, overhead.
4. Joint Design
Lap, T-joint, butt welds are common. Edge preparation is key.
5. Weld Inspection
We provide:
- Visual inspection
- Ultrasonic testing (UT)
- Radiographic testing (RT)
Certified to AWS D1.1 and ISO 3834.
FAQs
Q1: Is MIG good for aluminum?
Yes. Prime uses push-pull torches and spool guns for aluminum.
Q2: How thick can MIG weld?
Up to 1" steel with correct wire and amps.
Q3: Is MIG suitable for outdoor use?
Limited. Use stick welding or FCAW outdoors.
Q4: Is MIG better than TIG for production?
Yes—faster and more economical.
Q5: Can MIG welding be automated?
Yes. Prime operates 4 robotic MIG welding lines.
Contact Us
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://primecustomparts.com

We Provide:
- MIG, TIG, Spot Welding
- Welded sheet metal parts
- Fixtures, base frames, panels
- ISO, AWS, SGS compliant
- Worldwide shipping & inspection reports
Final Words
MIG welding is the cornerstone of reliable fabrication. From mass production to tight-tolerance parts, Prime delivers ISO-certified MIG services tailored to global industries.
👉 Request a quote now and let’s build stronger together.