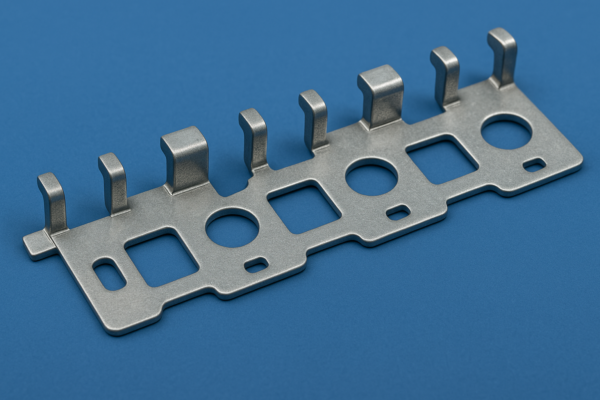
What is rotor stamping and how does it enhance motor performance?
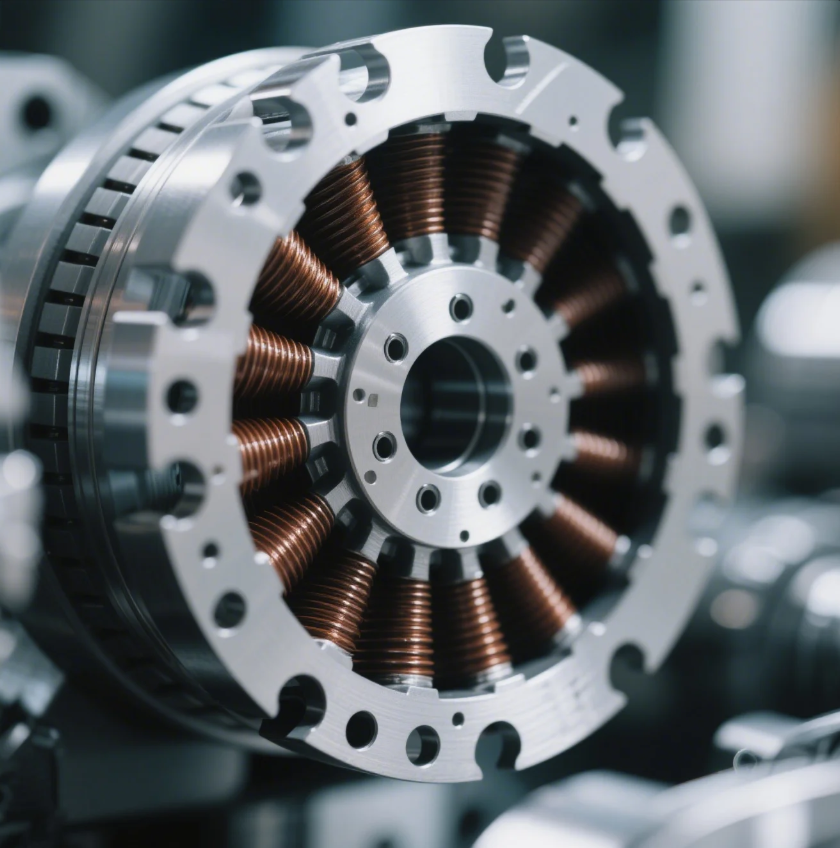
Manufacturers often face overheating, vibration, or energy loss due to poorly stamped motor cores.
Rotor stamping is a precision process that forms laminated steel sheets into the rotating core of electric motors.
Understanding how it works helps reduce power loss and extend equipment life.
LOOP_START
What is motor stamping?
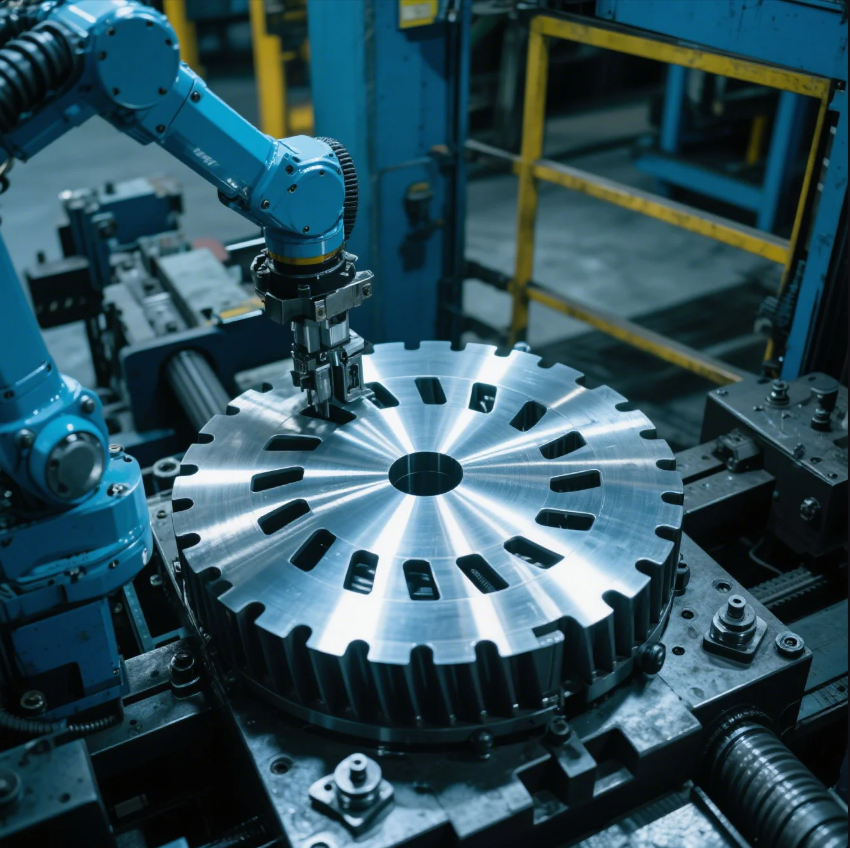
Poor motor efficiency often starts with uneven or misaligned core laminations.
Motor stamping produces thin electrical steel laminations used to build the stator and rotor cores in electric motors.
Why motor stamping matters
| Component | Stamping Purpose |
|---|---|
| Rotor Laminations | Create the rotating magnetic core of the motor |
| Stator Laminations | Form the stationary part that guides the magnetic field |
| Core Stack Assembly | Laminations are stacked to form a low-loss magnetic core |
Our precision approach at Prime
At Prime, we use progressive die stamping with ±0.01 mm tolerance for rotor sheets. For a U.S. client building industrial fans, our precise stamping reduced heat generation by 12%—leading to longer motor life and better energy ratings.
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What is the difference between stamping and press brakes?
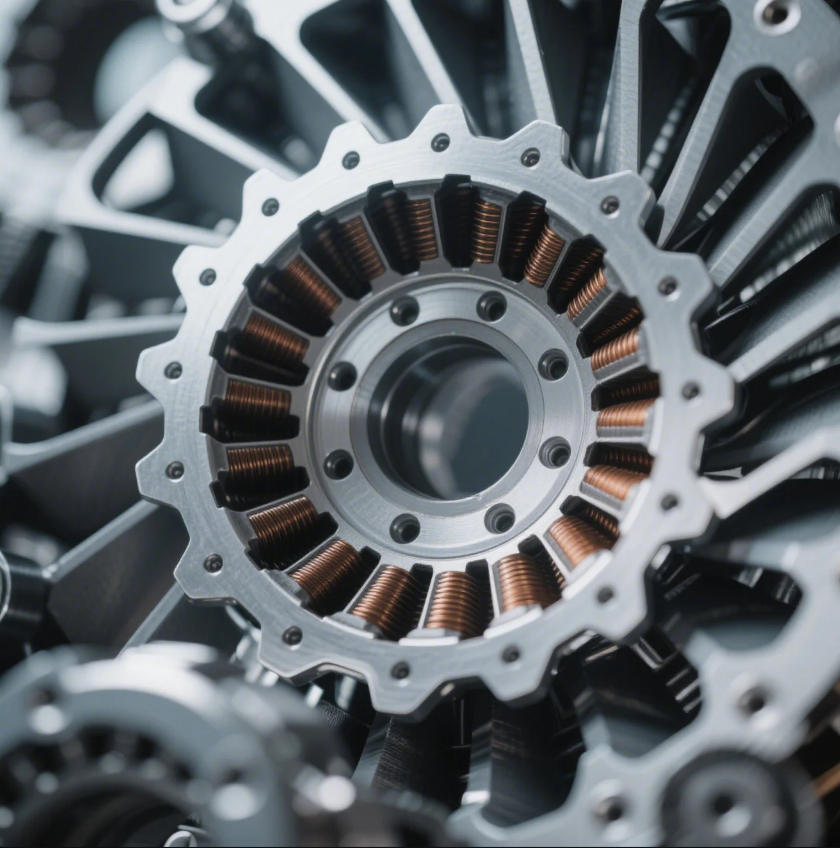

Some buyers confuse stamping with bending, leading to the wrong process for their parts.
Stamping uses dies to shape metal sheets through punching or forming; press brakes are for bending and folding metal.
Side-by-side comparison
| Feature | Stamping | Press Brake |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Type | Punch + die sets | Top punch and bottom die (V-block) |
| Application | Laminations, motor parts, brackets | Enclosures, cabinets, panels |
| Material Thickness | Typically thinner sheets | Can handle thicker metal |
| Volume Efficiency | Best for high-volume runs | Ideal for small batch or custom work |
Why the difference matters
Stamping offers high-speed production and consistency—ideal for motors and automotive components. Press brakes suit low-volume or angled parts. At Prime, we guide clients to the right process depending on tolerance, cost, and part shape.
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What is automotive stamping?
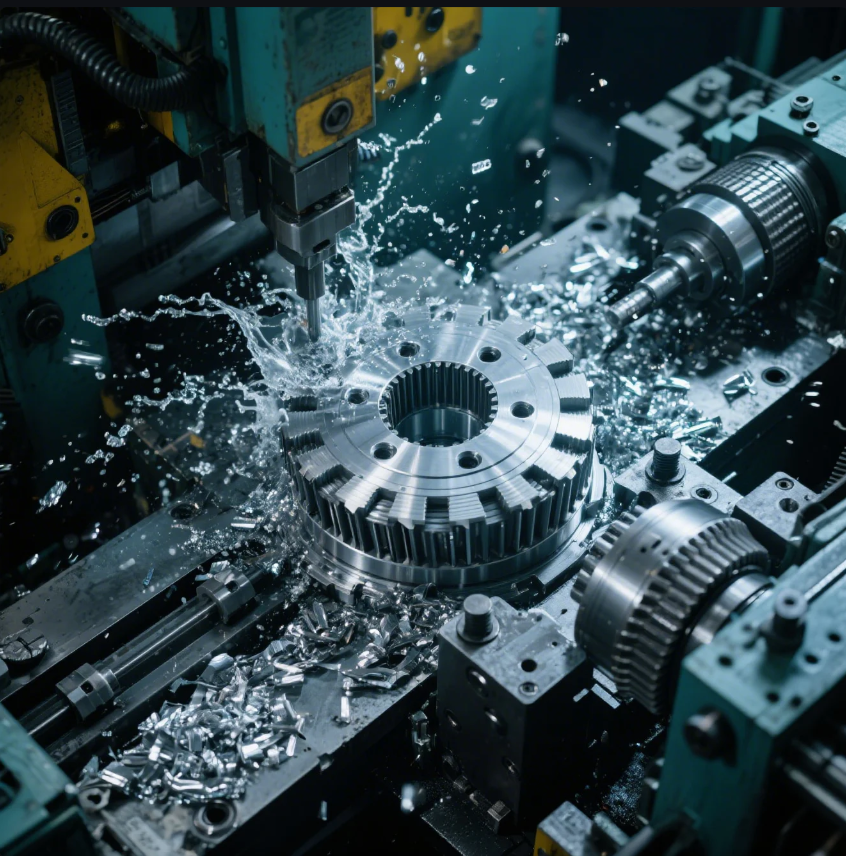
Automotive production demands lightweight, strong, and repeatable components.
Automotive stamping forms structural and body parts by pressing sheet metal into shape using custom dies.
Parts made by stamping
| Component Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Outer Panels | Hoods, fenders, trunk lids |
| Safety Parts | Seat belt mounts, crash brackets |
| Powertrain Supports | Battery holders, engine brackets |
How it ties back to motor stamping
Many electric vehicles use rotor and stator stampings made with similar die technology. At Prime, we supply both automotive body parts and motor core laminations—this helps EV makers source multiple components from a single trusted partner.
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What is the stamping process?
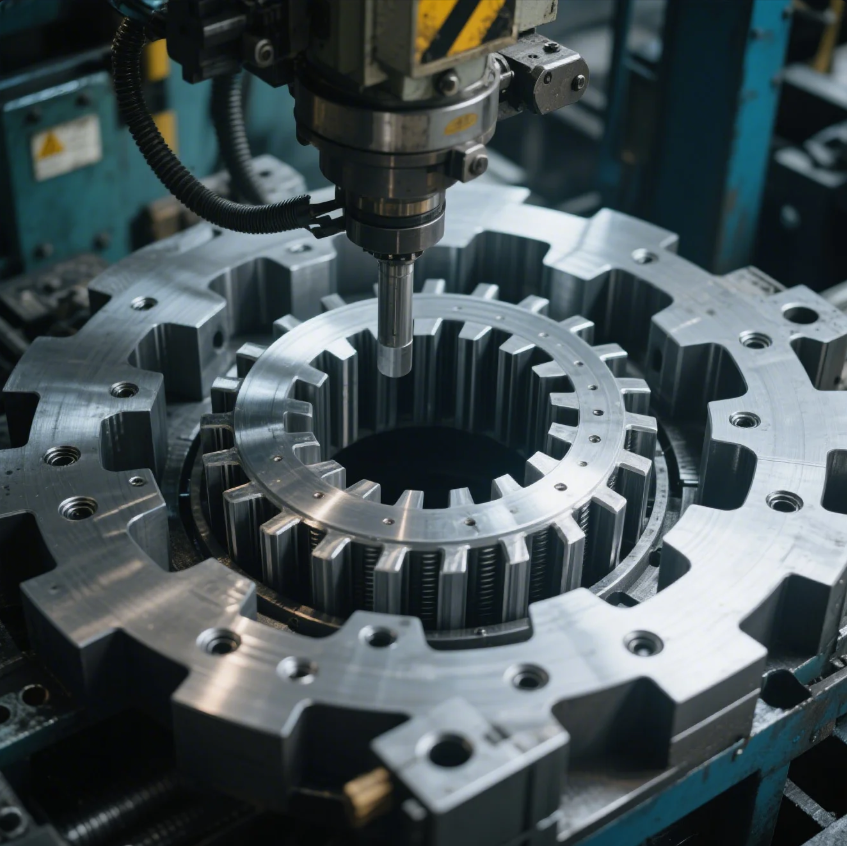

Some assume stamping is a simple punch and cut—it’s more complex and precise.
Stamping is a forming process that uses a die and press to shape metal sheets into precise components, including motor cores.
Core stages in the stamping process
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Material Feeding | Coil or blank sheets are fed into the machine |
| Punching/Forming | Metal is cut or shaped using matched dies |
| Ejecting & Stacking | Laminations are released and stacked for later assembly |
| Quality Inspection | Dimensions and burrs are checked for each batch |
Stamping at Prime: Consistency at scale
Our 10 automated production lines can stamp over 1 million motor laminations monthly. We use servo-driven presses and real-time monitoring systems to avoid deformation, burrs, or tool misalignment. This ensures consistent quality and on-time global delivery for clients in Europe, North America, and the Middle East.
LOOP_END
Conclusion
Rotor stamping ensures efficient, low-loss motor performance through precise lamination shaping and stacking.
Need a supplier for custom motor stampings? Contact Prime for free expert consultation, fast samples, and ISO-certified lamination production—we deliver tight-tolerance parts on time, worldwide.