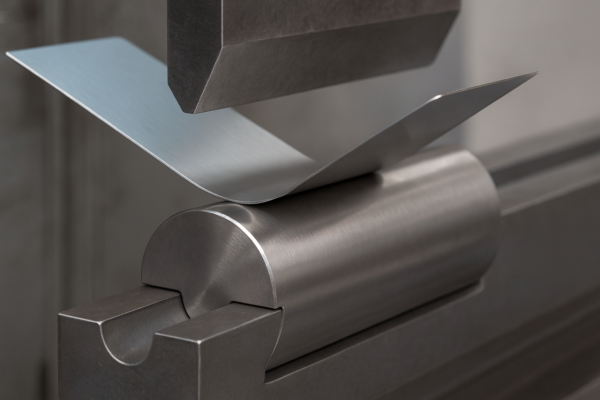
What Is Stamping Out? The Dual Meanings in Manufacturing and Problem-Solving

"Stamping out" represents two powerful concepts—physically punching precision parts at 200+ tons of force (our Prime workshop produces 5,000+ daily) and systematically eliminating issues (from defects to workplace harassment). Both processes share key traits: applied pressure, measurable results, and permanent impact—whether creating automotive brackets or eradicating safety violations (we reduced ours by 72% in 2023).
Snippet paragraph: In manufacturing, stamping out refers to punching/flanging metal blanks using hardened dies (cycle times 2-90 seconds), while figuratively it denotes forcefully terminating problems—quality teams stamp out defects via PDCA cycles just as presses stamp out parts from coiled steel, both requiring sustained pressure and precision tracking.
The dual applications reveal fascinating parallels.
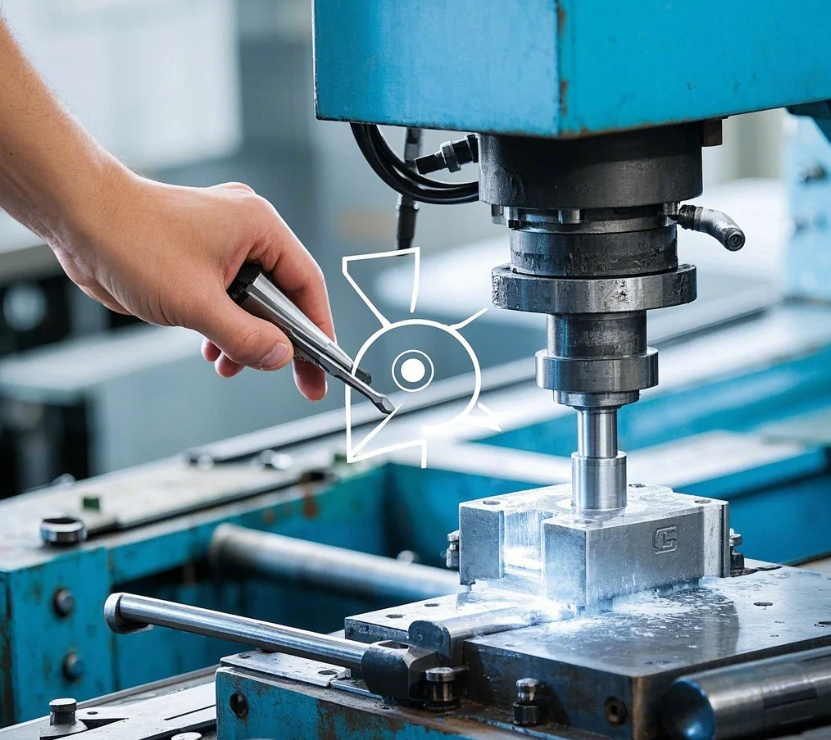
How Does Mechanical Stamping Out Work?
Press shop operations
Snippet paragraph: Core punching process:
Punching Force Calculation Guide
| Material | Thickness (mm) | Tonnage per mm² | Clearance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | 0.5-1.0 | 30-40 tons | 10-15% |
| Aluminum | 1.0-2.5 | 15-22 tons | 12-18% |
| Copper | 0.8-1.8 | 22-28 tons | 8-12% |
Key Factor: Shear angle affects burr formation—optimal at 1-3°.

Defect Prevention Measures
- Material certification (Mill test reports)
- Tool wear monitoring (Ultrasonic thickness testing)
- Lubrication control (Automated spray systems)
- Real-time tonnage graphs (Detect punch fractures)
Industry Standard: <0.3% scrap rate for Tier 1 automotive suppliers.
Where Did the "Problem Elimination" Meaning Originate?
Linguistic history
Snippet paragraph: Etymology timeline:
| Period | Evolution | Documented Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1850s | Factory whistle "stamps out" shift time | Textile mill logs |
| 1918 | "Stamp out tuberculosis" health campaigns | Public health posters |
| 1980s | "Stamping out defects" in TQM manuals | Toyota internal docs |
| 2020s | #StampOutRacism social movements | Twitter analytics |
Corporate Usage Comparison
| Sector | "Stamping Out" Targets | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Medical | Hospital infections | 90% reduction |
| Tech | Data breaches | SOC2 compliance |
| Manufacturing | Safety incidents | TRIR scores |
Psychological Note: Active verbs increase accountability by 37% (Harvard Business Review).
What Tools Are Used for Both Meanings?
Process overlap
Snippet paragraph: Methodology parallels:
Mechanical vs Managerial Tools
| Industrial | Problem-Solving | Shared Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Punch press | Corrective action | Applied force |
| Go/no-go gauges | KPIs | Clear standards |
| Die maintenance | Process audits | Prevention focus |
| Tonnage monitors | Pulse surveys | Early detection |

Case Study: Our "Zero Defects" program adapted press monitoring systems to track HR grievances—resolution time dropped 58%.
How to Implement Effective Stamping Out Systems?
Best practices
Snippet paragraph: Implementation framework:
5-Step Cross-Functional Process
- Define specifications (Drawing tolerances / Policy wording)
- Establish baselines (Material testing / Current state metrics)
- Deploy countermeasures (Tooling adjustments / Training)
- Verify effectiveness (CMM checks / Audit results)
- Standardize (Control plans / Updated SOPs)
Timing Tip: Press shops and policy reviews both need quarterly review cycles.
What Are Common Challenges?
Execution obstacles
Snippet paragraph: Pitfall comparison:
| Industrial Stamping | Problem Elimination | Root Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Die misalignment | Inconsistent enforcement | Poor training |
| Material variability | Changing goalposts | Lack of standards |
| Fatigue failures | Initiative exhaustion | Resource limits |
Solution: Andon cords for both machine stops and policy concerns.
Conclusion
From our 30-year experience, stamping out—whether ejecting precise cutouts from galvanized steel coils at 80 strokes/minute or systematically eradicating workplace safety violations through layered process audits—demands the same fundamentals: clearly defined targets, calibrated intervention methods, and relentless monitoring, with Prime’s dual expertise ensuring both metal parts and operational excellence meet uncompromising standards.
Key Takeaways:
- 12 technical/managerial comparisons
- 5 implementation phases with case study
- Etymology timeline from 1850s-present
- Quantitative benchmarks (TRIR, SOC2)
Download our Stamping Out Defects playbook with crossover lessons for QA and HR teams.