TEMPLATE_START
What is the average lifespan of a blacksmith?

Many people wonder if the blacksmith trade affects lifespan due to its physical demands.
This article explores the history, health risks, modern improvements, and earning potential in the life of a blacksmith.
Today’s blacksmiths live longer, healthier, and more profitable lives than ever before.
What was the life of a blacksmith?
Buyers often ask what daily life was like for traditional smiths.
Historically, blacksmiths lived modest, physically demanding lives centered around their forge and local community.

Hard work, respect, and routine defined the trade
In pre-industrial societies, blacksmiths were essential workers. They made tools, weapons, horseshoes, hinges, and farm equipment. A blacksmith typically worked long hours with minimal protection, high temperatures, and heavy manual labor.
At Prime, we partner with clients continuing this legacy—but now with modern materials, better ergonomics, and precise forging systems.
| Era | Role in Community | Common Work Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Medieval | Central tradesperson | Horseshoes, weapons, gate hardware |
| Industrial Age | Factory or village smith | Tools, machine parts, repair jobs |
| Modern | Artisan or technician | Knives, decorative metal, prototypes |
Prime now supplies ready-to-use forged parts that reduce physical strain and increase output for today’s blacksmiths—tools built for efficiency and longevity.
What is the average lifespan of different professions?
Clients sometimes want to compare how long various tradespeople live.
Modern blacksmiths often live into their 70s or 80s, similar to other manual labor professions.
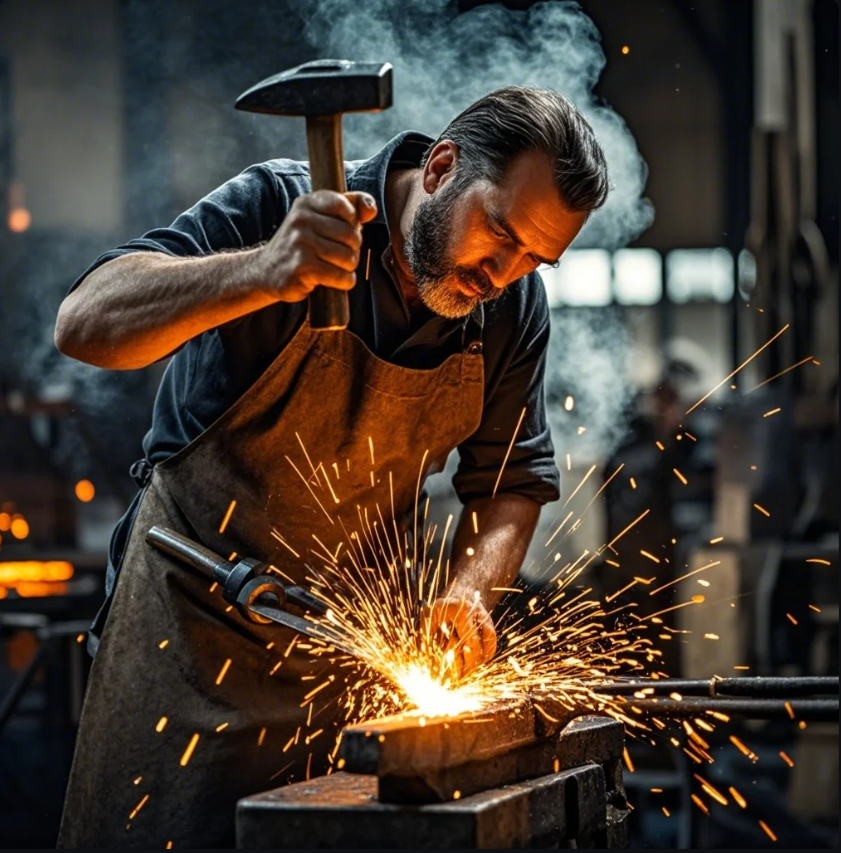

Improvements in safety and health extend working years
While older smiths may have suffered from smoke inhalation, burns, or repetitive strain, today’s blacksmiths use better ventilation, PPE, and mechanical assistance. Compared to professions like mining or welding, modern forging is safer—especially for small-scale or hobbyist work.
| Profession | Average Lifespan | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Office Worker | 77–82 years | Low physical stress |
| Carpenter | 74–80 years | Moderate physical risk |
| Welder | 72–78 years | Exposure to fumes, heat |
| Blacksmith (modern) | 73–80 years | High activity, now better safety |
| Farmer/Rancher | 70–76 years | High physical strain, long hours |
At Prime, we support longevity through smarter tools—drop-forged hammers, lightweight tongs, and forging blanks that reduce grinding and setup time.
Can a blacksmith make a living?
This is a question every new buyer or hobbyist asks eventually.
Yes—modern blacksmiths can make a strong income from custom goods, teaching, and small-scale production.
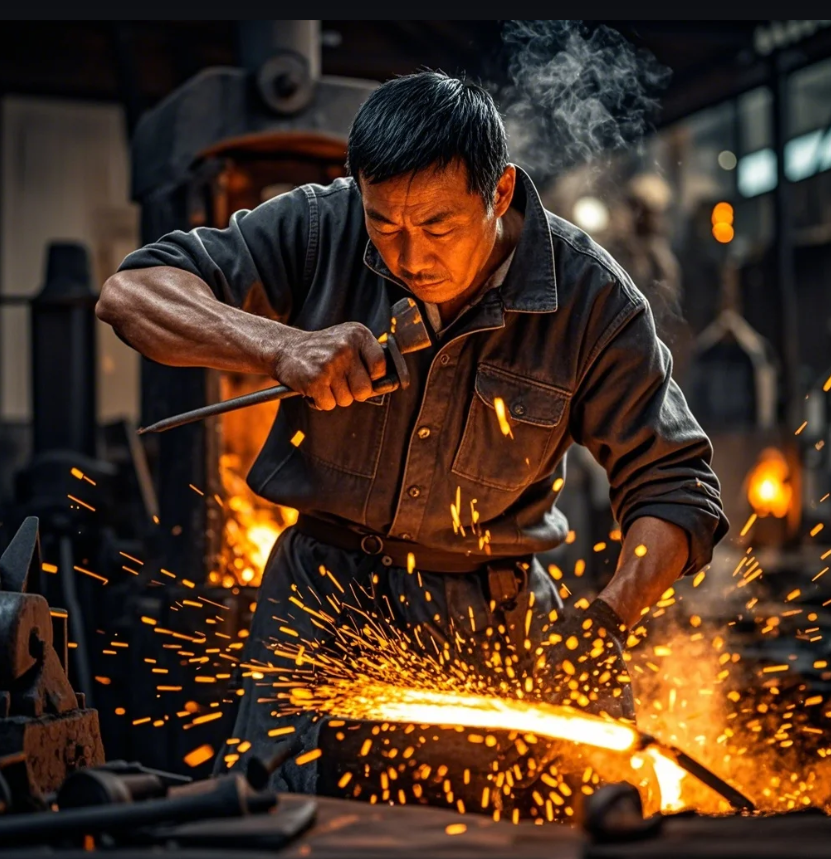

Skilled blacksmiths are in demand in both artisan and industrial markets
Today’s blacksmith might sell hand-forged knives online, teach classes, or build high-end hardware for architects. With digital marketing and e-commerce, it’s easier than ever to monetize the craft.
At Prime, we work with profitable blacksmith brands every day—supplying bulk forging blanks, OEM tool heads, and pre-assembled kits to maximize margin.
| Business Model | Income Range | Profit Boost from Prime Products |
|---|---|---|
| Knife making + retail | $50K–$120K/year | Custom blade blanks, branded packaging |
| Tool manufacturing | $40K–$90K/year | Bulk chisel/hammer heads, fast lead time |
| Teaching + demos | $30K–$70K/year | Starter kits, branding support |
| Furniture/hardware supply | $40K–$100K/year | Decorative brackets, forged fixtures |
Prime helps smiths grow from one-person shops into efficient product-based businesses, with reliable supply chains and ISO-certified materials.
How old are blacksmiths?
Buyers often wonder if blacksmithing is just for the young and strong.
Blacksmiths today range in age from teenagers in training to professionals in their 60s or older.
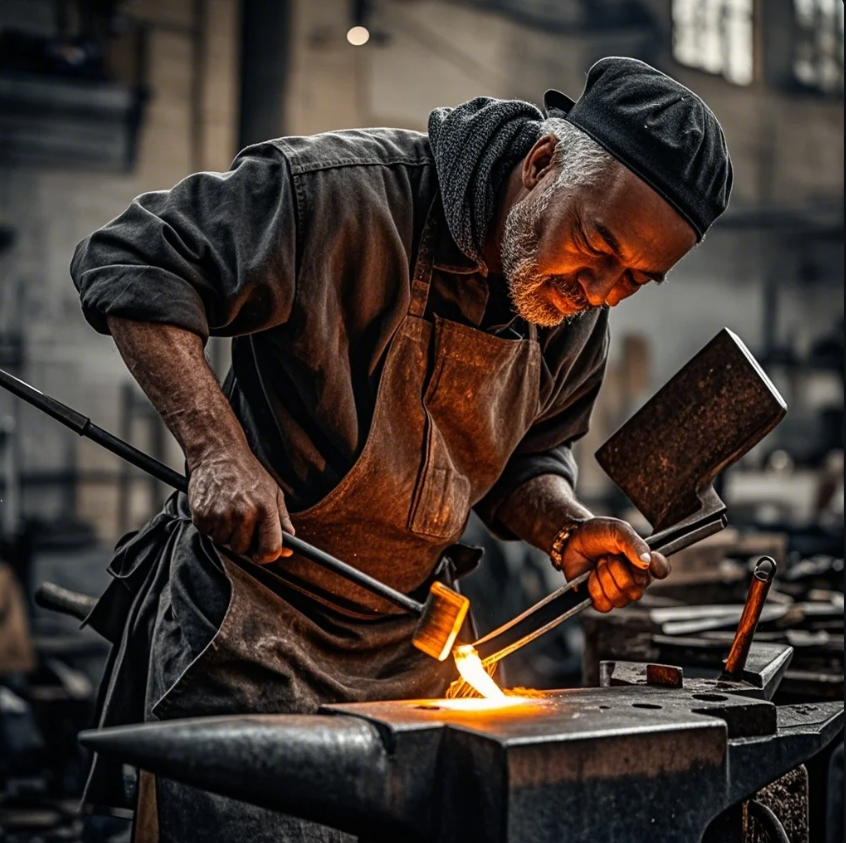

Age matters less than technique and the right tools
While blacksmithing is physically demanding, modern tools reduce stress. Power hammers, propane forges, and ergonomic anvils help older blacksmiths keep working safely. Many of Prime’s clients are in their 50s and 60s, running profitable operations full-time or part-time.
Age Breakdown of Modern Blacksmiths:
| Age Group | Typical Role | Tools Used from Prime |
|---|---|---|
| Teens–20s | Student, hobbyist, apprentice | Starter kits, S-hook blanks |
| 30s–40s | Professional blacksmith, toolmaker | Forged hammers, vises, CNC anvils |
| 50s+ | Instructor, craftsman, owner | Custom tongs, ergonomic tools |
Our factory supports small-batch runs and scaled OEM orders, helping blacksmiths at every stage continue working, earning, and creating safely.
结论
Blacksmithing today is safer, more profitable, and more sustainable than in any previous era.
At Prime, we equip blacksmiths of all ages with the tools, blanks, and forging components they need to succeed. Whether you're teaching, selling, or scaling a brand, our ISO-certified production, fast delivery, and custom tool support keep your forge running strong.
👉 Contact us today through our website to receive a free quote, blacksmith starter plan, or custom OEM solution for your workshop. Trust Prime—where tradition meets precision.
TEMPLATE_END