What Is the Metal Cage of a Car?

Every modern vehicle’s safety depends on its hidden metal skeleton – what we in manufacturing call the safety cell. At our facility, we produce the stamped components that form this crucial structure.
Snippet paragraph: The car’s metal cage, properly termed the "safety cell" or "passenger cage," consists of high-strength steel pillars, roof rails, and floor structures designed to maintain survival space during crashes while absorbing impact energy.
Let’s break down the components and engineering behind this life-saving structure.
LOOP_START
How Is a Car’s Safety Cell Constructed?
The passenger cage integrates multiple stamped and welded components in a carefully engineered layout.
Snippet paragraph: Modern safety cells use boron steel (up to 1500MPa yield strength) for A/B/C pillars combined with high-strength steel roof rails, creating a continuous load path that channels crash forces around the passenger compartment.
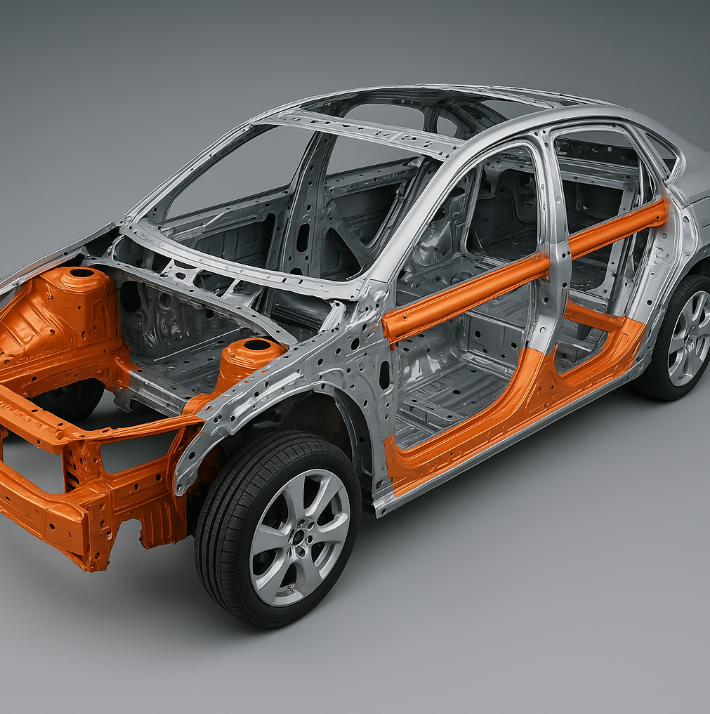

Primary Structural Elements
Vertical Components
- A-pillars (windshield supports)
- B-pillars (between doors)
- C/D-pillars (rear structure)
Horizontal Members
- Roof rail reinforcements
- Rocker panels (floor sides)
- Cross-car beams
Material Strength Distribution
| Component | Steel Grade | Thickness | Yield Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-pillar | Boron 1500 | 1.8mm | 1500MPa |
| Roof rail | DP1000 | 1.2mm | 1000MPa |
| Floor pan | DP600 | 0.9mm | 600MPa |
Manufacturing Processes
- Hot stamping for ultra-high-strength components
- Laser welding for precision joints
- Hydroforming for complex tubular sections
- Adhesive bonding between layers
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
What Materials Are Used in Safety Cells?
Automakers carefully balance strength, weight and cost when selecting cage materials.
Snippet paragraph: Today’s cages combine hot-stamped boron steel (22-35% of structure), dual-phase steels (50-60%), and aluminum alloys (in premium vehicles) – with advanced joining techniques creating crash-resistant monocoque structures.
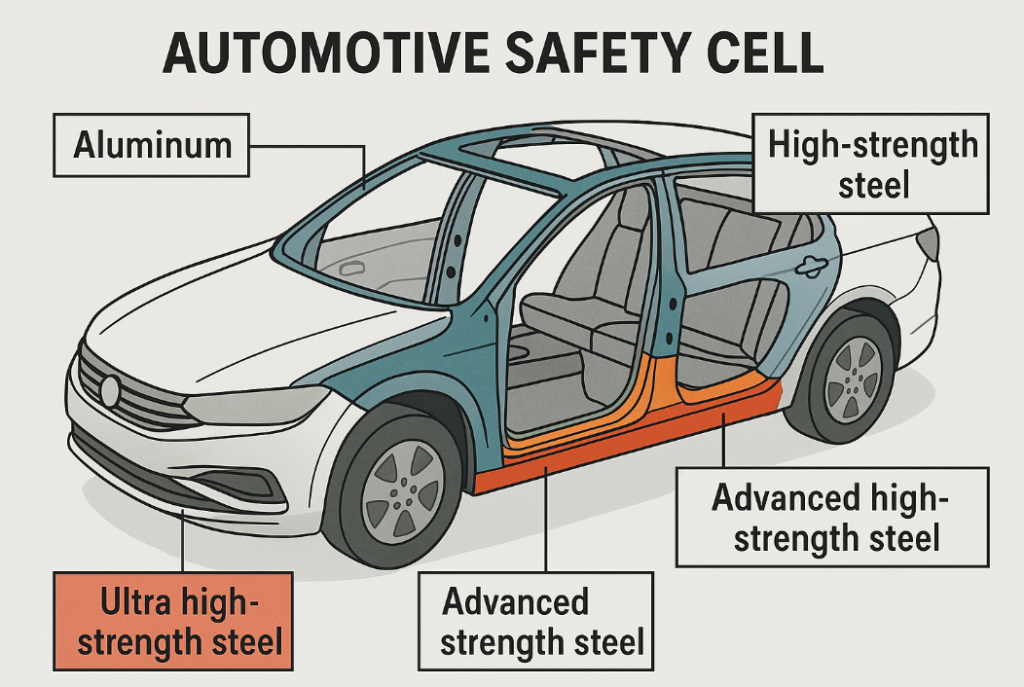
Material Composition Breakdown
Typical Mass Distribution
| Material | Usage % | Application Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Boron steel | 25% | Pillars, critical zones |
| DP600/800 | 55% | Floor, roof reinforcements |
| Aluminum | 15% | Luxury vehicle structures |
| Magnesium | 5% | Selective reinforcement |
Crash Performance Comparison
| Material | Energy Absorption | Weight Penalty | Cost Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boron | Excellent | High | $$$ |
| DP steel | Good | Moderate | $$ |
| Aluminum | Very Good | Low | $$$$ |
Emerging Technologies
- 3D-printed titanium nodes for stress points
- Carbon fiber reinforcement in hybrid structures
- Self-healing coatings for corrosion protection
LOOP_END
LOOP_START
How Do Safety Standards Influence Cage Design?
Global regulations directly shape the geometry and material selection of passenger cages.
Snippet paragraph: NCAP crash tests mandate specific deformation behaviors – requiring engineered crumple zones at front/rear while maintaining <125mm survival space intrusion in side impacts, achieved through multi-layer steel construction.

Regulatory Requirements
Key Crash Test Standards
| Standard | Test Speed | Allowable Intrusion |
|---|---|---|
| FMVSS 214 | 50km/h side | <150mm |
| Euro NCAP | 64km/h frontal | <100mm footwell |
| IIHS small overlap | 64km/h | Steering column <100mm |
Design Solutions for Compliance
| Requirement | Engineering Solution |
|---|---|
| Roof crush | High-strength roof bows |
| Side impact | Door beam reinforcements |
| Pedestrian safety | Energy-absorbing structures |
Testing Validation Methods
- Computer simulation (LS-DYNA software)
- Actual crash tests (30+ sensors)
- Sectional destructive testing
LOOP_END
Conclusion
The automotive safety cell represents decades of metallurgical and engineering advancement – a carefully balanced metal cage that saves lives while meeting stringent global safety standards.







