How to Choose the Right Plastic Material for Your Custom Parts?

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How to Choose the Right Plastic Material?
- What is the Best Plastic for Car Parts?
- How to Determine What Plastic is Used?
- What are the 7 Main Types of Plastic?
- FAQs
- Conclusion & Contact
Introduction
Are you struggling to pick the best plastic material for your project? You’re not alone. Many buyers find the plastic material selection process complicated.
Selecting the right plastic material ensures product reliability, quality, and cost efficiency. Consider use, environment, durability, and processing methods for best results. Many buyers lack clear standards, which can cause delays or increased costs.
Choosing the right plastic seems tricky. However, with clear criteria and expert support, you can save time and money. Keep reading to discover how to choose the best plastic for your custom parts with confidence.
How to Choose the Right Plastic Material?
Are you worried about product failure because of wrong material choices? I understand this concern well. Many of our clients once faced costly issues due to the wrong selection. As global manufacturing expands, engineering plastics now dominate many industrial sectors.
Start by understanding your part’s use, strength needs, and working temperature. Next, consider if the part needs chemical resistance or must meet any safety standards. You should always discuss the project with a trusted, ISO-certified plastic parts supplier.
For example, if your application requires excellent mechanical properties, look for materials like Polycarbonate or Nylon. When chemical exposure is involved, check a chemical compatibility chart to avoid costly errors.

Appearance also matters. Consider surface texture and color for brand identity. Prime supports custom logo engraving and color matching based on your requirements.
You should also ensure the chosen material can be molded within your part’s required tolerances. Plastic shrinkage can impact assembly fit, especially for high-precision injection molded parts.
Discussing these criteria with an experienced supplier helps avoid errors and get the most value. At Prime, I help clients identify the right options based on specific needs and international quality standards.
What is the Best Plastic for Car Parts?
Automotive parts need plastics that can stand up to heat, wear, and chemicals. Using the wrong plastic can cause early failure or safety problems. Today, many automotive OEMs use Nylon (PA) and Polypropylene (PP) for under-the-hood and interior components due to their unique properties.
For most car parts, Nylon (PA), Polypropylene (PP), and Polycarbonate (PC) offer the right mix of strength, durability, and temperature resistance. However, each application has different needs. Engine covers need heat resistance, while interior trims need aesthetics and stability. Always confirm with your supplier about material grades and certifications.
Many buyers also consider ABS and PC/ABS blends for dashboards and instrument panels, since they combine high impact resistance with excellent surface finish.
When evaluating plastic for car parts, look at impact test data and thermal performance charts. Regulatory compliance, such as ROHS and REACH, is also key for global export.
For lighting covers and transparent parts, polycarbonate is favored for clarity and toughness. In our experience, discussing project details and testing materials through sample trials avoids most quality issues.
Prime always provides certified material data sheets and compliance documentation for each order.
How to Determine What Plastic is Used?
Sometimes clients want to match a sample or need to know what plastic is in an existing part. This is a common pain point in sourcing, especially when reverse engineering or troubleshooting supply chain issues.
You can identify plastics by checking recycling codes, performing simple tests (like float/sink in water), or using lab analysis. Experienced suppliers can often match the plastic type based on appearance and usage context.
Basic tests include checking for a plastic recycling code on the product. For more accuracy, density testing and simple burn tests (see identification guide) can help differentiate materials, though these require care.

In industrial settings, FTIR analysis is a powerful tool for material identification, as is DSC testing for thermal properties. For reliable results, partner with ISO-certified testing labs or let your supplier handle the analysis.
Choosing the right plastic type directly impacts your cost, durability, and compliance with global import/export standards.
What are the 7 Main Types of Plastic?
Many clients ask about the common plastic types and their properties. Choosing the right one affects product life and cost. The seven primary categories help buyers simplify sourcing decisions.
The 7 main plastics are: PET, HDPE, PVC, LDPE, PP, PS, and Others (including Nylon, PC, etc.). Each has distinct strengths, weaknesses, and common uses.
For example, PET bottles offer clarity and barrier properties, while HDPE pipes are preferred for chemical resistance. PVC is well-known in building and electrical applications, and LDPE is used for bags due to its flexibility.
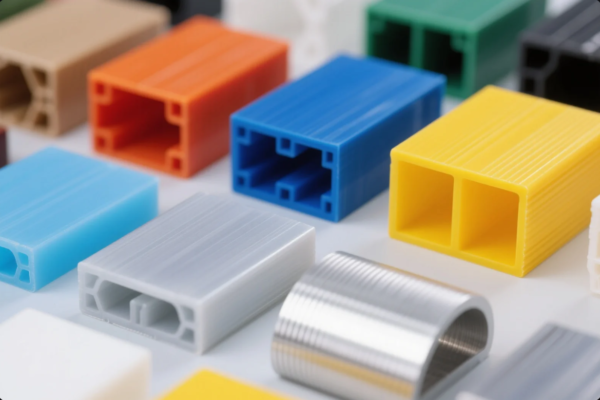

Polypropylene (PP) excels in fatigue resistance and is common in automotive and household goods. Polystyrene (PS) is often found in packaging and disposable items. The “Others” category includes specialty engineering plastics like Nylon, Polycarbonate, and POM.
It is essential to match the right type to your production process and expected lifetime.
Dive Deeper: Engineering Plastics vs Commodity Plastics
Not all plastics are equal. For critical custom parts, I always recommend engineering plastics like Nylon, Polycarbonate, or Acetal. These types offer higher strength, better heat resistance, and longer life. Commodity plastics like PP and PS are cost-effective but best for less demanding uses.
For buyers looking to balance performance and price, reviewing a plastics comparison chart is helpful. Also, many international buyers ask about recyclability and food safety standards, especially for regulated markets.
Understanding the global plastics market trends is key for staying ahead in sourcing and procurement.
Additional Images
FAQs
Q1: How do I know which plastic is food safe?
A: Look for FDA-compliant materials and check supplier certifications. Read more
Q2: Can Prime provide custom color matching?
A: Yes, we offer precise color matching and masterbatch development. Learn about custom color
Q3: How do I ensure my parts meet export standards?
A: Work with ISO-certified factories and request material data sheets and testing reports. What is ISO certification?
Q4: What file formats do you accept for part designs?
A: We accept CAD files in STEP, IGES, DWG, and more. See common CAD formats
Q5: How fast can Prime deliver samples and mass orders?
A: Standard samples ship in 7 days; mass orders depend on complexity but typically 15-25 days. Tips for fast prototyping
Q6: How to prevent packaging damage during shipping?
A: We use reinforced boxes, foam inserts, and custom trays. See packaging best practices
Q7: Do you serve small orders or only large quantities?
A: Prime specializes in B2B wholesale but supports pilot runs and sample batches. Learn about MOQ in plastics
Q8: Can I order parts with custom logos?
A: Yes, custom engraving, embossing, and pad-printing are available. About plastic branding
Q9: How do I get a quote?
A: Send us your design files, requirements, and estimated quantity by email. Contact Prime
Q10: What regions do you export to?
A: North America, Europe, Middle East, Australia, and worldwide. Global trade for plastics
Conclusion & Contact
Selecting the right plastic ensures reliable, cost-effective, and high-quality parts for your project. For custom plastic parts, work with a trusted, ISO-certified, and experienced supplier. Prime delivers consistent quality, fast turnaround, and supports flexible customizations for every order.
Ready to get started?
Contact us for a free expert consultation, tailored solutions, and a fast quote.
- Website: https://primecustomparts.com/
- Email: [email protected]
We guarantee prompt response, reliable quality, and global delivery for all your industrial needs.