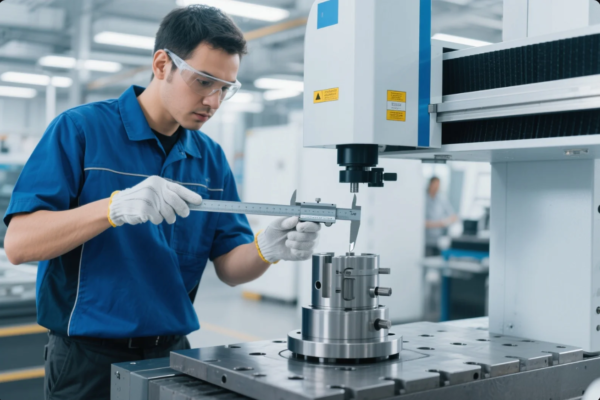
Quality Control of Metal Forging Parts: How to Ensure Accuracy and Durability?

Metal forging parts demand precision. Without proper quality control, costly failures occur. Here's how top manufacturers ensure durability.
Snippet paragraph: Quality control in metal forging involves material inspection, dimensional checks, hardness testing, and surface finish evaluation to guarantee part performance and longevity.
Want truly reliable forged components? The following methods separate quality parts from substandard ones.
Why Does Metal Forging Require Strict Quality Control?
Poor quality forging causes equipment failures. Additionally, defective parts increase maintenance costs dramatically.
Snippet paragraph: Strict quality control prevents material defects, dimensional inaccuracies, and structural weaknesses that compromise forged part functionality in critical applications.
Critical Quality Checkpoints
Manufacturers must verify multiple aspects:
| Checkpoint | Method | Acceptable Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Spectrometer analysis | Matches alloy specifications |
| Dimensional Accuracy | CMM measurement | ±0.1mm tolerance |
| Surface Integrity | Visual inspection | No cracks or folds |
| Hardness | Rockwell testing | HRC 30-35 (example range) |
Third-party certification provides unbiased validation of these tests.
What Are the Essential Quality Tests for Forged Parts?
Basic visual checks miss hidden defects. Therefore, comprehensive testing is non-negotiable.
Snippet paragraph: Essential forging tests include ultrasonic flaw detection, tensile strength measurement, impact resistance evaluation, and microstructural analysis for internal integrity assessment.

Destructive vs Non-Destructive Testing
Balancing these approaches reveals different quality aspects:
Destructive Methods
- Tensile testing until failure
- Cut-up metallurgical analysis
- Bend tests for ductility
Non-Destructive Methods
- Magnetic particle inspection
- Liquid penetrant examination
- X-ray defect detection
Each method serves specific detection purposes while maintaining different cost efficiencies.
How Does Process Control Improve Forging Quality?
Inconsistent processes create defective batches. Consequently, parameter monitoring prevents variations.
Snippet paragraph: Automated process control maintains optimal forging temperature, hammer pressure, cooling rate, and other variables that directly affect metallurgical properties and dimensional stability.

Key Controlled Parameters
Modern systems track these critical factors:
| Parameter | Monitoring Method | Optimal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Forging Temperature | Infrared pyrometers | 1100-1200°C (steel) |
| Deformation Rate | Strain gauges | 20-30% reduction |
| Cooling Speed | Thermal cameras | Gradual, controlled |
| Die Alignment | Laser measurement | <0.05mm deviation |
Automated alerts notify operators about deviations before quality suffers.
What Certifications Guarantee Forging Quality?
Self-reported quality lacks credibility. Instead, recognized certifications provide assurance.
Snippet paragraph: ISO 9001, AS9100, Nadcap, and material-specific certifications demonstrate a forger's commitment to standardized quality systems and traceable manufacturing processes.

Certification Comparison
| Standard | Coverage | Industry Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management | Global acceptance |
| AS9100 | Aerospace specific | Aviation sector |
| Nadcap | Special processes | High-value industries |
| PED | Pressure equipment | European markets |
Regular audits ensure continuous compliance rather than one-time achievements.
Conclusion
Rigorous testing, process control, and certifications ensure durable, precise forged metal components for critical applications worldwide.