What is Metal Forging?
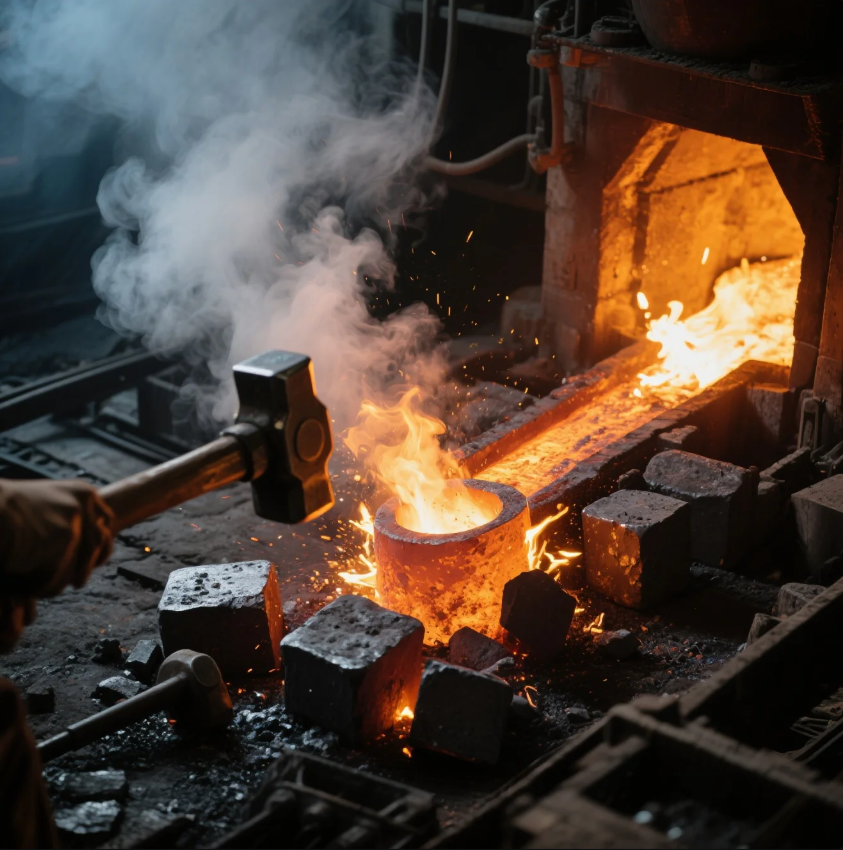

Metal forging is a process that shapes metal by applying compressive force. It's crucial in industries that require high-strength materials. Many clients struggle to choose between forging and other methods. Here’s why understanding forging matters.
Snippet paragraph: Metal forging involves shaping metal through compression, offering strength and durability for industrial parts.
Forging is used for items like automotive components, tools, and machinery. If you're unsure how it works or whether it suits your needs, keep reading.
How Does a Metal Forge Work?

Forging is a process of shaping metal using compressive force, typically applied with a hammer or press. The process starts with a heated metal blank placed between two dies. The dies then apply high pressure to mold the material into the desired shape. This results in a piece with a fine grain structure and excellent strength properties. A common method used in forging is the open-die process, which involves shaping the metal by hammering or pressing.
Key Steps in Metal Forging
- Heating: Metal is heated to a specific temperature for malleability.
- Shaping: Dies or hammers apply force to shape the metal.
- Cooling: The forged part is cooled to retain its strength.
The versatility of forging allows it to be used for producing a wide range of industrial parts, from automotive components to high-pressure valves.
What Are the 4 Types of Forging?
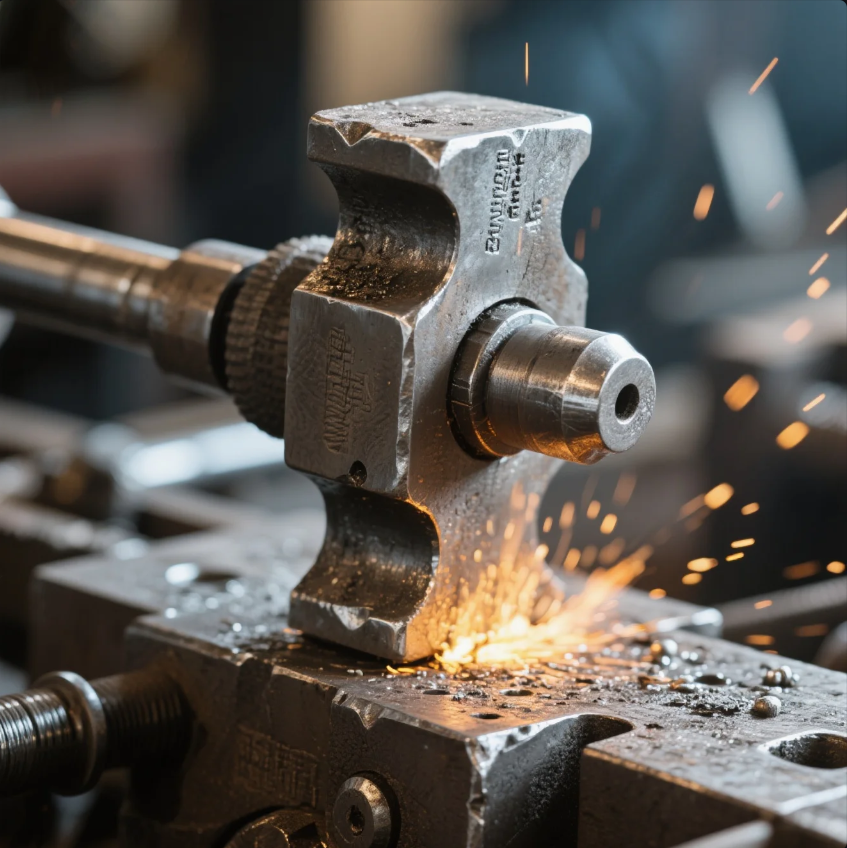

There are four main types of metal forging processes: open-die, closed-die, rotary, and die-forging. Each has its unique characteristics and is suited for different applications.
1. Open-Die Forging
In this process, the metal is deformed between flat or simple dies. It’s used for large parts that don’t need precise shapes but require strength.
2. Closed-Die Forging
Here, the metal is forced into a mold with a predefined shape. This is ideal for parts that require specific dimensions and fine details, such as gears and shafts.
3. Rotary Forging
This technique uses rotary motion to apply pressure to the metal. It’s suitable for producing parts with complex geometries.
4. Die-Forcing
This process applies high pressure to shape the metal into precise forms. It's often used for small parts that require tight tolerances.
Each type of forging has its advantages. Open-die forging is typically used for large components, while closed-die forging offers more intricate shapes. Choosing the right method depends on your product's requirements.
What Metals Cannot Be Forged?
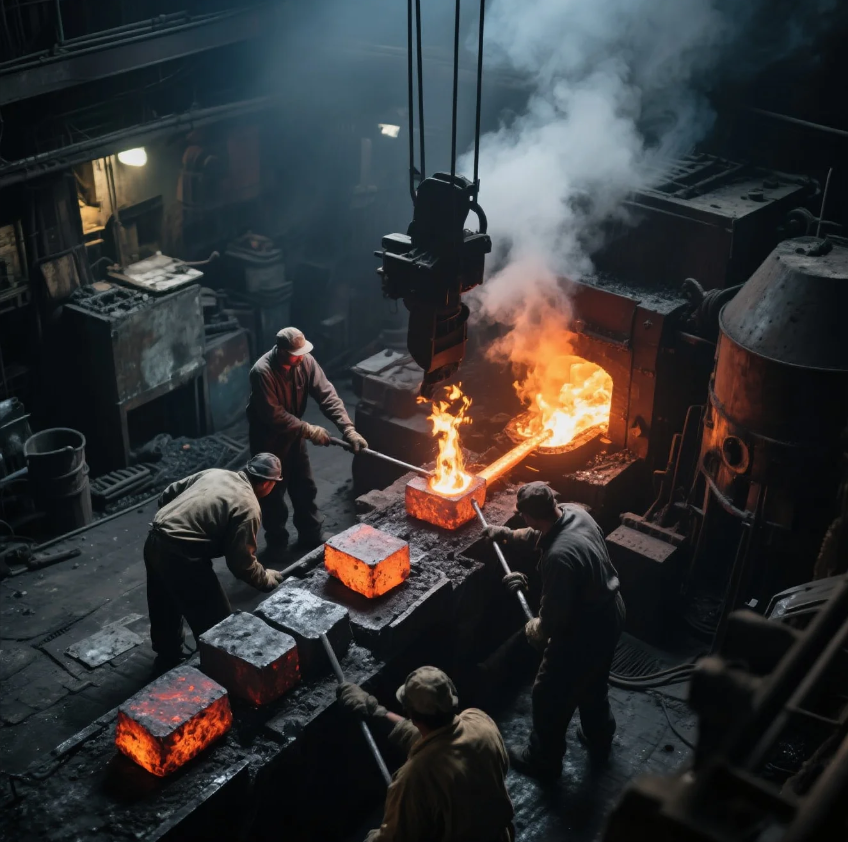

While many metals can be forged, some materials present challenges that make them unsuitable for the process. Metals that are too brittle or that have low ductility typically cannot be forged.
Metals that cannot be easily forged include:
- Cast Iron: It’s too brittle to withstand the pressures of forging.
- High-carbon steel: It can crack during the forging process due to its hardness.
- Certain aluminum alloys: These may lack the necessary ductility for forging.
Materials like titanium, though tough to forge, can be used in specialized forging processes, provided the right conditions are met. Working with a supplier like Prime ensures that you can choose the most appropriate material for your needs.
What is the Difference Between Metal Casting and Metal Forging?
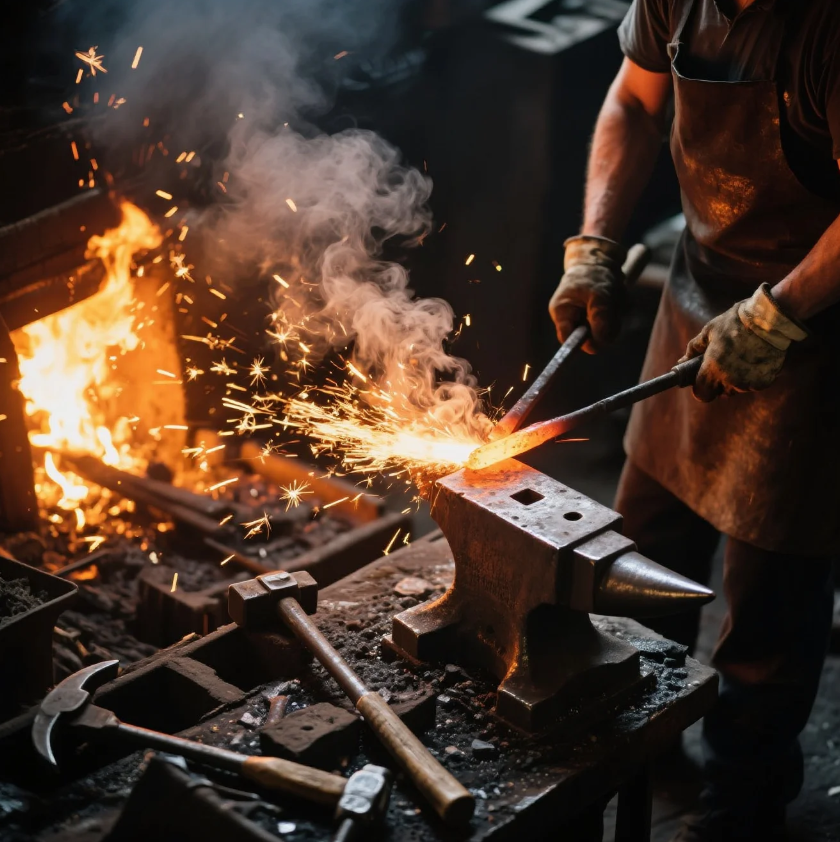

Metal casting and metal forging are both processes used to shape metal, but they differ in technique, applications, and the properties of the final products.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Metal Forging | Metal Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses compression to shape heated metal. | Uses molten metal poured into molds. |
| Material Properties | Results in stronger, denser material. | Can produce more intricate shapes but may have weaker material. |
| Precision | Offers high precision and tight tolerances. | Can vary in precision, depending on mold and casting methods. |
| Cost | Typically higher due to machinery and labor. | Lower for simple shapes but may need additional finishing. |
While forging enhances the strength and durability of parts, casting allows for more complex shapes to be formed without the need for extensive pressure. However, forged parts tend to have better mechanical properties due to the grain structure produced during the process.
Conclusion
Metal forging offers strength and durability, making it ideal for high-demand industrial applications. It’s a choice many manufacturers make to ensure that their parts are built to last. For expert advice on forging processes and products, get in touch with Prime today. Our years of experience and ISO certifications guarantee high-quality forged parts with fast delivery.