What is the Only Way to Forge Steel?
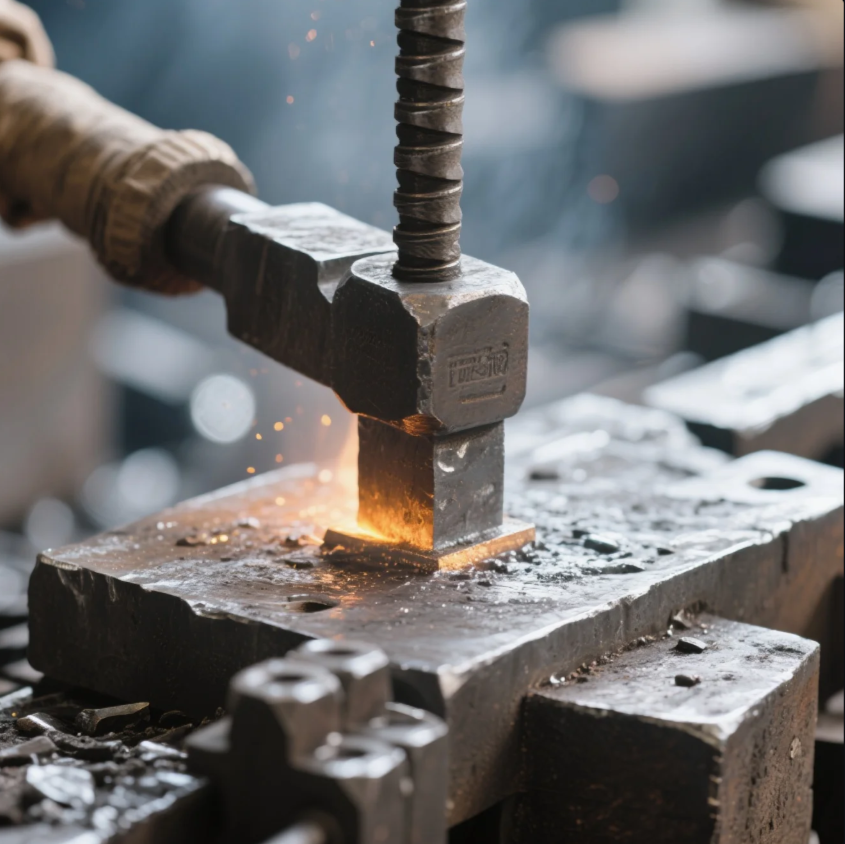

Forging steel is an essential skill in metalworking, particularly for creating strong, durable components. But what is the best method to forge steel? In this article, we’ll explore how steel is forged, including the techniques and tools used in both ancient and modern blacksmithing. Whether you're interested in historical forging methods or contemporary techniques, understanding the process is key to successful metalworking.
Snippet paragraph: Forging steel requires high heat to make it malleable, and it is usually done using a forge or furnace, with tools like hammers and anvils for shaping.
Let’s dive into how steel is forged and the techniques that have been developed over the centuries.
How Do You Forge Steel?
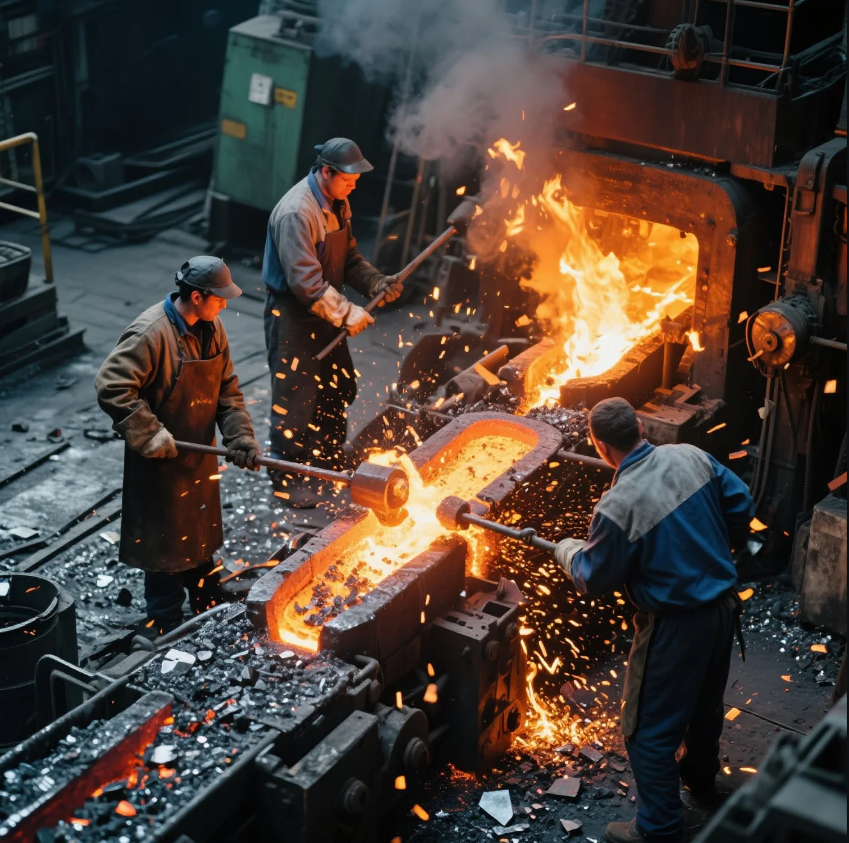

Forging steel involves heating the metal to a high temperature until it becomes malleable, then shaping it by applying force. This process can be done in a variety of ways, depending on the specific needs of the project. The most common method of forging steel involves using a forge or furnace to heat the material and then applying pressure with tools like hammers or presses.
Steps in Forging Steel:
- Heating the Steel: Steel is heated to a temperature where it becomes malleable (usually around 1,300°F to 2,200°F). This can be done in a coal forge, gas forge, or electric furnace.
- Shaping the Steel: Once the steel is hot, it is placed on an anvil or die, and a hammer or press is used to shape it into the desired form.
- Quenching and Cooling: After the steel is shaped, it is often cooled rapidly (quenched) in water or oil to harden the metal.
- Finishing: The final step includes additional processes like grinding, polishing, or heat treatment to refine the shape and properties of the steel.
Forging steel requires careful temperature control and consistent application of pressure to ensure that the material is shaped without cracking or weakening.
How Did Ancient Blacksmiths Make Steel?
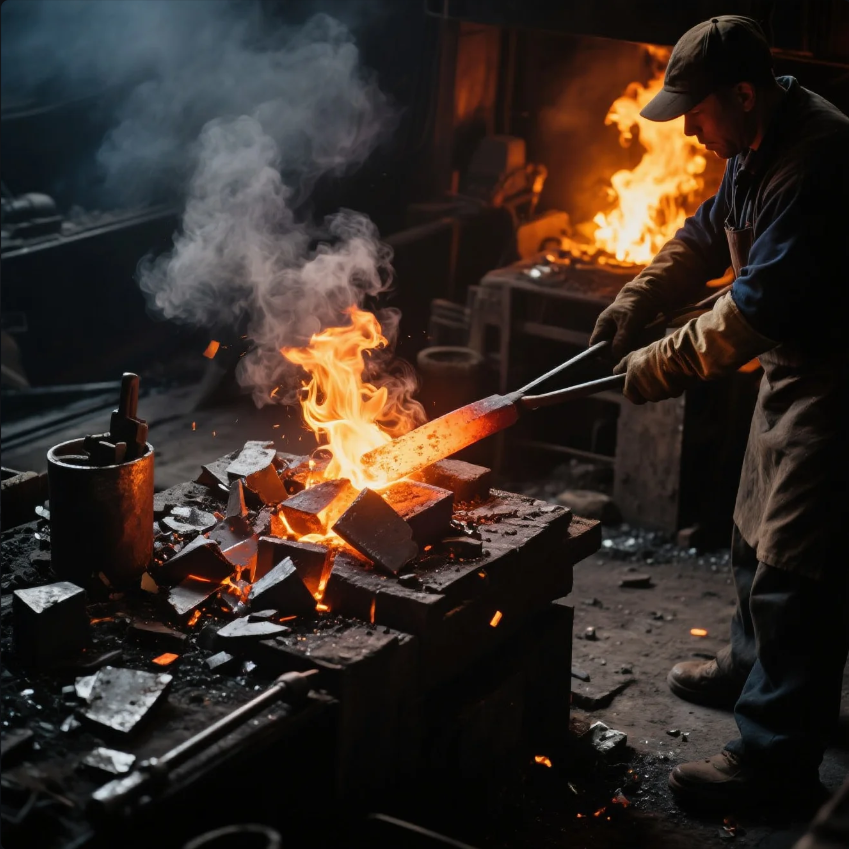

Ancient blacksmiths didn’t have modern forges or advanced machinery, but they still managed to produce steel through a process called bloomery smelting. This was the earliest form of steel production and involved heating iron ore with charcoal in a furnace.
Steps in Ancient Steelmaking:
- Heating the Iron Ore: Blacksmiths would heat iron ore in a simple furnace made from clay or stone. The heat was generated by burning charcoal, which acted as both a fuel and a reducing agent.
- Extracting the Iron: The process caused the iron ore to lose its oxygen content, leaving behind a spongy mass of iron called a "bloom."
- Forging the Bloom: The bloom was then hammered and shaped into a solid piece of iron or steel. Some of the iron was further processed into steel by heating and adding carbon, creating the first steel.
- Forging Steel: The steel was hammered to remove impurities and improve its quality, making it suitable for tools, weapons, and other useful items.
Although ancient blacksmiths didn’t have access to modern steel production techniques, their methods laid the foundation for the forging processes we use today.
Can You Forge Steel with Wood?

While wood cannot be used directly to forge steel, it can play a role in the forging process. Wood is often used as a fuel source to create the heat necessary for forging. In traditional blacksmithing, charcoal, made from wood, is often used in forges to generate high temperatures needed to make steel malleable.
Wood’s Role in Forging:
- Fuel Source: Charcoal, made from wood, is one of the most common fuel sources for blacksmithing. It burns at high temperatures, providing the heat needed for steel forging.
- Supporting Tools: Some forging tools, like hammers or certain types of anvils, might have wooden handles or bases, but wood itself is not used to directly shape the metal.
While wood is integral to the process, it is not a material that can directly forge steel. The key element in forging steel is heat, which can be generated by burning wood or using modern gas forges.
Can You Forge Steel with a Propane Torch?

Yes, you can forge steel with a propane torch, but it's more suitable for small-scale or hobbyist projects. A propane torch can heat steel to the necessary temperature to make it malleable, but it doesn’t produce the high, consistent temperatures of a full forge or furnace.
Forging Steel with a Propane Torch:
- Small Projects: Propane torches are ideal for smaller pieces or delicate work, like making knife blades or tools with precise shaping.
- Localized Heating: Since a propane torch produces a focused flame, it’s useful for heating specific areas of a workpiece rather than heating an entire piece of steel.
- Limitations: While it can heat steel for forging, a propane torch can’t provide the same high heat levels as a traditional forge, which is necessary for larger or tougher steel parts.
For serious forging projects, a larger forge or furnace would be more suitable, but a propane torch can still be effective for smaller projects or as a supplemental tool.
Conclusion
The only way to forge steel effectively is to apply significant heat and force, usually using a forge or furnace. While propane torches and other tools can aid in smaller-scale projects, they aren’t as efficient for larger, more demanding forging tasks. From ancient blacksmithing methods to modern forges, forging steel requires heat and skill. If you’re interested in forging steel at home or for a professional project, ensure you have the right equipment and a good understanding of the process. Prime can help with high-quality forged parts for any application. Contact us today for more information and a custom quote.