How Do You Harden Steel Without a Forge?

Hardened steel is essential for creating tools, knives, and other parts that need to withstand wear and tear. While traditional forging methods involve a forge, there are ways to harden steel without one. Whether you’re working at home or in a small workshop, this guide will explore how you can harden steel without needing a full forge setup.
Snippet paragraph: You can harden steel at home using methods like quenching, using a propane torch, or even an oven. These techniques offer cost-effective alternatives for steel hardening.
Let’s explore the various methods you can use to harden steel without the need for a forge.
How Do You Harden Steel at Home?
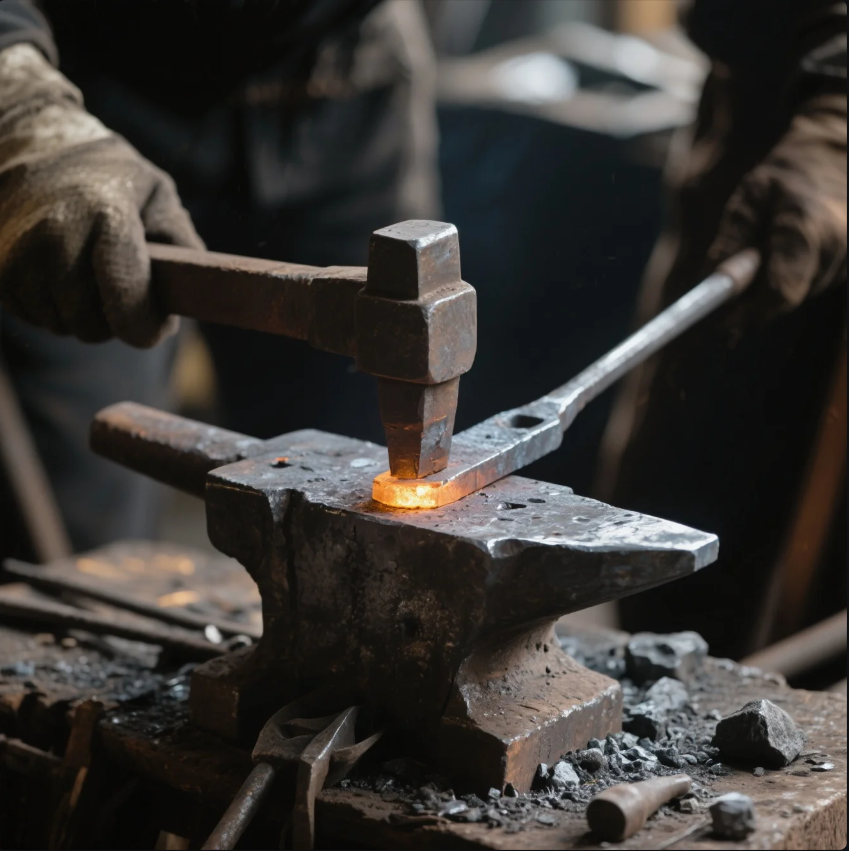

Harden steel at home by heating it to the right temperature and then cooling it rapidly (quenching). The process involves heating steel until it becomes austenitic, then quenching it in a suitable liquid. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to harden steel without a forge:
Steps to Harden Steel at Home:
- Heat the Steel: Use a heat source, such as a propane torch, an electric stove, or even a grill, to heat the steel. You need to heat the steel to between 1,300°F and 1,500°F (700°C to 815°C), depending on the type of steel you're using.
- Check Temperature: You can check if the steel is at the right temperature by the color of the steel. It should be bright red or orange. You can also use a thermometer for more precision.
- Quench the Steel: Once the steel reaches the required temperature, immediately submerge it in a quenching liquid such as water, oil, or brine.
- Cool the Steel: After quenching, the steel will cool rapidly and harden. It’s important to let the steel cool naturally after quenching to avoid cracking.
This method is ideal for small items like knives, chisels, and tools that require a hard edge. The key is to heat the metal evenly and quench it quickly to harden the surface.
What Liquid is Used to Harden Steel?

The liquid used to harden steel is known as a quenching medium, and it plays a crucial role in the hardening process. The most common liquids used for quenching steel include:
Common Quenching Liquids:
- Water: Water is the most basic quenching medium and can quickly cool steel, making it hard. However, it can lead to cracking, especially with high-carbon steels, due to the rapid cooling rate.
- Oil: Oil is a safer and more controlled quenching medium than water. It cools the steel at a slower rate, reducing the risk of cracking and warping. Vegetable oil, motor oil, or specialized quenching oils are commonly used.
- Brine (Saltwater): A mixture of salt and water (brine) cools steel even faster than water, providing a very hard surface. However, the risk of cracking is higher, and the steel should be carefully monitored.
- Polymer Solutions: These are newer, specially formulated quenching fluids that provide controlled cooling to reduce the risk of cracking and distortion.
The choice of quenching liquid depends on the desired outcome and the type of steel you're hardening. Oil is generally the most versatile and forgiving option for home hardening.
How to Harden Steel with a Propane Torch?
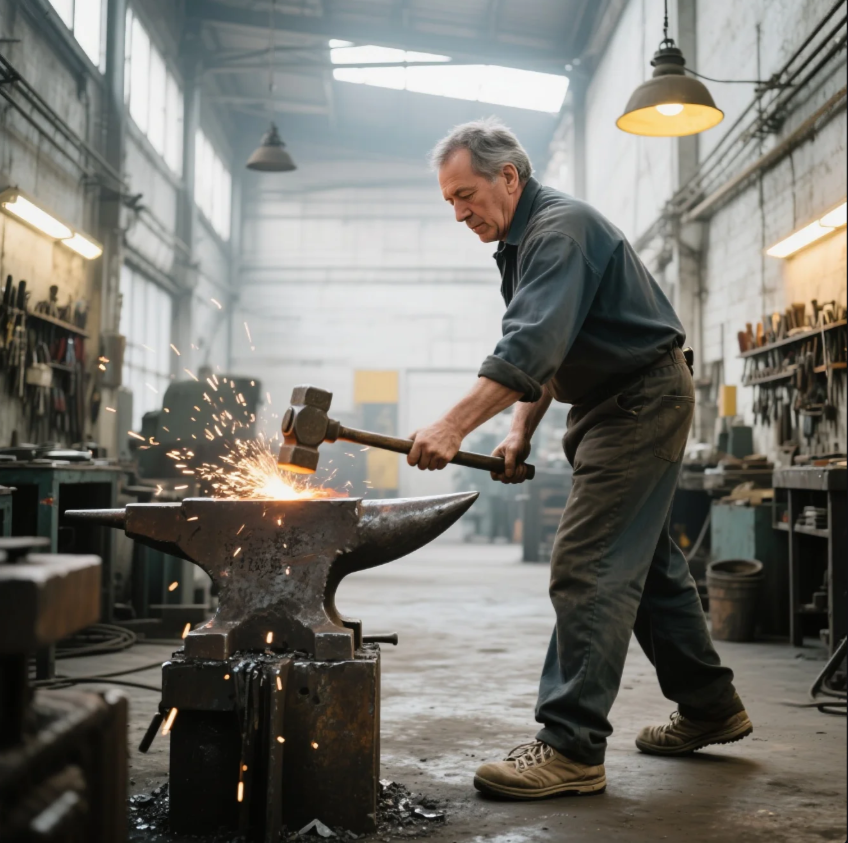

You can harden steel with a propane torch by heating a specific area of the steel and then quenching it in the appropriate liquid. This is especially useful for smaller projects like blades or tools where localized hardening is needed.
Steps to Harden Steel with a Propane Torch:
- Prepare the Steel: Place the steel on a heat-resistant surface like an anvil or metal plate. Ensure the steel is clean and free of rust or contaminants.
- Heat the Steel: Use the propane torch to heat the area of the steel you want to harden. Focus the flame on the steel and heat it evenly until it reaches a bright red or orange color.
- Quench the Steel: Once the steel is heated, quickly immerse the heated section into a quenching medium (oil, water, or brine).
- Cool the Steel: Let the steel cool in the quenching liquid, and once it’s cool, it should be hardened.
This method works best for smaller, localized areas of steel but requires precision to avoid overheating or causing damage to the material.
Can You Harden Steel in an Oven?

Yes, you can harden steel in an oven, and this method is often used for heat-treating smaller parts, like knives or tools, at home. An oven provides a consistent and controlled heat source, making it easier to maintain the correct temperature for hardening.
Steps to Harden Steel in an Oven:
- Preheat the Oven: Set your oven to the required temperature, typically between 1,300°F and 1,500°F (700°C to 815°C), depending on the type of steel.
- Place the Steel in the Oven: Put the steel on a heat-resistant surface inside the oven, ensuring it’s not in direct contact with the oven walls or racks.
- Heat the Steel: Allow the steel to heat for 15-30 minutes, depending on the size of the piece and the type of steel. The steel should reach an even, bright red or orange color.
- Quench the Steel: Once the steel is heated, remove it carefully (using heat-resistant gloves or tongs) and immediately submerge it in a quenching liquid (oil or water).
- Cool the Steel: After quenching, let the steel cool in the liquid, and then allow it to air-cool.
Using an oven for hardening is an easy and controlled way to harden steel at home, but it’s most effective for smaller items that fit in a standard oven.
Conclusion
Hardening steel without a forge is entirely possible, and you can achieve excellent results using a variety of methods. From using a propane torch to hardening steel in an oven, there are multiple ways to make steel harder for tools and small projects. The key is to properly heat the steel, choose the right quenching liquid, and ensure careful cooling to prevent cracks or damage. If you’re looking for high-quality, hardened steel parts or need expert advice on hardening techniques, reach out to Prime for guidance and custom solutions.