How Hot Does a Forge Need to Be to Melt Steel?
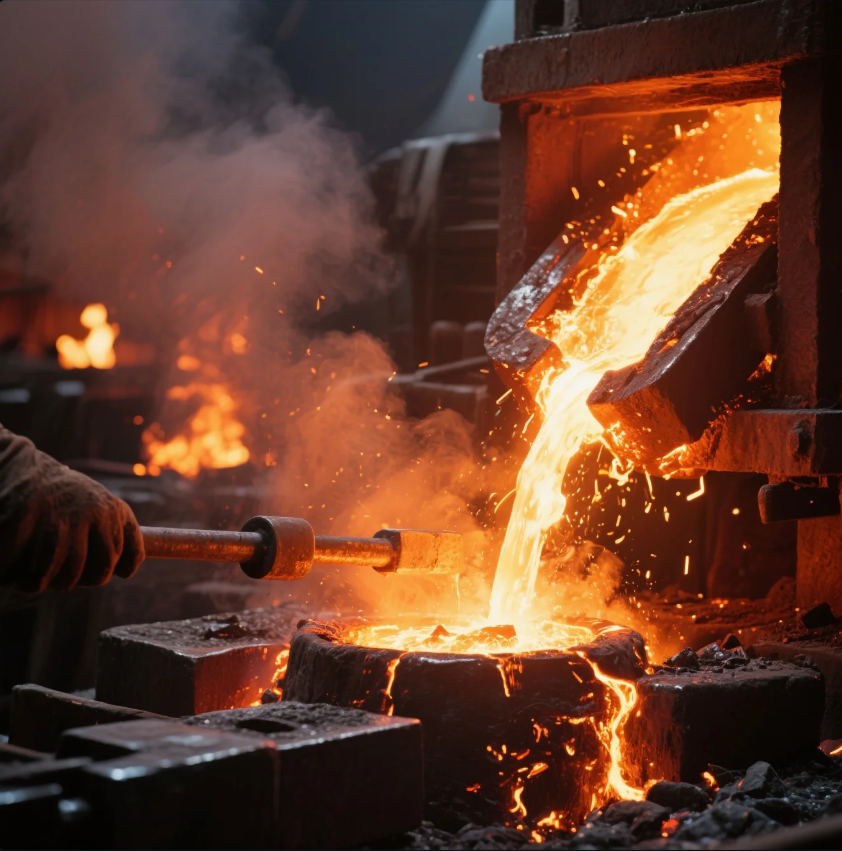

Forging steel requires high temperatures to make it malleable, but melting steel takes much more intense heat. Many people wonder what temperature is necessary for a forge to melt steel, especially if they are considering melting or working with metal at home. In this article, we’ll dive into the temperature requirements for melting steel and whether a standard forge can reach those temperatures.
Snippet paragraph: Melting steel requires temperatures above 2,500°F (1,370°C), far higher than most forges can achieve for forging.
Let’s explore how hot a forge needs to be for steel and if it’s possible to melt steel with a standard forge.
How Hot Does a Forge Need to Be for Steel?

To forge steel, a forge needs to reach temperatures of around 1,300°F to 2,200°F (700°C to 1,200°C). This is hot enough to make steel malleable for shaping, but it is not hot enough to melt steel.
Temperature Requirements for Forging Steel:
- Forging: Steel is typically heated to about 1,500°F (815°C) for forging. At this temperature, the steel becomes soft enough to shape but still retains its solid form.
- Melting: Steel, on the other hand, melts at temperatures around 2,500°F (1,370°C). This is much higher than the heat needed for forging, so standard forges used in blacksmithing won’t reach this temperature.
For blacksmithing, it’s generally unnecessary to melt the steel, as the goal is to shape it through controlled heating, rather than liquefying the material.
What Temperature Does Forged Steel Melt?
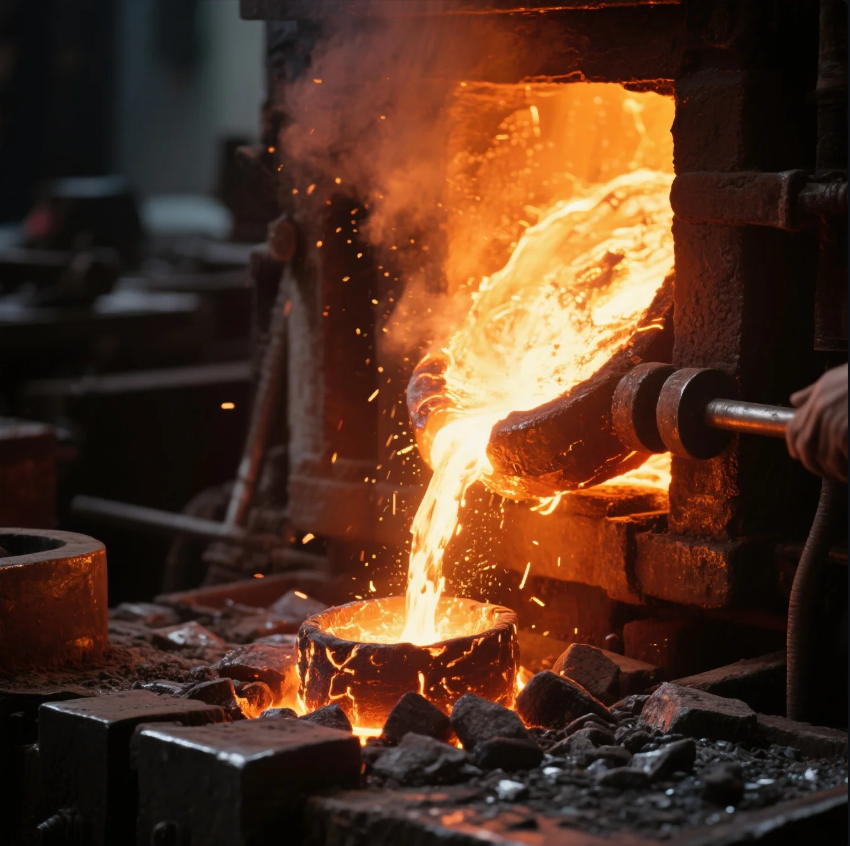

Forged steel, or steel that has been heated and shaped, melts at temperatures around 2,500°F (1,370°C). Steel is an alloy primarily made of iron, with carbon and other elements that influence its melting point. The exact temperature can vary slightly depending on the specific alloy of steel.
Melting Point of Steel:
- Mild Steel: Mild steel typically melts at about 2,500°F (1,370°C), depending on its composition.
- High-Carbon Steel: High-carbon steels may melt at slightly higher temperatures due to their increased carbon content.
A typical forge, even a high-quality propane or coal forge, operates well below this temperature, making it unsuitable for melting steel. Forges are designed to heat steel to temperatures sufficient for shaping, not for turning it into liquid.
How Much Heat Does It Take to Melt Steel?
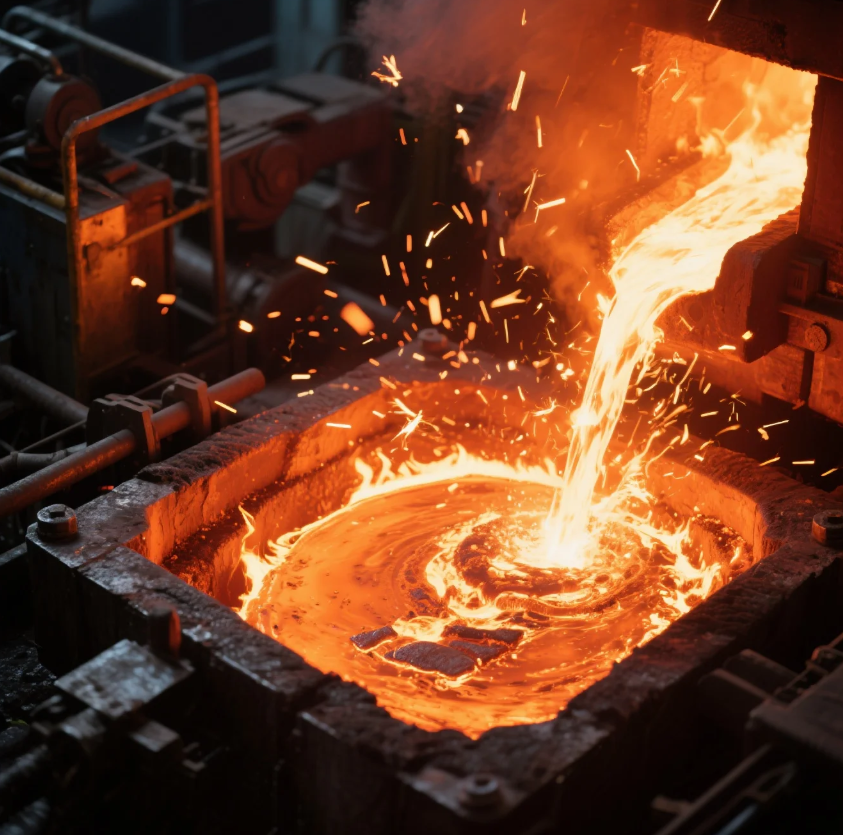

To melt steel, it requires a substantial amount of energy. As mentioned earlier, the temperature required to melt steel is around 2,500°F (1,370°C), which is significantly higher than the heating capabilities of most home forges.
Energy Required for Melting Steel:
- Temperature: Steel requires temperatures between 2,500°F and 2,800°F (1,370°C to 1,538°C) to melt fully.
- Furnaces vs. Forges: To melt steel, specialized furnaces (like induction furnaces or electric arc furnaces) are required, as they can generate the much higher temperatures necessary for this process.
While forges are excellent for heating steel to a malleable state, they are not capable of reaching the temperatures required for melting steel, as they are designed primarily for shaping rather than liquefaction.
Can You Use a Forge to Melt Metal?
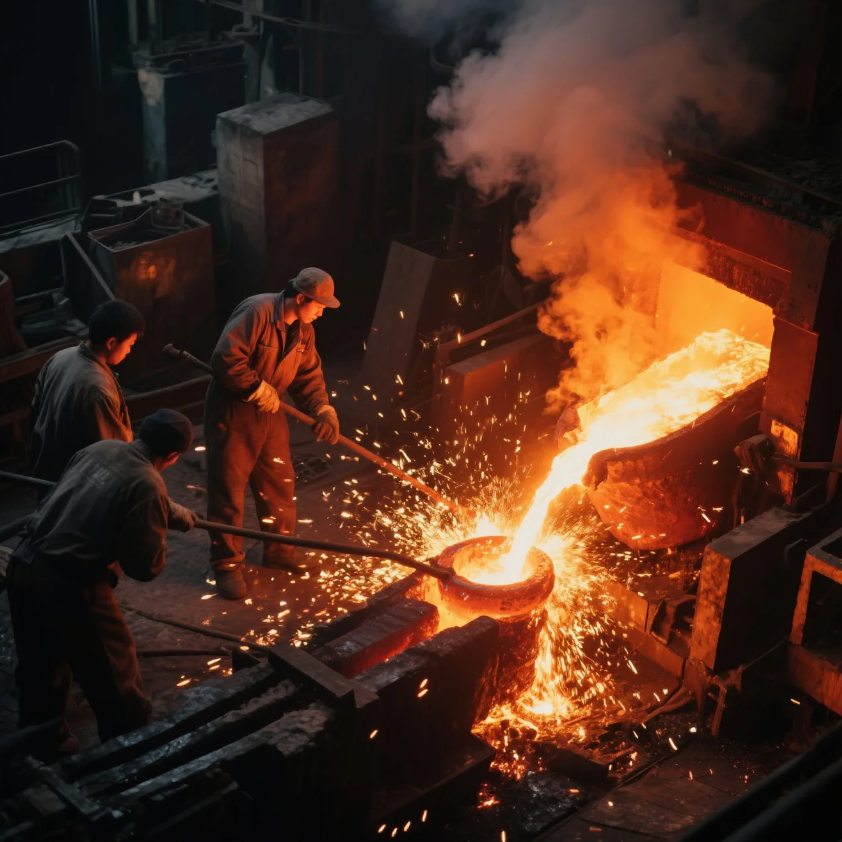

Standard forges are generally not capable of melting steel, as they don’t generate the temperatures required to bring the material to its melting point. A typical blacksmith’s forge operates at temperatures that allow the metal to become malleable but not liquid.
Types of Metal Forges:
- Coal and Charcoal Forges: These forges operate at temperatures around 2,000°F (1,093°C), which is suitable for forging but not for melting.
- Propane Forges: A propane forge can reach temperatures between 2,000°F and 2,300°F (1,093°C to 1,260°C), which is sufficient for most forging but still falls short of the melting point of steel.
- Furnaces: To melt metal, a furnace or induction heater is required, which can reach much higher temperatures (up to 3,000°F or more).
If your goal is to melt metal, you would need equipment specifically designed for that purpose, such as a foundry furnace or an induction furnace, which can achieve the necessary temperatures.
Conclusion
While a standard forge can heat steel to temperatures high enough for forging (around 1,300°F to 2,200°F), it cannot melt steel, which requires temperatures of about 2,500°F (1,370°C). If you’re looking to melt steel, a furnace or induction heater designed for metal casting is required. For most blacksmithing projects, though, a forge is more than sufficient for heating and shaping steel into the desired form. At Prime, we specialize in high-quality forged parts that are shaped and treated for durability and precision. Contact us today to learn more about our forging services.