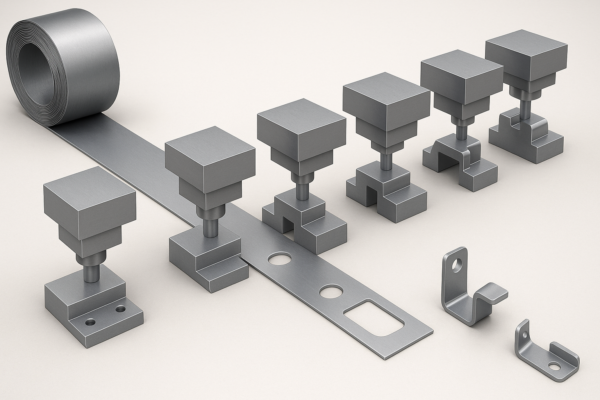
From Design to Production: How Are Metal Forged Parts Manufactured Step by Step?

Creating durable forged metal components requires a precise, multi-stage manufacturing process—from material selection to final inspection. At Prime Manufacturing, we follow strict ISO-certified procedures to ensure every forged part meets peak strength, dimensional accuracy, and reliability.
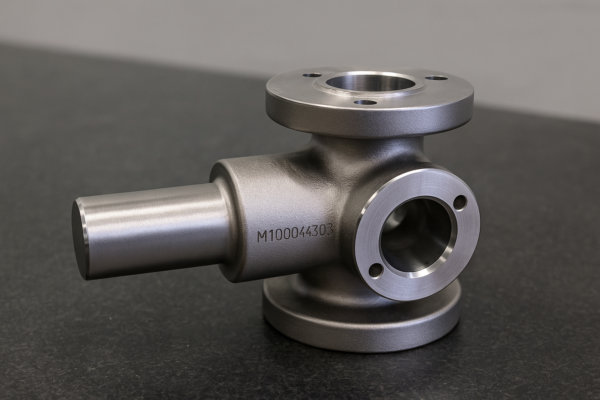
Metal forging transforms raw billets into high-performance parts through heating, shaping, heat treatment, and finishing—resulting in 30-50% stronger components than casting while minimizing material waste and defects.
Curious how your forged parts are made? Below, we break down the full production workflow, highlighting key quality control checkpoints that ensure flawless results.
1. How Does the Forging Design Process Work?
A well-engineered forging starts with design optimization.
✔ CAD Modeling (ensures exact dimensions & grain flow alignment)
✔ Finite Element Analysis (FEA) (simulates stress points before forging)
✔ Die Design (determines optimal press forces and flash reduction)
Critical Forging Design Considerations
| Factor | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Draft Angles | 3°-5° for easier die release |
| Fillets & Radii | Prevents stress concentrations |
| Parting Line | Minimizes machining needs |
| Grain Flow | Follows load direction |
Our engineers use AI-driven simulation to predict forging defects early, cutting prototyping costs by 40%.
2. What Raw Materials Are Used in Metal Forging?
Material selection defines strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
✔ Carbon Steel (cost-effective for high-strength parts)
✔ Alloy Steel (heat-treatable for extreme conditions)
✔ Stainless Steel (corrosion-resistant for harsh environments)
✔ Aluminum/Titanium (lightweight aerospace applications)
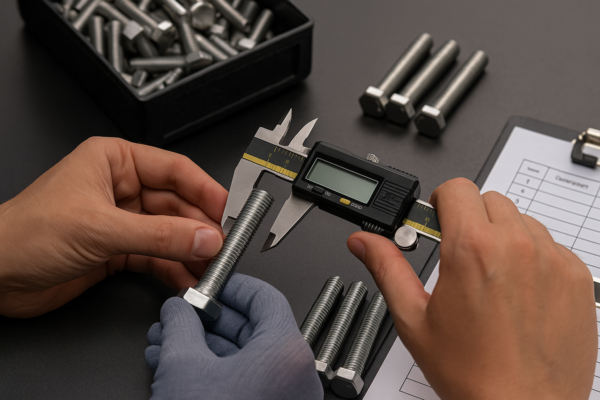
Material Testing Before Forging
- Spectroscopy (verifies alloy composition)
- Ultrasonic Inspection (checks for internal flaws)
- Hardness Testing (ensures uniform properties)
We source certified billets and conduct 100% material testing to guarantee top-tier inputs.
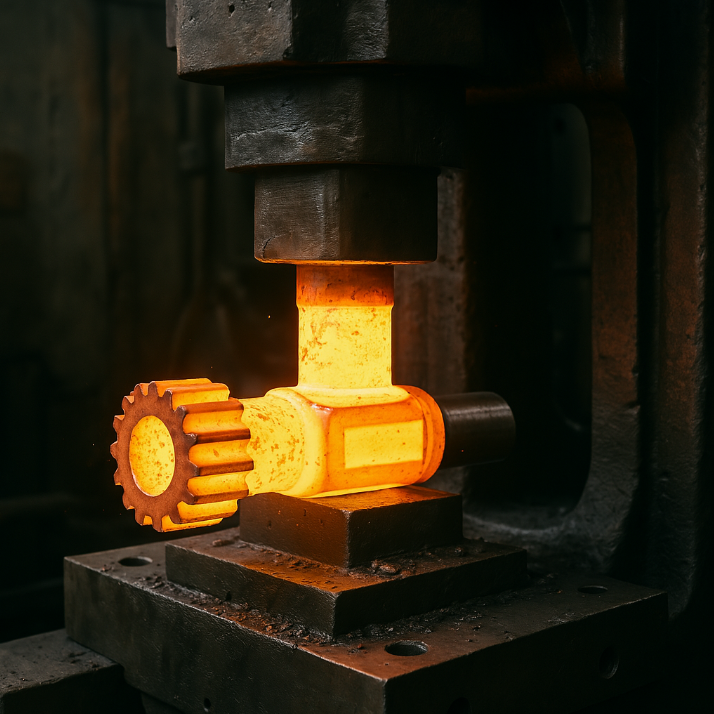
3. What Happens in the Heating & Forging Stage?
Controlled heating and compression transform raw metal into near-final shapes.
✔ Induction Heating (quick, uniform heating to 1100-1300°C)
✔ Open-Die Forging (for large, simple shapes)
✔ Closed-Die Forging (for precision complex geometries)
Closed-Die Forging Process Steps
- Billet Cutting (CNC saws for exact weights)
- Preheating (induction furnaces for uniform temp)
- Preforming (blocker die shapes rough geometry)
- Finish Forging (final die achieves tight tolerances)
- Trimming (removes excess flash)
Our 16,000-ton hydraulic presses deliver ±0.2mm tolerances, reducing post-forging machining.
4. Why Is Heat Treatment Critical After Forging?
Heat treatment fine-tunes mechanical properties for end-use conditions.
✔ Normalizing (refines grain structure)
✔ Quenching & Tempering (enhances hardness & toughness)
✔ Stress Relieving (prevents warping during machining)
Heat Treatment Parameters by Material
| Material | Process | Temperature | Cooling Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Quench & Temper | 850°C | Oil/Water |
| Alloy Steel | Austenitizing | 950-1100°C | Air/Water |
| Aluminum | Solution Treating | 480-520°C | Water Quench |
Our in-house heat treatment ensures consistent hardness (HRC 32-45) for demanding applications.
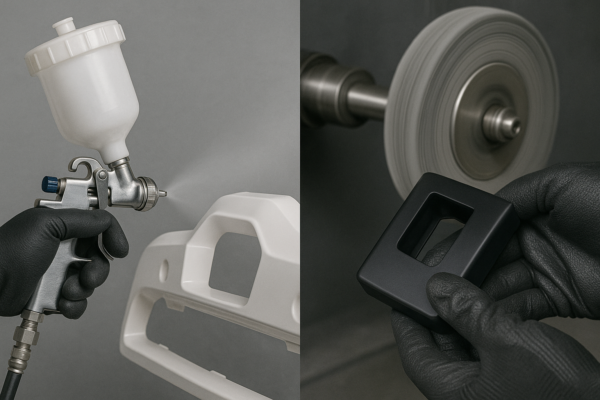
5. What Finishing & Quality Checks Are Performed?
Final processing ensures dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
✔ CNC Machining (achieves tight tolerances if needed)
✔ Shot Blasting (removes scale & improves fatigue life)
✔ Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) (checks for cracks or defects)
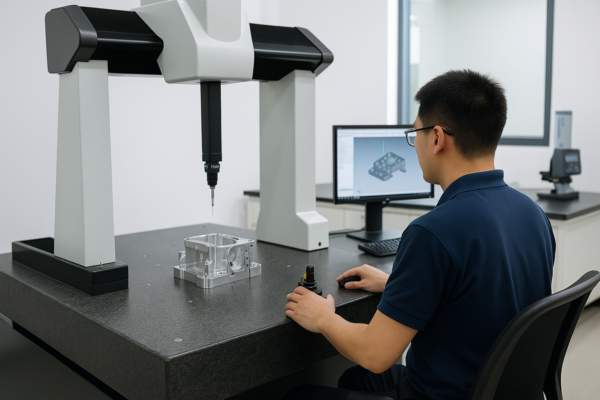
Final Inspection Checklist
- Dimensional Verification (CMM scanning)
- Ultrasonic Testing (internal flaw detection)
- Magnetic Particle Inspection (surface crack checking)
- Load Testing (validates strength under pressure)
Prime’s quality control ensures zero defect shipments, backed by full material certifications.
6. How Does Prime Optimize the Forging Supply Chain?
Efficient logistics ensure fast, reliable deliveries worldwide.
✔ Just-In-Time (JIT) Production (reduces inventory costs)
✔ Automated Packaging (prevents shipping damage)
✔ Global Export Compliance (meets EU/NA regulations)
We ship 90% of orders within 4 weeks, with real-time tracking from forging to delivery.
Conclusion
Metal forging is a science-driven process combining precise design, controlled forming, and stringent quality checks to produce ultra-durable parts. At Prime Manufacturing, our 30 years of forging expertise ensures high-performance components for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Need optimized forged solutions? Request a free DFM (Design for Manufacturing) review today!