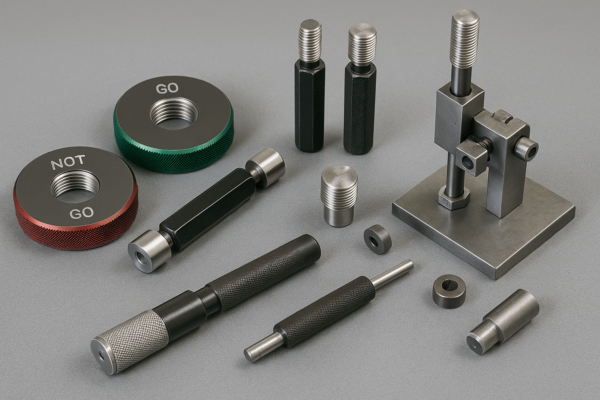
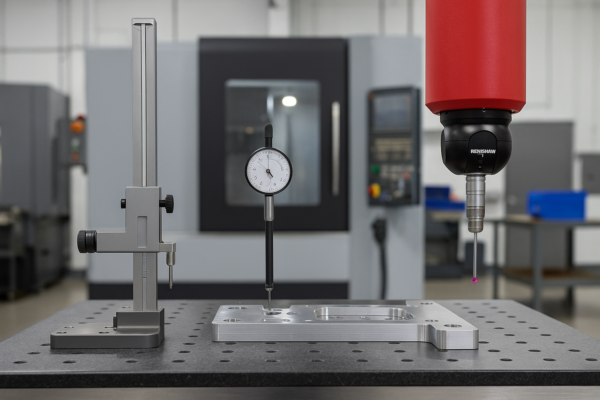
How Can I Achieve High Precision in Metal Stamping and Deep Drawing Parts?
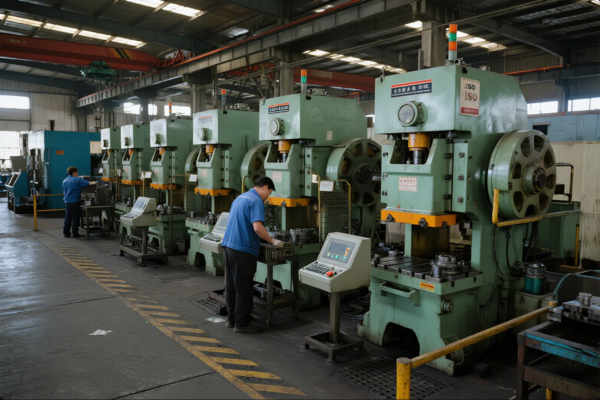

Many buyers face frustrating delays, unstable part quality, or communication issues when sourcing high-precision stamped or deep drawn metal parts. Even experienced procurement teams struggle to balance cost, quality, and speed in a global supply chain.
To achieve high precision in metal stamping and deep drawing, you need deep process understanding, strict tolerance control, informed material selection, and a manufacturing partner with proven systems and global export experience. This guide covers every essential knowledge point—from design to delivery—to help you choose, control, and succeed.
If you’re a sourcing manager, engineer, or technical buyer, read on for a complete blueprint you can apply directly to your project.
Deep Drawing vs. Progressive Die Metal Stamping: What’s the Difference?
Most industrial buyers want to know: “Which process is best for my part?” Mistakes in process selection lead to excess cost, missed tolerances, or design changes.

Deep drawing transforms flat metal into deep, seamless shapes (e.g., cups, enclosures, battery cases) using a punch and die. Progressive die stamping passes metal strip through a series of dies, cutting, bending, and shaping features with each stage—ideal for high-volume, multi-feature parts like connectors and terminals.
Explore The Fabricator’s technical guide, or Matmatch’s process overview.
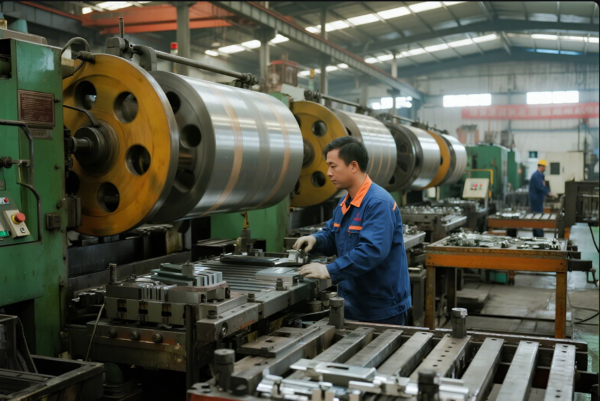

Deep Drawing vs. Progressive Stamping—Selecting the Optimal Process
To decide, review part geometry, depth-to-width ratio, annual demand, and secondary features:
| Factor | Deep Drawing | Progressive Die Stamping |
|---|---|---|
| Part Geometry | Deep, seamless, round/rectangular | Flat/complex, features at multiple stages |
| Volumes | Medium to high | High (50,000+ pcs/year) |
| Material Use | Efficient for deep shapes | More scrap, but high speed |
| Examples | Filter housings, sensor cans | Connectors, terminals, brackets |
| Tooling Complexity | Medium to high | High, but automated |
Deep drawing often reduces welds or joins, improving strength and sealing. Progressive stamping combines blanking, piercing, bending, coining, and forming, all in one high-speed press cycle.
See examples at Hudson Technologies, Wiegel Tool Works, and Siemens.
Key Steps in the Metal Stamping Process
Understanding every step gives buyers confidence to specify, troubleshoot, and control their orders.
- Blanking: Cuts the initial part outline from metal sheet.
- Piercing: Adds holes or slots for assembly or function.
- Bending/Forming: Shapes parts to the required angles or curves.
- Coining/Embossing: Stamps fine details, logos, or contacts.
- Flanging: Bends edges for reinforcement or assembly.
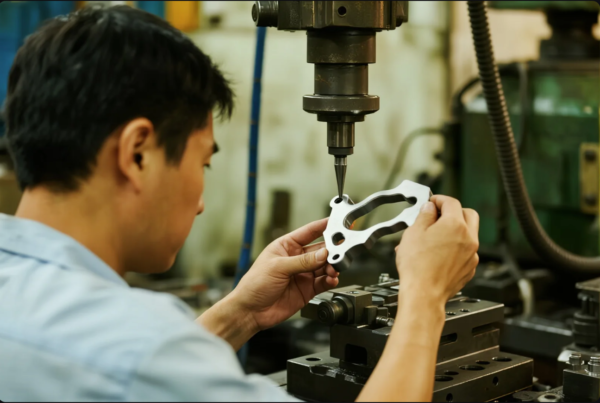

Each operation must be engineered to control stress, springback, and burr formation. Sequence and die design are critical for consistent dimensions and surface finish.
Learn more at Assembly Magazine, TWI Global, and Metal Supermarkets.
How to Choose the Best Material for Your Stamped Parts
Material choice drives cost, tool life, quality, and downstream performance. Many buyers overlook this in RFQs, causing surprises later.

Steel delivers strength and moderate cost for auto, industrial, and structural parts. Aluminum is light and corrosion-resistant, perfect for electronics, consumer goods, and aerospace. Copper provides unmatched conductivity for connectors and contacts.
See Make It From Metal’s material guide and AZoM’s database.
Choosing by Application and Compliance
- Steel (CRS, HRS, stainless): Best for safety-critical, structural, or load-bearing parts (Atlas Steels)
- Aluminum (1100, 3003, 5052, 6061, 7075): Low density, corrosion resistance, easy forming (Alcoa)
- Copper/Brass/Bronze: For all electronic, thermal, or specialty contact functions (Aurubis)
Prime supplies full batch traceability and RoHS/REACH certificates for global compliance.
Understanding Tolerances and GD\&T in Metal Stamping
Many buyers ask: “How tight can my tolerances be?” Without knowledge of real-world standards, you risk either overspending or failed assembly.
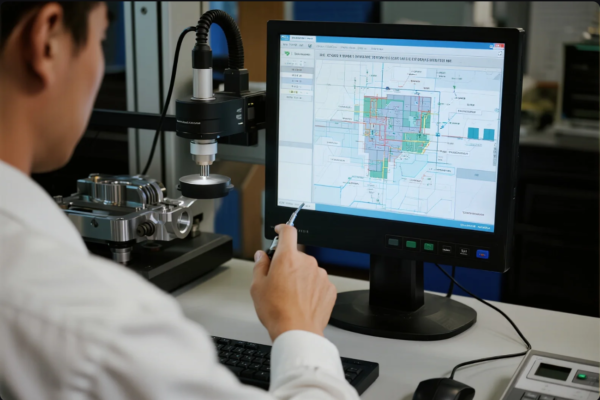

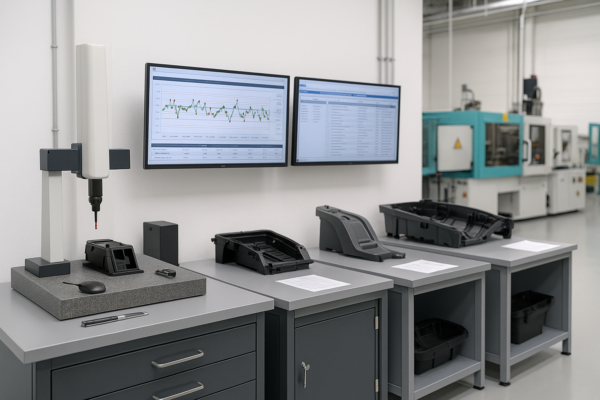
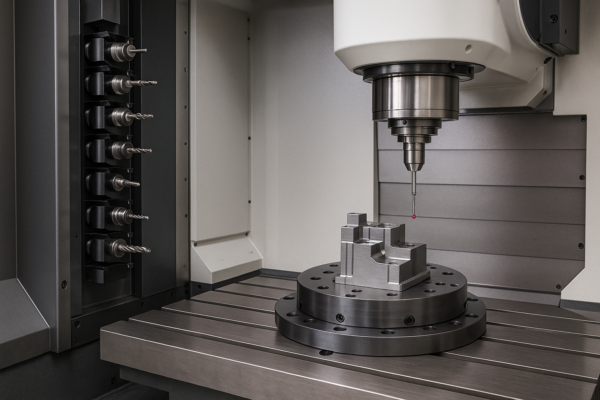
Typical stamping tolerances are ±0.1mm to ±0.05mm. Deep drawn and progressive parts can reach ±0.02mm with premium tooling and digital inspection. True position, flatness, and perpendicularity can be measured and reported using modern CMMs and vision systems.
See CNC Masters’ tolerance guide, Engineering.com on stamping QC, and Hexagon MI.
Tolerance Table Example
| Feature | Standard Tolerance | Tight Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Blanking | ±0.1mm | ±0.05mm |
| Bending Angle | ±1° | ±0.5° |
| Hole Diameter | ±0.1mm | ±0.05mm |
| Flatness | 0.2mm/100mm | 0.05mm/100mm |
Prime supplies CMM inspection, FAI, and SPC charts on request.
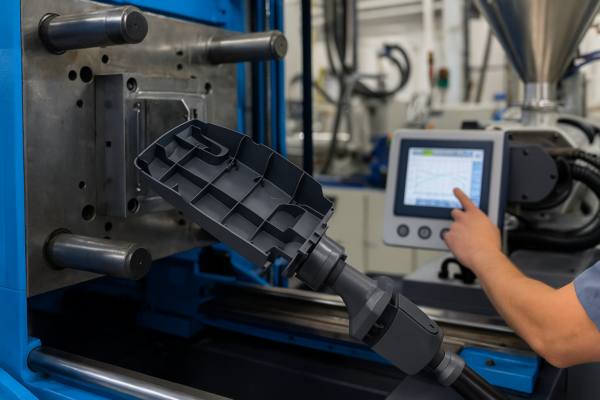
Tooling Design: Die Types, Costs & Optimization
Great parts require great tooling. Underestimating die complexity leads to hidden costs and schedule slips.

Progressive dies cost more to build but are faster for high volumes. Transfer dies and compound dies suit large, complex or low-volume parts. Tool steels (D2, SKD11, DC53, Carbide) are chosen for wear resistance. Modern dies use sensors to monitor force and detect issues in real time.
Learn about die design at Rotec Engineering, Autodesk Moldflow, and Die Science.
Cost Factors and Tips
- Tooling amortization: Higher initial cost, lower per-part cost at volume
- Quick-change tooling: Reduces downtime, improves flexibility
- Pilot runs & simulation: Prove-out before mass production (RapidMade prototyping)
- Tool maintenance: Scheduled sharpening for stability
Prime’s in-house die team reduces lead time and enables fast revisions.
Quality Control & Certification: How Leading Suppliers Ensure Stability
Quality cannot be “inspected in”—it must be built into every process step.
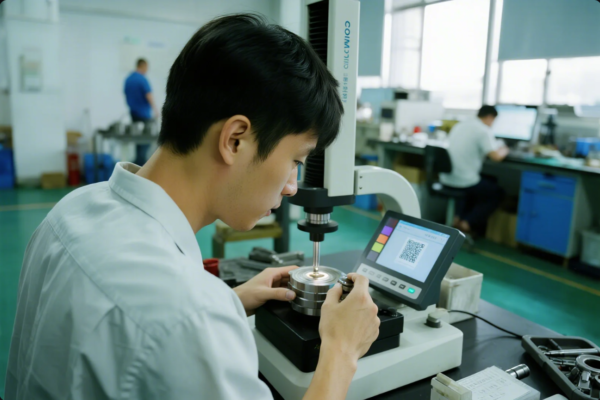

Prime is ISO 9001 certified and can provide PPAP, FAI, IMDS, RoHS/REACH, and COC documents for global automotive, aerospace, and electronics clients. In-line sensors, barcode tracking, and SPC allow us to catch errors early and guarantee compliance.
See ISO 9001 info, QIMA’s QC best practices, and Global Sources audit advice.
Inspection Systems & Documentation
- CMM and vision system inspection (Hexagon MI)
- Batch and process traceability (SGS)
- Export packaging photos for shipment verification (Export Packaging Association)
- Live video audits for remote clients
Surface Treatments, Assembly & Value-Added Operations
Adding the right finish boosts performance and customer appeal.
- Plating (Zn, Ni, Cr, Tin): Corrosion and wear protection (Finishing.com)
- Powder coating, painting: Color and electrical insulation
- Anodizing (for Al parts): Hardness and color for aluminum
- Threading, tapping, welding: Ready-for-assembly components
- Kitting and custom labeling: For direct-to-line use
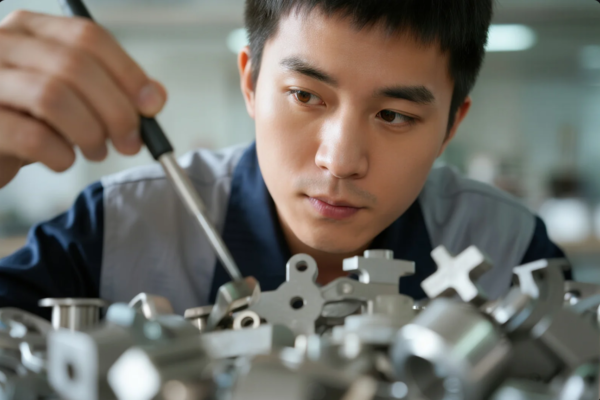

Prime manages all surface treatments in-house or through audited partners.
Packaging, Export, and Global Logistics Considerations
Exporting requires robust packaging and smart logistics.

We design packaging to prevent corrosion, abrasion, and drop damage. Moisture-barrier bags, desiccant, and VCI paper are used for sensitive items. Every carton is labeled with barcodes and shipping info for rapid customs clearance.
More on global shipping: DHL, FedEx, Maersk, and export packaging at Export Packaging Association.
Prime supports EXW, FOB, CIF, DDP and all major INCOTERMS.
Common Applications of High Precision Stamped Parts
Our stamped and deep drawn parts are used worldwide in:
- Automotive: Chassis brackets, battery housings, airbag sensors (Dana Automotive)
- Aerospace: Instrument cases, EMI/RF shields, relay covers (PCC Aerostructures)
- Electronics: USB shells, connectors, lead frames (Connex USA)
- Medical: Implant housings, surgical instrument handles (Metal Stamping for Medical)
- Home Appliances: Door brackets, timer gears (Micro Stamping Corp)
FAQs About Custom Metal Stamping Parts
Q1: What is your minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
A: From 100 to 10,000 pcs, depending on complexity and setup.
Q2: What tolerances can you achieve?
A: Typically ±0.1mm, down to ±0.02mm for critical features (CNC Masters tolerance).
Q3: Can I get prototype samples?
A: Yes, see our RapidMade prototyping process.
Q4: Do you support DFM/engineering advice?
A: Absolutely—our engineers provide design for manufacturability feedback.
Q5: Can you deliver globally?
A: Yes, with DHL, FedEx, and Maersk.
Q6: Can you supply PPAP, IMDS, FAI, and full quality documents?
A: Yes, for auto, aerospace, and medical buyers (ISO 9001 info).
Q7: Are your parts RoHS/REACH compliant?
A: Yes, all materials are checked (SGS).
Q8: Can I visit the factory or do remote audits?
A: Yes, live video audits available (Global Sources).
Conclusion & Contact
Choose Prime for high-precision stamping, deep drawing, and custom CNC machining. Get stable quality, on-time delivery, global export, and responsive support.
Website: https://primecustomparts.com/
Email: [email protected]
Contact us now for free technical review, fast quote, and a supply chain you can trust!







