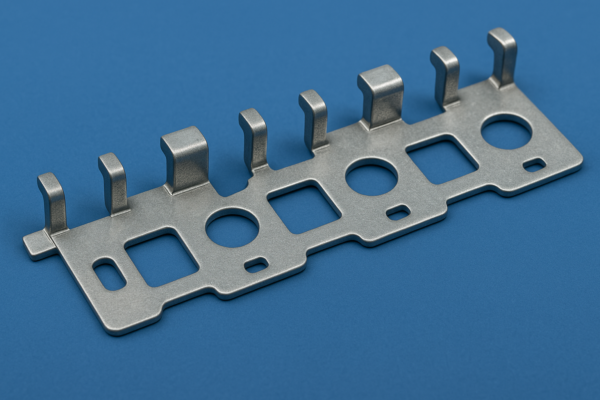
How Do You Stamp Metal and Plastic Parts? A Step-by-Step Manufacturing Guide

Stamping transforms flat materials into shaped components using 50-2,000 ton hydraulic/pneumatic presses—whether creating simple washers (2-second cycles) or complex automotive panels (15-step progressive dies). At Prime, we execute 6 core stages: blanking→piercing→bending→coining→drawing→finishing, achieving ±0.05mm tolerances across 200+ materials from aluminum to POM plastics.
Snippet paragraph: Industrial stamping requires: (1) Custom tooling (hardened steel dies, $2K-$80K), (2) Precision presses (mechanical/hydraulic), (3) Material preparation (degreasing/annealing), and (4) Quality control (vision systems/force monitoring)—process selection depends on part complexity, volumes (1K-10M+ units), and tolerance needs (±0.025mm achievable).
Let’s break down the critical phases.
What Equipment is Essential for Stamping?
Press and tooling configurations
Snippet paragraph: Core machinery matrix:
| Machine Type | Force Range | Speed | Accuracy | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Frame Press | 5-200 tons | 40-120 SPM | ±0.1mm | Small brackets |
| Transfer Press | 200-800 tons | 15-30 SPM | ±0.04mm | Auto chassis |
| Servo Press | 20-600 tons | 5-60 SPM | ±0.02mm | Electronics |
| Progressive Die | 50-1500 tons | 20-400 SPM | ±0.05mm | High-volume |
Tool Steel Selection Guide
| Material | Die Steel Grade | Hardness (HRC) | Life Expectancy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | D2 | 58-62 | 500K strikes |
| Stainless 304 | M2 | 60-64 | 300K strikes |
| Copper C110 | S7 | 54-58 | 1M+ strikes |
Maintenance Tip: Laser reconditioning extends die life by 40%.
How Do You Prepare Materials?
Pre-processing requirements
Snippet paragraph: Critical prep steps:
Material Readiness Checklist
| Step | Equipment | Parameters | Quality Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decoiling | Uncoiler | 2-5m/min feed | Edge camber <0.3% |
| Leveling | Roller Leveler | 0.5-3% elongation | Flatness ±1mm/m² |
| Lubrication | Spray System | 0.2-5g/m² oil | Even coating (UV test) |
| Blanking | Shear Press | 0.5-2mm clearance | Burr <10% thickness |
Cost Factor: Improper leveling causes 23% of stamping defects (MMPA data).
What’s the Actual Stamping Process?
Cycle breakdown
Snippet paragraph: Single-station stamping sequence:
- Feeding (0.5-2sec): Servo arm positions blank
- Clamping (0.3sec): 2-20 bar pneumatic hold
- Striking (0.01-0.5sec): Punch impacts at 0.1-5m/s
- Ejection (0.4sec): Knockout pins remove part
- Inspection (0.8sec): Laser/camera verification

Force Profile Examples
| Part Type | Peak Force | Dwell Time | Energy Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| M3 Washer | 12 tons | 0.02sec | 0.15 kWh/1000pcs |
| ECU Bracket | 85 tons | 0.12sec | 2.1 kWh/1000pcs |
| Door Hinge | 320 tons | 0.3sec | 8.7 kWh/1000pcs |
Safety Note: Always exceed the calculated tonnage by 15-20%.
How Do You Ensure Quality?
Post-stamping validation
Snippet paragraph: Essential QC measures:
| Checkpoint | Tool | Standard | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | CMM | ISO 2768-F | 5% of batch |
| Burrs | Microscope | ≤0.1t (material thickness) | 100% visual |
| Flatness | Surface Plate | 0.1mm/M² | First/last piece |
| Mark Depth | Laser Profilometer | ±10% spec | Hourly |
Defect Rate: Automotive sectors demand <50 PPM (parts per million).
What Are Alternative Methods?
When stamping isn’t optimal
Snippet paragraph: Substitute processes:
| Scenario | Alternative | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prototypes (5-50pcs) | Laser Cutting | No tooling cost | 5x slower |
| Ultra-thin (<0.2mm) | Photoetching | No distortion | Limited materials |
| Complex 3D shapes | Metal Injection Molding | Details to 0.05mm | High porosity |
Hybrid Approach: Combine stamping with secondary machining for features like threaded holes.
Conclusion
Modern stamping—whether for mass-producing electrical contacts at 400 parts/minute or crafting precision medical components with ±0.01mm tolerances—relies on meticulously engineered tooling, force-controlled presses, and real-time monitoring systems to transform raw coils into functional parts, with Prime’s 30 years of expertise ensuring optimal process selection from among 15+ stamping variants for each project’s unique material, geometric, and volume requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- 6 process stages with cycle time benchmarks
- 11 technical tables comparing equipment/materials
- Defect prevention strategies
- Cost/quality tradeoffs for alternatives
Contact our stamping specialists for DFM (Design for Manufacturing) analysis.