What Are the Applications of Plastic in Industrial Manufacturing?
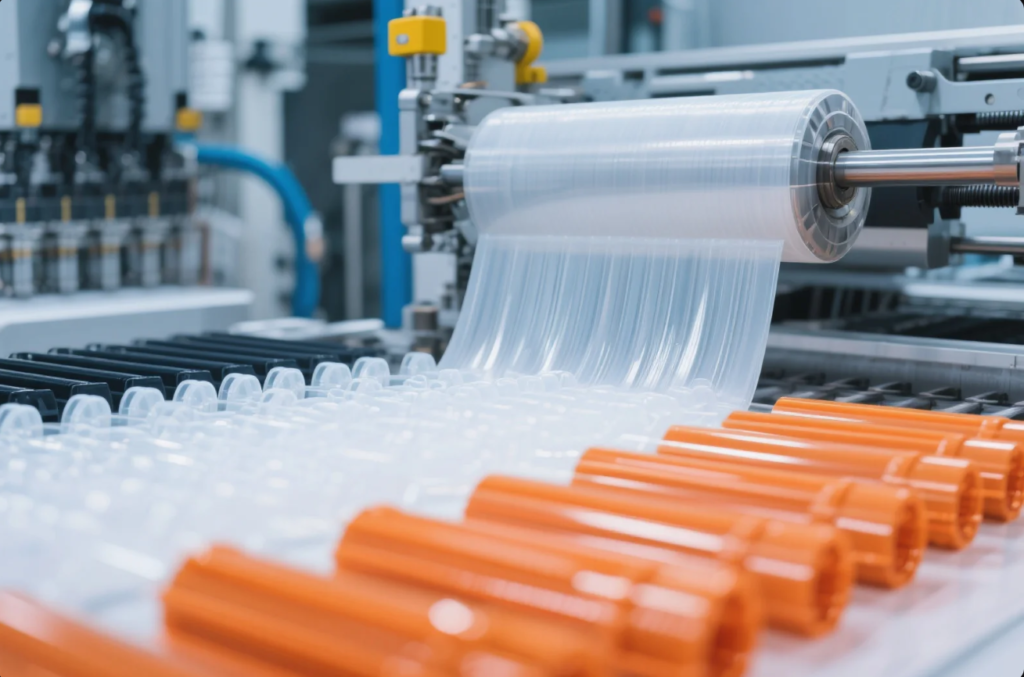

Plastic materials are integral to industrial manufacturing, offering versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness across various applications.
Plastics are used in packaging, automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer products. Each application requires specific plastic types and manufacturing processes. Understanding these helps ensure product quality and cost-efficiency.
If you\’re sourcing plastic parts, knowing the right materials and techniques is critical. Let’s break down key applications, types, and processes that matter in real-world manufacturing.
What Are the Applications of Plastics?
Manufacturers often struggle with selecting suitable plastic materials for specific functions. The wrong choice can lead to weak components, failure under stress, or customer complaints.
Plastic is used in automotive interiors, electronic housings, medical devices, consumer packaging, and industrial components. Each application requires plastic with specific durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
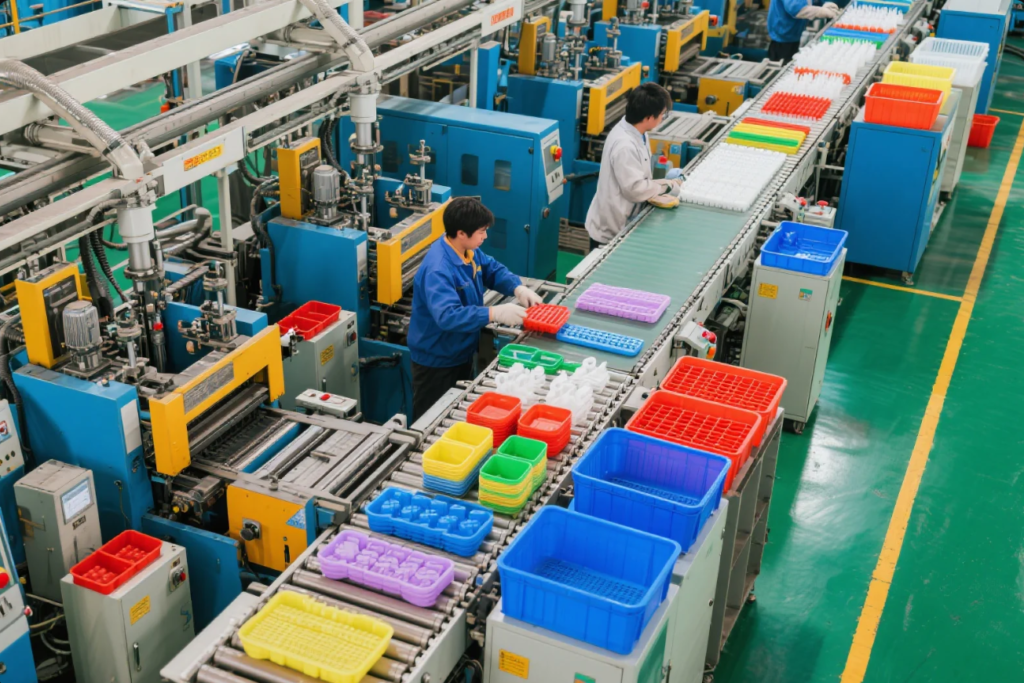

Common Industrial Applications of Plastic
Plastics play a major role in industries thanks to their low weight, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility.
Key Industrial Applications
| — | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Dashboards, bumpers | ABS, PP | |||||||
| Electronics | Casings, connectors | PC, PVC | |||||||
| Medical | Syringes, implants | PET, PE | |||||||
| Packaging | Bottles, containers | HDPE, LDPE | |||||||
| Construction | Pipes, insulation | PVC, PS | (Recycling Today, British Plastics Federation, [Contract Manufacturing | LMC Industries](https://lmcindustries.com/knowledge-center/understanding-the-process-of-plastic-parts-manufacturing/?utm_source=chatgpt.com "Understanding")) |
I once worked on a project where the customer initially chose metal enclosures for electronic devices. After switching to custom plastic parts, they reduced product weight by 60% and cut manufacturing costs significantly. Prime’s experience in providing custom plastic parts with ISO certification ensures quality and cost-efficiency across industries.
What Are the 7 Main Types of Plastic?
With so many plastic types available, it\’s hard to know which to use. Choosing incorrectly affects part performance and reliability.
The 7 main types of plastic are PET, HDPE, PVC, LDPE, PP, PS, and Others (like PC or nylon). Each has unique properties suited for different applications.
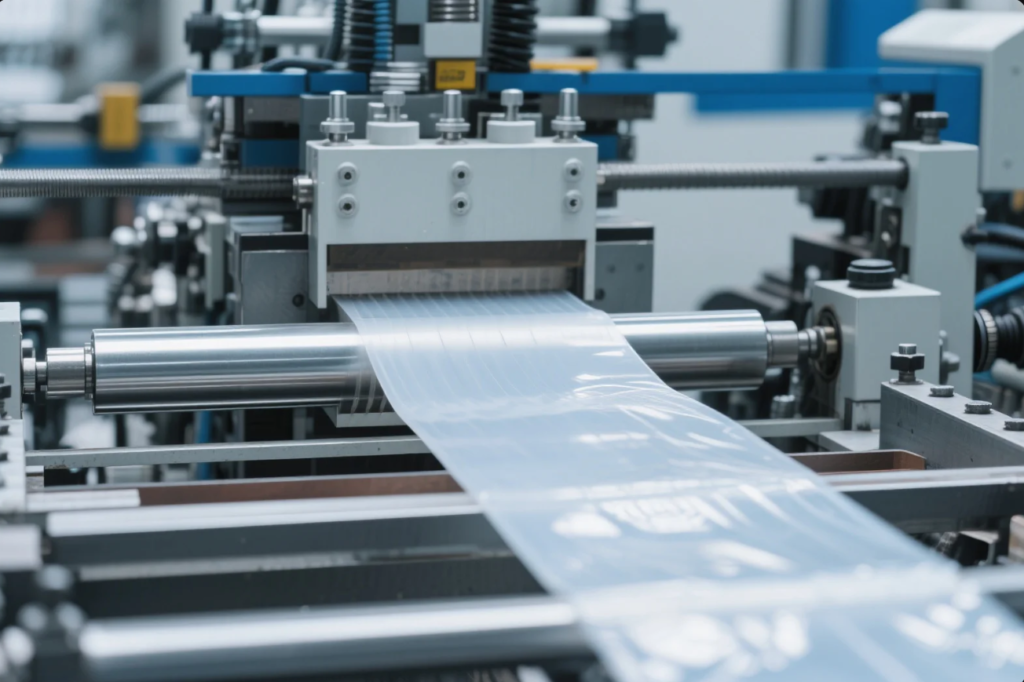

Properties of Common Plastics
Understanding different plastic types helps you match materials to functional and environmental needs.
Summary of Plastic Types
| — | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Polyethylene Terephthalate | Bottles | Clear, strong, recyclable | |||||||
| HDPE | High-Density Polyethylene | Pipes | Durable, chemical-resistant | |||||||
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride | Cable insulation | Rigid, weather-resistant | |||||||
| LDPE | Low-Density Polyethylene | Bags | Flexible, low-cost | |||||||
| PP | Polypropylene | Hinges, containers | Fatigue-resistant | |||||||
| PS | Polystyrene | Foam packaging | Lightweight, rigid | |||||||
| Others | e.g. PC, Nylon | Lenses, gears | Heat-resistant, tough | (Formlabs, California Industrial Rubber, Deskera) |
In one of Prime’s recent export orders to the Middle East, we provided custom injection molded PP parts for agricultural irrigation systems due to their high chemical resistance and durability under sun exposure.
What Is the Process of Plastic Stamping?
Many people think stamping only applies to metal. But plastic stamping is also widely used for thin, flat plastic components.
Plastic stamping uses dies and presses to cut and shape thin plastic sheets. It\’s ideal for gaskets, insulators, nameplates, and packaging inserts.
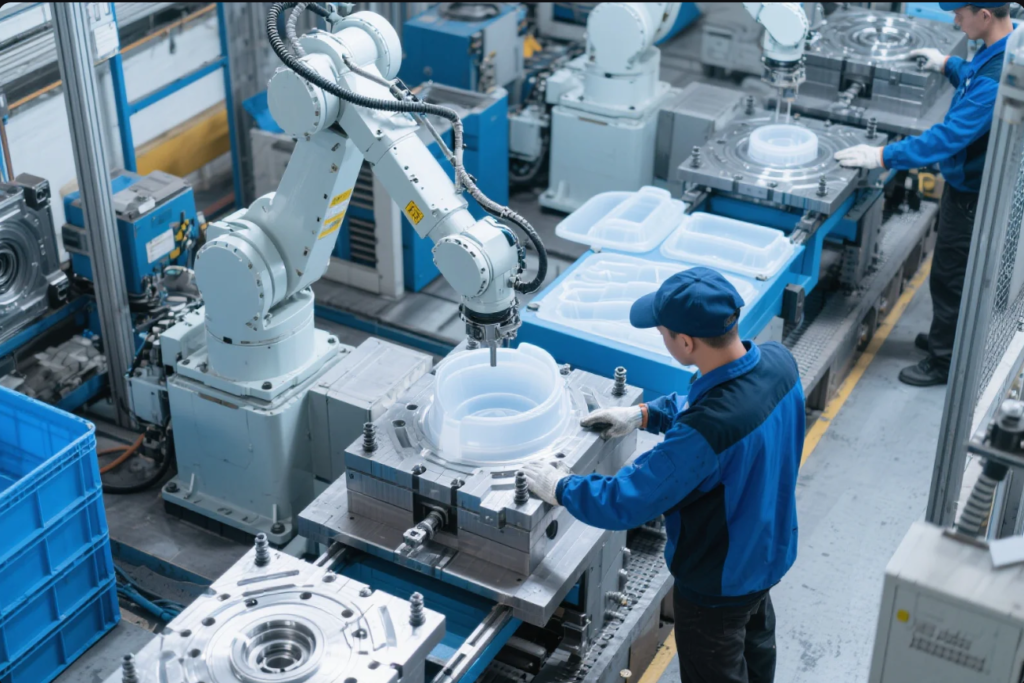

How Plastic Stamping Works
This process provides precision parts in large volumes with low tooling costs.(ideastampi.com)
Basic Steps in Plastic Stamping
- Material Selection: Choose plastic sheets based on thickness, type, and durability.
- Die Creation: Design cutting dies based on part geometry.
- Stamping: Use hydraulic or mechanical presses to shape the plastic.
- Trimming & Cleaning: Remove excess material and inspect.
- Packaging: Bundle stamped parts for shipment.
Comparison: Plastic vs Metal Stamping
| — | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastics | Metals (steel, aluminum) | ||||||
| Tooling Cost | Lower | Higher | ||||||
| Part Flexibility | Higher | Lower | ||||||
| Recyclability | High | Medium | ||||||
| Best For | Lightweight parts | Structural parts | (Plastics Europe, California Industrial Rubber) |
At Prime, we’ve refined our plastic stamping capabilities to serve electronics and packaging industries globally. Our custom die-cut plastic gaskets have been shipped to clients in Europe with less than 1% defect rate, thanks to our ISO-backed quality control.
What Are Five Uses of Plastic in Manufacturing?
Customers often underestimate plastic’s versatility. But plastic parts are crucial in everything from machinery to medical tools.
Top five uses of plastic include housing for electronics, auto interior parts, disposable medical components, custom packaging, and safety gear. Plastic meets diverse requirements like weight reduction, chemical resistance, and insulation.
Examples of Plastic Applications
Each use case shows how choosing the right plastic adds value to product design and performance.
Top 5 Plastic Uses
- Electronics: Plastic casings for laptops, TVs, switches.
- Automotive: Bumpers, dashboards, clips, trims.
- Medical: Disposable syringes, IV bags, test tubes.
- Packaging: Food containers, bottles, blister packs.
- Construction: Pipe insulation, wall plugs, spacers.
During a U.S. trade show, I met a buyer looking to switch from metal to plastic for HVAC spacers. Prime\’s custom-molded plastic solutions helped him cut part cost by 30% and meet fire-retardant standards. Our rapid prototyping and short lead times gave his team a competitive edge.
FAQs
Q: What are the environmental impacts of plastic use in manufacturing?A: While plastics offer numerous benefits in manufacturing, their environmental impact is significant due to issues like non-biodegradability and pollution. Efforts are ongoing to develop biodegradable plastics and improve recycling processes.
Q: Can plastic parts withstand high temperatures?A: Certain plastics, like polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) and polyether ether ketone (PEEK), are engineered to withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for applications like automotive engine components.
Q: How does plastic compare to metal in terms of durability?A: Plastics are generally less durable than metals in terms of strength and heat resistance. However, they offer advantages like corrosion resistance, lighter weight, and flexibility, which can be beneficial depending on the application.
Q: Are plastic components cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing?A: Yes, plastic components are often more cost-effective due to lower material and production costs, especially for high-volume production runs.
Q: What are the latest advancements in plastic manufacturing?A: Advancements include the development of biodegradable plastics, improved recycling methods, and the integration of nanotechnology to enhance material properties.
Conclusion
Plastic plays a vital role in industrial production, from auto parts to electronics. Choosing the right plastic type and supplier ensures better quality, performance, and cost control.
Shandong Prime International Trade Co., Ltd. delivers custom plastic parts with ISO-certified quality, fast lead times, and export-ready packaging. We have over 20 years of experience and 10 production lines to meet your volume needs.
Contact Prime today for expert guidance, free quotes, and tailored plastic component solutions. Email us at [email protected] or visit https://primecustomparts.com to get started.