What Are the Applications of Plastic Molding?
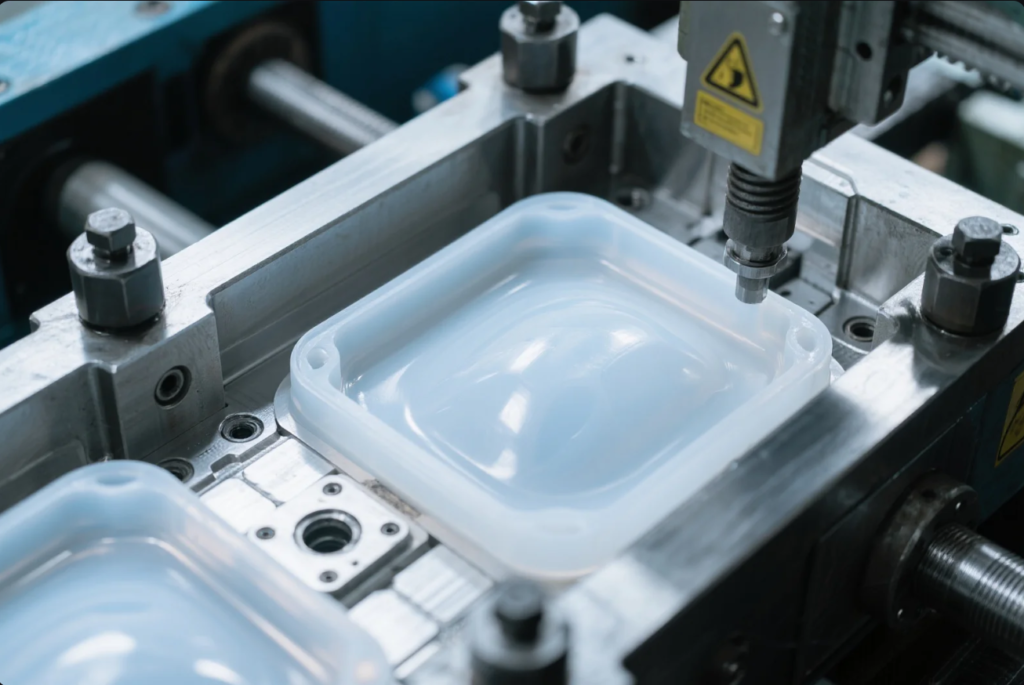

Plastic molding is the backbone of modern manufacturing—from automotive to architecture, it\’s everywhere.
Plastic molding is used to create complex plastic components for industries such as automotive, medical, electronics, construction, and consumer goods. It supports mass production with high repeatability, material efficiency, and design flexibility.
This guide explores the broad and specialized applications of plastic molding. We’ll look at how it\’s used across various sectors and why companies rely on it for cost-effective, scalable manufacturing.
What Is Plastic Moulding Used For?
Plastic molding is widely used for mass-producing functional, decorative, and structural parts in industries across the globe.
Plastic molding is used to manufacture components like housings, caps, handles, automotive panels, medical syringes, toys, containers, gears, and more. It offers durability, precision, and low unit costs.
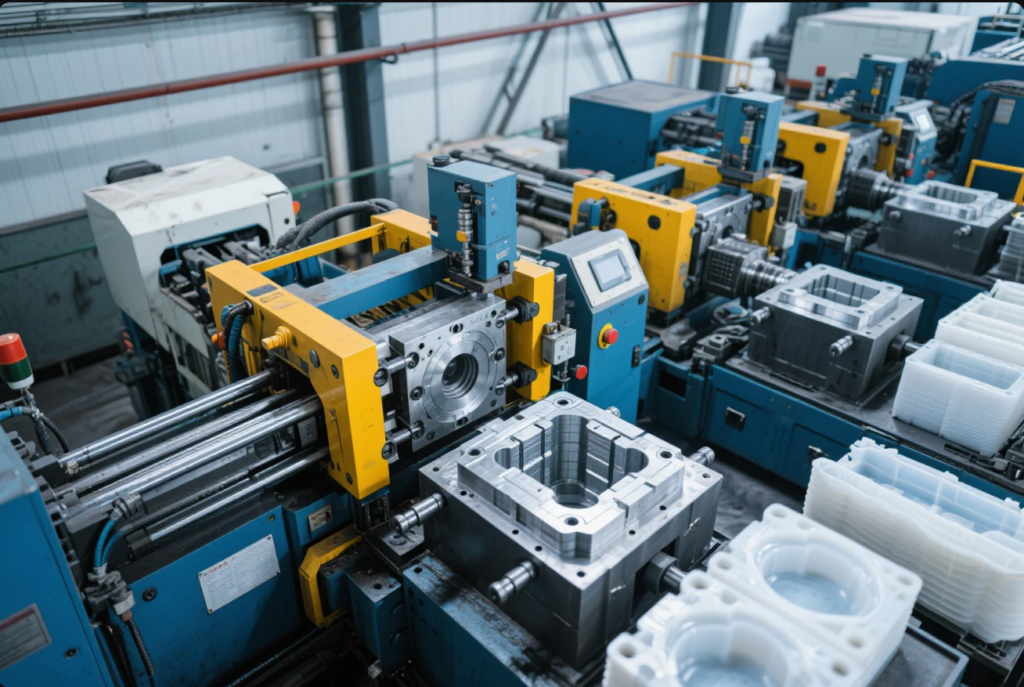

Key Industries Using Plastic Molding
| — | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Dashboards, bumpers, clips | ABS, PP, Nylon | ||||
| Medical | Syringes, test tubes, containers | PE, PET, PC | ||||
| Electronics | Phone cases, connectors, keyboards | PC, PVC, ABS | ||||
| Consumer Goods | Toys, packaging, bottle caps | HDPE, LDPE, PS | ||||
| Industrial | Machine guards, containers, gears | Nylon, PA, POM |
I worked with a client who sourced injection molded housings for their electronics from Prime. We helped reduce their cost per part by 40% while improving cosmetic appearance using custom molds and ISO-certified processes.
What Are the Applications of Moulding?
Molding isn’t just one process. It includes a family of techniques such as injection molding, blow molding, compression molding, and rotational molding.
Applications of molding include producing hollow bottles (blow molding), solid parts (injection molding), rubber seals (compression molding), and large containers (rotational molding).
Overview of Molding Techniques and Their Uses
| — | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | Mobile phone cases | High-precision, small parts | ||||
| Blow Molding | Water bottles, tanks | Hollow containers | ||||
| Compression Molding | Electrical insulators | Thermoset plastics, rubber components | ||||
| Rotational Molding | Storage bins, kayaks | Large hollow parts | ||||
| Extrusion Molding | Pipes, tubing | Continuous profiles |
Each of these molding types suits different product needs. Prime specializes in injection molding for precision plastic parts, and blow molding for custom hollow products used in both packaging and automotive fuel systems.
What Are the Applications of Plastic?
Plastic is everywhere in industrial and consumer sectors due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and moldability.
Applications of plastic include automotive interior parts, consumer electronics, healthcare disposables, food packaging, and mechanical parts. Plastic replaces metal, wood, and glass in many cases.
Top 5 Functional Applications of Plastic
- Automotive: Instrument panels, fuel tanks, headlight covers
- Electronics: Laptops, phones, cable insulation
- Medical: IV bags, syringes, diagnostic tools
- Packaging: Bottles, wraps, pouches
- Construction: Pipes, wall panels, insulation
During a recent export project to Europe, Prime supplied flame-retardant molded ABS panels for telecom cabinets. These plastic parts not only reduced total product weight by 35% but also passed V0 fire safety ratings.
What Are the Applications of Plastic in Architecture?
Architects and builders increasingly use plastics for performance and sustainability.
Plastic in architecture is used for roofing sheets, facade panels, window frames, piping, insulation, skylights, and floorings. It enhances energy efficiency and design versatility.
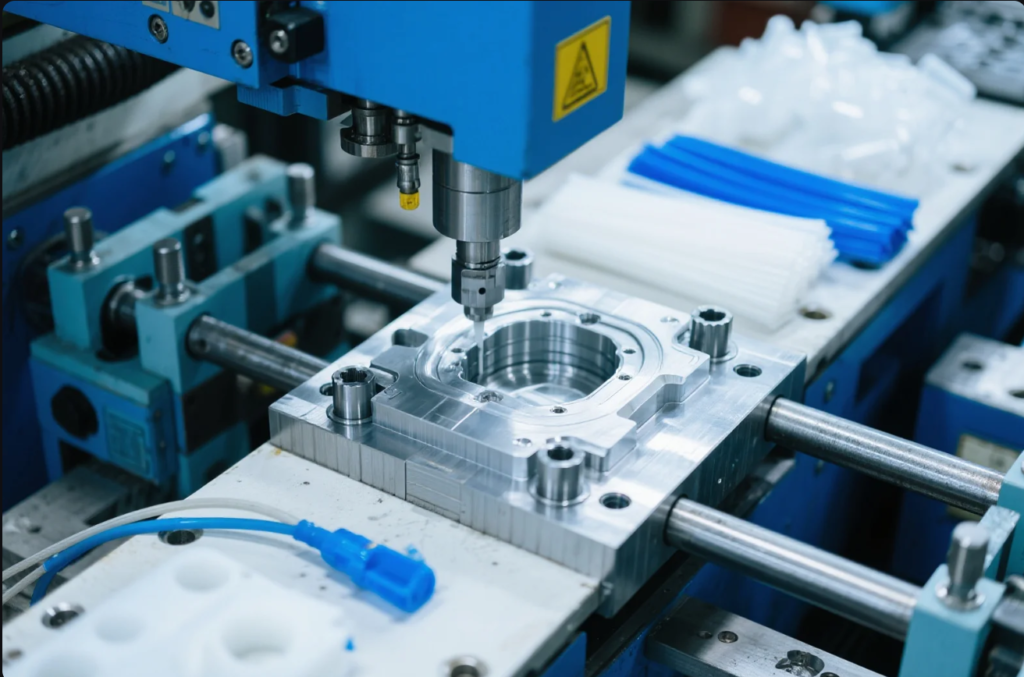

Why Plastics Matter in Building Design
| — | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roofing | Corrugated plastic sheets | Lightweight, weather-resistant | ||||
| Windows & Doors | UPVC frames | Thermal insulation, low-cost | ||||
| Facades | Polycarbonate or acrylic panels | Light transmission, aesthetics | ||||
| Plumbing | PVC, CPVC, and PEX piping systems | Corrosion resistance, easy install | ||||
| Insulation | EPS and XPS foam boards | Thermal performance |
In a recent construction project in the UAE, we provided polycarbonate molded panels for architectural canopies. The transparent finish reduced lighting costs and the material maintained structural integrity under intense desert sun.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between plastic molding and plastic extrusion?A: Molding shapes plastic inside a cavity; extrusion pushes melted plastic through a die to form continuous shapes like pipes.
Q: Which plastic molding method is the most common?A: Injection molding is the most widely used due to its precision, repeatability, and material efficiency.
Q: Are molded plastic parts recyclable?A: Yes, most thermoplastics used in molding—like HDPE, PP, and PET—can be recycled if sorted and processed properly.
Q: What is the lifespan of plastic in construction?A: Plastic pipes and panels in architecture can last over 50 years with proper installation and UV protection.
Q: How can I reduce tooling costs for plastic molding?A: Choose standardized mold bases, limit part complexity, and partner with experienced suppliers like Prime to optimize mold design.
Conclusion
Plastic molding powers modern manufacturing—from precise phone cases to durable construction panels. It delivers cost-effective, scalable, and high-quality parts across nearly every industry.
Shandong Prime International Trade Co., Ltd. offers end-to-end plastic molding services with custom tooling, fast turnaround, and ISO-certified quality. With over 20 years of experience and 10 production lines, Prime delivers molded plastic solutions that meet global standards.
📩 Contact us now at [email protected]🌐 Visit https://primecustomparts.com for free quotes, expert consultation, and tailored product solutions.







