What is Cold Forging vs Hot Forging?
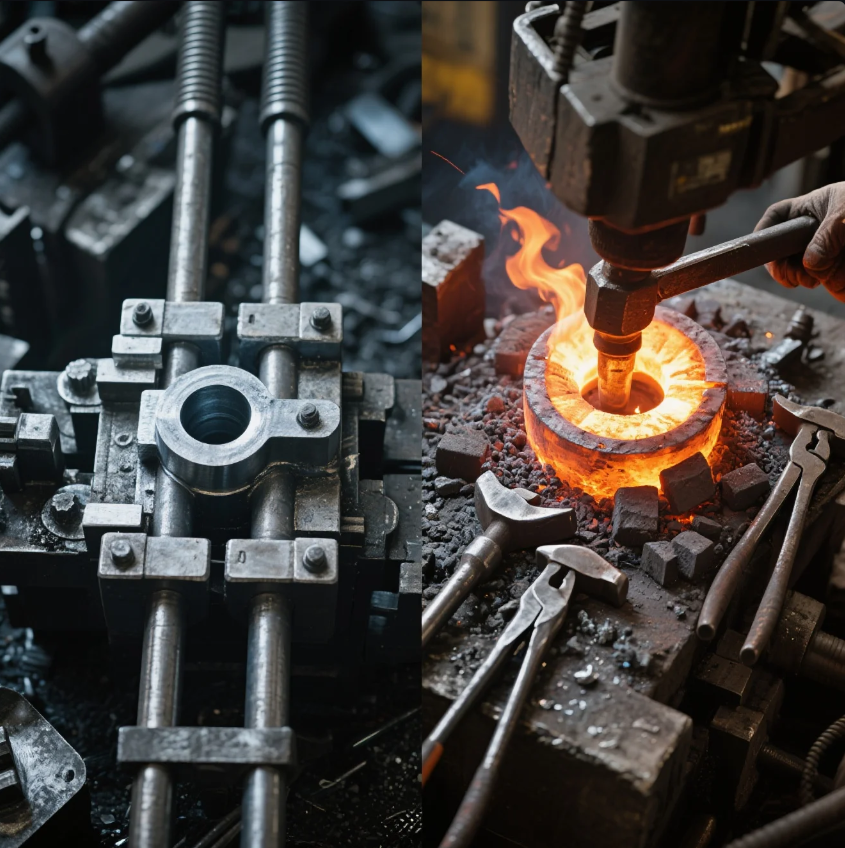
Cold forging and hot forging are two distinct metal forming processes, each with its own advantages and applications. Understanding the differences between the two methods can help you choose the best one for your project, whether you need high-strength parts or precise, cost-effective components. This article explores the differences between cold forging and hot forging, their benefits, and their limitations.
Snippet paragraph: Cold forging and hot forging each have their advantages. Cold forging offers precision, while hot forging provides greater material strength.
Let’s break down what each process involves and how they compare.
Which is Better, Hot Forging or Cold Forging?

The choice between hot forging and cold forging depends on the specific needs of your project. Both methods have their strengths and are suited for different applications.
Hot Forging
Hot forging involves heating the metal to a temperature above its recrystallization point before applying force to shape it. This allows the metal to flow more easily, reducing the amount of force required and making it easier to shape the material.
Advantages of Hot Forging:
- Increased Material Strength: The high temperature allows the metal to become more malleable and easier to shape, resulting in stronger parts with fewer internal defects.
- Better for Larger Parts: Hot forging is ideal for producing larger, more complex parts, especially those that need to withstand heavy loads or high stress.
Cold Forging
Cold forging, on the other hand, involves shaping the metal at room temperature or near room temperature. The metal is usually compressed into molds or shaped using punches and dies.
Advantages of Cold Forging:
- Higher Precision: Cold forging is better for creating parts with tight tolerances and smooth finishes.
- No Need for Heating: This can be a cost-effective process, as there’s no need to invest in heating equipment or manage high temperatures.
- Work Hardening: The process increases the hardness of the material, making it more durable.
Which is Better?
- Hot forging is better for creating large, complex parts where strength is paramount.
- Cold forging is better for producing small, high-precision parts with tighter tolerances and smoother surfaces.
Ultimately, the choice depends on your specific project requirements.
What Are the Disadvantages of Cold Forging?

While cold forging offers many benefits, it also has some limitations that may make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Disadvantages of Cold Forging:
- Limited to Ductile Metals: Cold forging is most effective with materials that are ductile and can be shaped without breaking. Metals that are too hard or brittle can crack under the pressure.
- Lower Material Strength: While cold forging can work-harden materials, it generally does not produce the same material strength as hot forging, especially for larger parts.
- Higher Tooling Costs: Cold forging requires specialized tools and dies, which can lead to higher initial setup costs for smaller production runs.
- Limited to Smaller Parts: Cold forging is typically better suited for smaller parts that can fit in the press and have precise dimensions.
Despite these limitations, cold forging remains an excellent choice for high-precision parts and applications where the benefits of work-hardening outweigh the drawbacks.
What is an Example of Cold Forging?

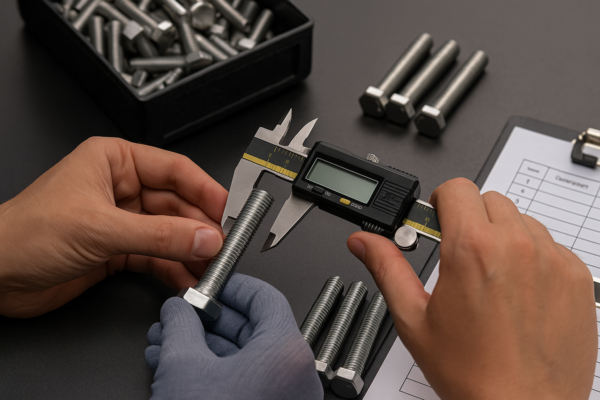
An excellent example of cold forging is the production of fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, and screws. These components are often cold-forged to achieve precise dimensions, high surface quality, and excellent material properties without the need for heating the metal.
Common Cold Forging Examples:
- Fasteners: Nuts, bolts, and screws made from steel or aluminum.
- Small Automotive Parts: Parts like pins, shafts, and connectors, which require high precision and tight tolerances.
- Electronic Components: Small, intricate parts used in electronics, such as connectors or housings.
Cold forging is widely used in industries where precision and consistency are crucial.
What Are the Benefits of Cold Forging?

Cold forging offers several key advantages, especially for producing small, precise components.
Benefits of Cold Forging:
- High Precision and Tolerance: Cold forging is ideal for parts that require tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, which is essential for industries like automotive and electronics.
- Increased Material Strength: The work-hardening effect improves the strength and hardness of the material, making cold-forged parts more durable.
- No Need for Heating: Since no heat is required, cold forging is an energy-efficient process and can be more cost-effective in certain situations.
- Minimal Waste: Cold forging typically results in less material waste compared to other processes like casting, as the material is formed by compression rather than melting.
Cold forging is especially beneficial for high-volume production of small to medium-sized parts where strength, precision, and low material waste are important.
Conclusion
Both cold forging and hot forging offer distinct advantages depending on the application. Hot forging excels in creating larger parts with greater strength, while cold forging is best for small, high-precision components. Each method has its own unique set of benefits and limitations, so it’s important to choose the right process based on your specific needs. At Prime, we specialize in both cold and hot forging, offering high-quality, durable parts for all your manufacturing needs. Contact us today for expert guidance and a custom quote.