What’s the Hardest Thing to Weld?

Introduction: Why Welding Quality Is the Key
If you buy industrial components, you know poor welding quality leads to costly rework, missed deadlines, or even failed projects. I have faced issues with suppliers unable to handle demanding welding jobs, especially with metals like titanium and cast iron. Many global buyers research on TheFabricator.com and WeldingAdvisers.com before choosing suppliers, knowing that strong welding quality is non-negotiable.
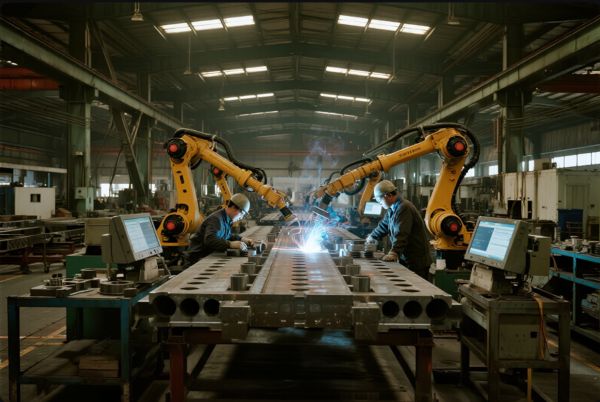

For B2B buyers, choosing a supplier who masters difficult materials and advanced welding is vital. This guide will help you understand what makes some metals challenging, what really works for safe welding, and how a qualified partner like Prime delivers reliable results for buyers worldwide.
What Is the Most Difficult Thing to Weld?
It’s common for sourcing managers to discover that aluminum, titanium, magnesium, and certain grades of high-carbon and stainless steels create endless headaches. These materials crack, warp, or contaminate easily, leading to failed inspections and urgent troubleshooting. As reported on TWI Global and MillerWelds.com, even minor mistakes can turn high-value projects into loss-makers.
Among all industrial metals, titanium, magnesium, high-carbon steels, and certain aluminum alloys are considered the most difficult to weld. They react with air, develop cracks, or form porosity if not handled perfectly. Proper shielding, process control, and material knowledge are essential for success.

Why Are These Materials Challenging?
Titanium absorbs oxygen or nitrogen even at room temperature, which destroys weld strength unless you use a perfectly sealed argon environment. Some magnesium alloys, popular in the automotive and aerospace sectors, can burn or become brittle without low heat input and advanced shielding.
In my experience, suppliers without specialized equipment, such as glove boxes or high-purity shielding, frequently fail to meet the demands of aerospace or medical device manufacturers. Stainless steels, such as 304 and 316, are easier but can suffer from sensitization if not cooled properly, leading to corrosion or weld decay.
| Material | Key Welding Issue | Industry Use |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Oxygen contamination | Medical, Aerospace, Defense |
| High-carbon steel | Cracking, hard HAZ | Power, Heavy Equipment, Construction |
| Aluminum alloys | Oxide layer, porosity | Electronics, Automotive |
| Magnesium | Brittle, burns easily | Automotive, Aerospace |
| 300/400 SS | Sensitization, warping | Food Processing, Medical |
For buyers needing custom welding parts suppliers with real expertise, I always recommend checking not only ISO certification but also NDT (non-destructive testing) experience, as seen in global supplier profiles on Thomasnet.
Prime uses AWS- and ISO-certified operators, argon glove boxes, and robotic welding lines—standards recommended by American Welding Society. Our commitment to pre-weld analysis and strict process control keeps defect rates near zero.
Why Do Welders Drink Milk After Welding?
A classic question in the industry: many buyers from North America and Europe still see welders drink milk after working with galvanized steel or zinc-coated parts. The belief is that milk helps the body resist metal fume fever—a real occupational hazard.
There is no scientific proof that drinking milk prevents fume-related illness. Milk may relieve throat irritation, but only PPE, fume extraction, and correct working practices protect welders. Always look for suppliers who follow safety standards such as those outlined by OSHA and HSE UK.

I once visited a factory in India where welders drank milk after every shift. Despite their beliefs, cases of metal fume fever still happened until the company invested in extraction fans and proper training, referencing guidelines from CDC NIOSH.
Today, Prime mandates annual safety training and audits based on International Labour Organization recommendations.
What Is the Easiest Thing to Weld?
Most buyers and engineers agree: mild steel is the king of weldability. On popular industry sites like Lincoln Electric and The Fabricator, you’ll find countless guides to welding mild steel for everything from automotive frames to industrial racks.
Mild steel welds are easy to produce, strong, and resistant to warping. With the right filler rod and basic MIG or stick process, nearly any shop can deliver clean, reliable welds. This is why it is the first choice for mass production and prototyping.
I have sourced tens of thousands of mild steel brackets and chassis, and suppliers with ISO 9001 and robotic welding always achieve the fastest turnaround.

| Material | Weldability | Industrial Use |
|---|---|---|
| Mild steel | Very high | Automotive, Machinery |
| Stainless | Moderate | Medical, Food |
| Aluminum | Challenging | Consumer electronics |
| Cast iron | Low | Construction |
Prime’s 10 production lines handle high-mix, low-volume and high-volume mild steel jobs, supporting customers from Alibaba, Global Sources, and DirectIndustry.
Which Materials Are Difficult to Weld?
Difficult-to-weld materials don’t just fail during fabrication—they can also cause problems in the field, leading to recalls or warranty claims. According to ESAB and Weld Guru, cast iron, titanium, and high-strength steels are the most troublesome for even experienced fabricators.
Cast iron is infamous for cracking unless preheated and cooled slowly. Titanium requires absolute cleanliness and argon shielding. High-strength steels must be welded with careful heat management to avoid brittleness or micro-cracks.
Prime’s team always analyzes the material safety data sheets (MSDS) before project launch. We also reference best practices from ASM International and Engineering Toolbox to select the correct process, filler, and cooling regimen.
| Metal | Failure Mode | Process Control Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Cast iron | Crack, porosity | Preheat, slow cool, nickel filler |
| Titanium | Air contamination | Sealed argon box, full cleaning |
| High-strength steel | Brittle, crack | Low-heat process, correct filler, NDT |
| Magnesium | Burn, brittle | Fast weld, inert gas, immediate inspection |
Deep Dive: Prime’s Approach to Complex Welding
Each project starts with a technical meeting, often referencing standards like ISO 3834 for welding quality. We analyze 2D and 3D drawings, use simulation tools, and recommend process improvements based on Weld.com guides.
We always validate with samples and share digital weld logs with clients. For global shipments, our logistics partners follow Incoterms 2020 and best practices from Freightos.

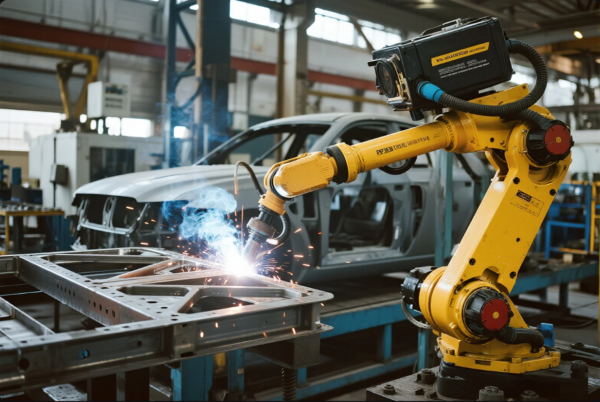
Case Study: Welding Aluminum for EV Battery Housing
A US customer required 6000 series aluminum housings, with zero leaks and uniform thickness. By referencing process standards from The Aluminum Association, we used AC TIG, automated cleaning, and full X-ray testing.
The result: first-batch approval, no rework, and 30% faster delivery compared to the previous supplier.
Prime supports urgent projects for construction, machinery, energy, and more.
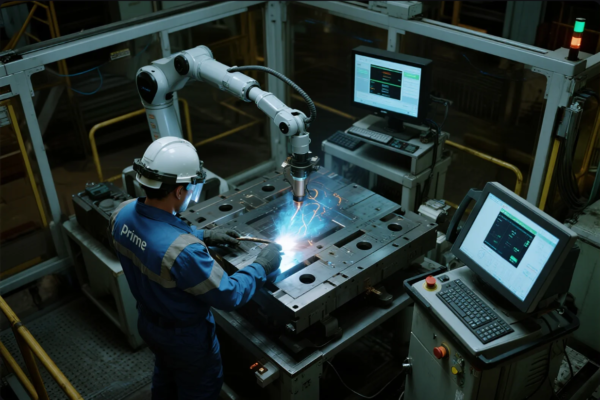
Image Gallery: Real-World Welding Quality

FAQs: Welding Challenges and Solutions
Q: Which weld joint type offers the highest strength?
A: Full-penetration TIG joints are the gold standard. See Weld Guru for joint types.
Q: Can aluminum welds be as strong as steel welds?
A: Yes, with process controls and correct filler. Details at Lincoln Electric.
Q: What causes post-weld cracking?
A: Often rapid cooling or the wrong filler. The Welding Academy explains more.
Q: What is the best way to avoid weld contamination?
A: Cleanliness and shielding gas. See Fronius.
Q: Does Prime provide full traceability?
A: Yes, from batch number to operator, with digital inspection reports.
More on our quality management.
Q: What industries does Prime support?
A: Automotive, energy, medical, and more. View our industry cases.
Q: Minimum order for custom welded parts?
A: No MOQ for samples. Volume production available.
Q: How does Prime ensure secure global delivery?
A: Export cartons, shockproof packaging, and insurance per Incoterms.
Conclusion: Choose Prime for Reliable Welding
For global buyers who demand certified welding and consistent quality, Prime is the proven choice. Our experienced engineers, digital QA, and advanced production lines keep your projects on track. Don’t risk delays or returns—work with a supplier trusted by Alibaba, Global Sources, and industry leaders around the world.
Contact & Consultation
- Website: https://primecustomparts.com/
- Email: [email protected]
- Alibaba: PrimeCustomParts on Alibaba
- Global Sources: PrimeCustomParts on Global Sources







