Understanding Thread Types, Coatings, and Failure Prevention in Industrial Metal Fasteners?

Industrial metal fasteners are the silent heroes holding together machines, bridges, vehicles, and buildings worldwide. Yet, every year, failures from poor thread selection, substandard coatings, or overlooked design details cost companies millions. For B2B buyers, engineers, and quality leaders, deep knowledge of threads, surface finishes, and preventive practices means the difference between trouble-free production and costly recalls.
This complete guide dives deep into every major thread type, modern coatings, and the root causes of fastener failure. You’ll find actionable checklists, prevention strategies, and direct links to global standards and engineering tools—so your projects run stronger, longer, and safer.
Different Thread Types in Metal Fasteners: Metric, UNC, UNF, and More
In global supply chains, using the wrong thread standard causes delays, safety risks, and even legal claims. Always specify and check threads carefully—especially when machines, vehicles, or assemblies cross borders.
Global Thread Standards
- Metric (M): Used worldwide, governed by ISO 261/965. M10×1.5, for example, means 10mm diameter, 1.5mm pitch. Most new equipment, electronics, and Asian/European projects default to metric.
- UNC/UNF: Inch-based Unified Thread Standard for the US and Canada. UNC (Unified Coarse) is robust for general use; UNF (Unified Fine) is common in auto, aerospace, and applications where more threads per inch mean better holding power.
- BSW/BSF: British Whitworth and Fine threads, legacy for restoration or UK vintage machinery (Namrick UK).
-
Specialty:
- Acme/Trapezoidal: High-load or motion-control systems (Nook Industries)
- Self-tapping: Sheet metal, plastics (TR Fastenings)
- Left-hand, custom, or proprietary: For anti-loosening or safety applications.
How to check threads:
Use a digital caliper and thread pitch gauge to confirm. Never mix standards—failure is guaranteed if UNC nuts are forced onto metric bolts.
Thread engineering calculators:
- Bolt Depot’s thread chart
- Engineering Toolbox’s pitch/tap size guide
- McMaster-Carr’s thread selector
Dive Deeper: Thread System Table
| Thread Standard | Use Region | Sample Callout | Common Applications | Technical Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric (M) | Global | M12 × 1.75 | Machines, auto, robotics | ISO |
| UNC/UNF | US/Canada | 1/2-13 UNC | Heavy equipment, trucks | ASME |
| BSW/BSF | UK/Legacy | 3/8 BSW | Vintage, marine | Namrick |
| Acme | Global/Industrial | 1"-5 ACME | Power, linear actuators | Nook |
| Self-tapping | Global | ST4.2 × 13 | Electronics, HVAC | TR Fastenings |
Tip: For international projects, specify thread type, pitch, and standard in all drawings and POs. Use a sample and first-article inspection for new suppliers.
Surface Coatings and Treatments for Metal Fasteners: Zinc Plating, Galvanizing, and Black Oxide

The right coating is what separates a fastener that fails in months from one that lasts decades. Coatings protect from rust, abrasion, chemical attack, and sometimes provide color coding or lubricity.
Common Fastener Coatings
- Zinc Plating: Cost-effective, shiny, used in interior and light-duty exterior. Protects for 12–72 hours in salt spray. See AZO Materials.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Heavy zinc (up to 80 microns), for outdoors, bridges, or marine use. Complies with ISO 1461 and ASTM A153.
- Black Oxide: Matte, black, light corrosion resistance. Used for tool, electronic, or aesthetic projects (Finishing.com).
- Dacromet/Geomet: High-tech, eco-friendly, 1000+ hours salt spray. Favored in auto, wind, and solar (NOF Metal Coatings).
- Nickel/Chrome: For shiny, medical, food, or design-critical parts. Adds wear and chemical resistance (ThomasNet).
- Phosphate, PTFE: Primers, lubricity, paintable or anti-seize (The Fabricator).
- Anodizing: For aluminum fasteners. Hardens, colors, and insulates (Aluminum Anodizers Council).
How to specify:
Write out the coating standard, minimum thickness, and salt spray hour in all RFQs. Get batch test reports—SGS, Bureau Veritas, or your own sample test using ASTM B117.
Case example:
A railway supplier switched to Geomet-coated bolts for exposed rail joints, resulting in zero rust and longer maintenance intervals.
Dive Deeper: Coating Performance Comparison
| Finish Type | Salt Spray (hrs) | Typical Use | Industry Resource |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc Plating | 12–72 | Indoor, machinery | AZO Materials |
| Hot-Dip Galvanize | 500+ | Construction, marine | Galvanizing.org.uk |
| Black Oxide | 24 | Tools, electronics | Finishing.com |
| Dacromet/Geomet | 1000+ | Automotive, wind, solar | NOF Metal Coatings |
| Nickel/Chrome | 48–240 | Decorative, medical | ThomasNet |
| Phosphate/PTFE | 12–48 | Automotive, lubricity | The Fabricator |
Tip: Request real sample photos from your supplier, or order a sample pack for lab testing before the main order.
Common Causes of Fastener Failure and How to Prevent Them in Design and Assembly
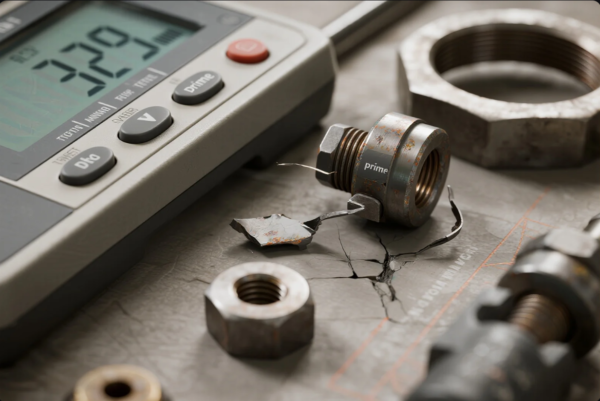

Failure isn’t random—it’s usually a missed step in design, sourcing, or assembly. The most common root causes include mismatched threads, poor coating choice, and improper torque during installation.
Key Fastener Failure Risks
- Thread Mismatch: Mixing metric and UNC/UNF threads is the #1 assembly error in international projects (Bolt Depot’s troubleshooting).
- Coating Deficiency: Inadequate or wrong coatings for environment (AZO Materials), such as using zinc-plated bolts in marine jobs.
- Material Selection: Using a soft grade when a high-strength one is required (Matmatch), or wrong material for chemical exposure.
- Improper Tightening: Under- or over-torque causes either loosening or bolt breakage. Always use torque specs from Fastenal and a calibrated Norbar digital torque wrench.
- Fatigue: Neglecting preload, vibration locking, or periodic inspection in high-cycle systems (Bolt Science).
- Reuse of Damaged Fasteners: Any stretch, rust, or thread deformation means the fastener is unsafe to reuse.
Prevention strategies:
- Insist on batch-certified, ISO/ASTM-compliant fasteners (Prime).
- Use locknuts, washers, or Loctite adhesive for vibration-prone joints.
- For all critical joints, require first-article and pre-shipment inspection by QIMA or SGS.
- Train assembly teams with step-by-step work instructions and digital torque tools.
Dive Deeper: Failure Mode Table
| Failure Mode | Typical Root Cause | Solution/Best Practice | More Info |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stripped Threads | Wrong standard, overtighten | Confirm threads, use calibrated tool | Mitutoyo |
| Corrosion | No/wrong coating | Specify/test coating, lab test samples | SGS |
| Fatigue Fracture | No preload, vibration | Lock washers, measure torque | Bolt Science |
| Overload/Shear | Soft/undersized bolt | Certified grade, proper load calcs | Matmatch |
| Loosening | No lock/torque, vibration | Locknuts, Loctite, split washer | Loctite |
FAQs: Everything You Need to Know About Industrial Metal Fasteners
How can I verify my supplier’s certification?
Request ISO, DIN, or ASTM certificates and validate with SGS or TÜV Rheinland.
Is RoHS or REACH compliance available for fasteners?
Yes. For electronics or EU projects, require RoHS and REACH documents.
Is black oxide good for outdoor use?
No, use hot-dip galvanized or stainless steel for maximum durability.
Where do I get torque specs?
See Fastenal’s chart or Engineering Toolbox.
Can I get custom threads or coatings?
Yes, top suppliers like Prime, Bossard, and TR Fastenings offer full customization.
How do I ensure the shipment matches my spec?
Book pre-shipment checks with QIMA or Bureau Veritas.
What’s the safest way to pay for fasteners from overseas?
Use Alibaba Trade Assurance, PayPal, or a HSBC L/C.
Contact Prime

Prime is your ISO-certified global supplier for all major thread types, coatings, and industrial fastener solutions. Our engineers and export team help you specify, source, and inspect every detail, serving clients in North America, Europe, Asia, and worldwide.
- Website: https://primecustomparts.com/
- Email: [email protected]
Request a technical review, get a fast quote, or order custom samples. Build better, source smarter, and prevent failure—choose Prime for your next project.







